Definition Integrity In Cryptography
The information maintains its integrity during transit and while being stored. To maintain data integrity in cryptography hash functions which return a deterministic output from an input value are used to map data to a fixed data size.

Information Assurance Business Continuity Disaster Recovery Consulting Business
And γράφειν graphein to write or -λογία-logia study respectively is the practice and study of techniques for secure communication in the presence of adversarial behavior.

Definition integrity in cryptography. Integrity involves maintaining the consistency accuracy and trustworthiness of data over its entire lifecycle. Cryptography and encryption are terms that many might treat as synonymous. It refers to the quality of the message sent and received as it is.
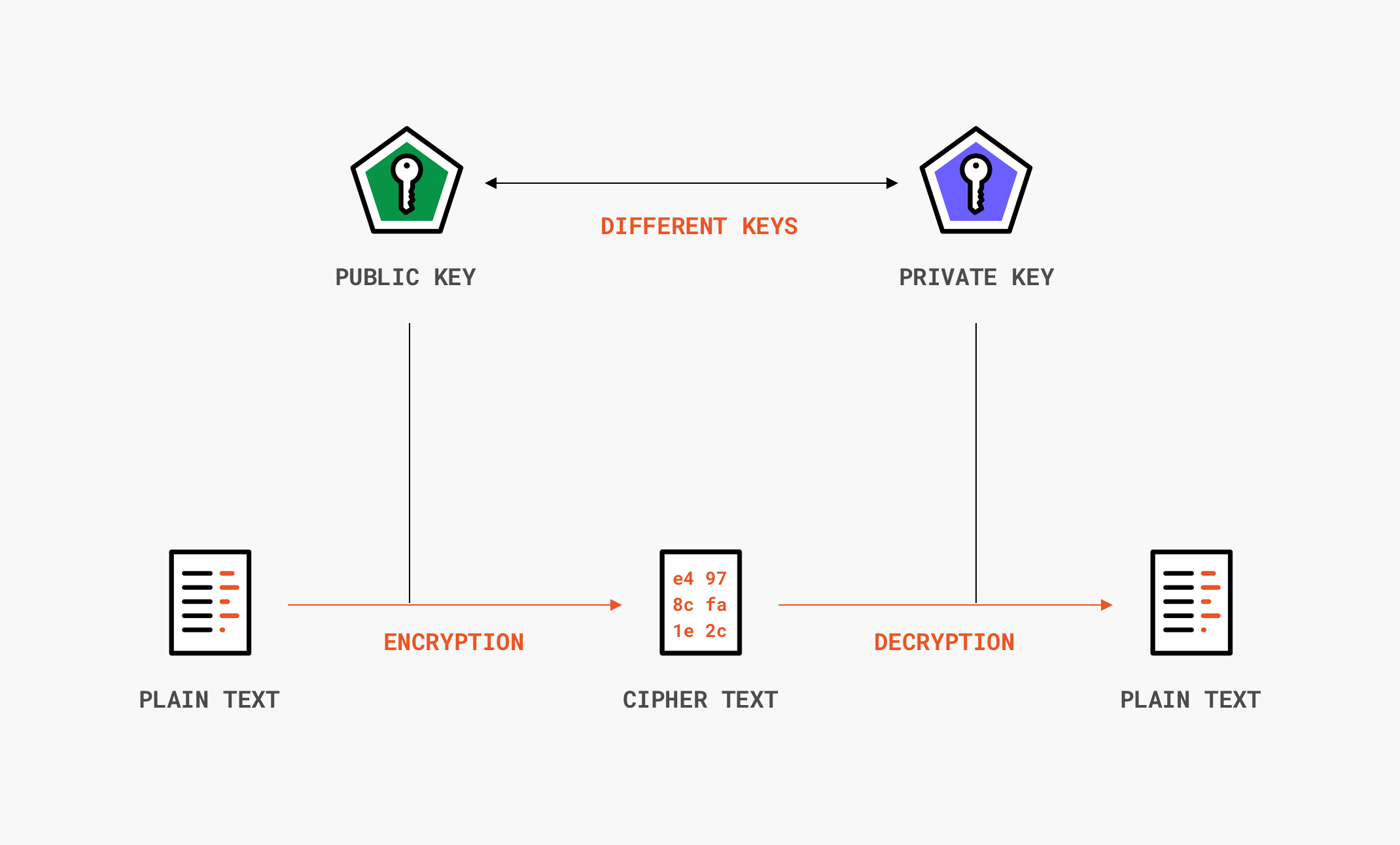
The discipline that embodies the principles means and methods for the transformation of data in order to hide their semantic content prevent their unauthorized use or prevent their undetected modification. The process is depicted in the following illustration. They only provide for confidentiality not integrity.
Security controls focused on integrity are designed to prevent data from being modified or misused by an unauthorized party. It is used to generate the checksums on data files. I would like to know which one is correct.
The first definition - the one I always used - is the following. The focus of this chapter is on data integrity and cryptographic tools used to achieve the same. According to this definition we can have data authenticity without data integrity.
Essentially this definition exactly means that an adversary will not be able to tamper with a ciphertext to produce a ciphertext that encrypts a plaintext that is in any way related to the original plaintext. The discipline concerned with communication security eg confidentiality of messages integrity of messages sender authentication non-repudiation of messages and many other related issues regardless of the used medium such as pencil and paper or computers. A digital signature is merely a means of signing data as described earlier in the section Asymmetric Encryption to authenticate that the message sender is really the person he or she claims to be.
NIST SP 800-59 under Cryptography from ANSDIT. Information only has value if it is correct. Integrity of information refers to protecting information from being modified by unauthorized parties.
Cryptography or cryptology from Ancient Greek. Non-repudiation - Sender cannot deny hisher intentions in the transmission of the information at a later stage Authentication - Sender and receiver can confirm each Cryptography is used in many applications like banking transactions cards computer passwords and e- commerce transactions. Threats to Data Integrity When sensitive information is exchanged the receiver must have the assurance that the message has come intact from the intended sender and is not modified inadvertently or otherwise.
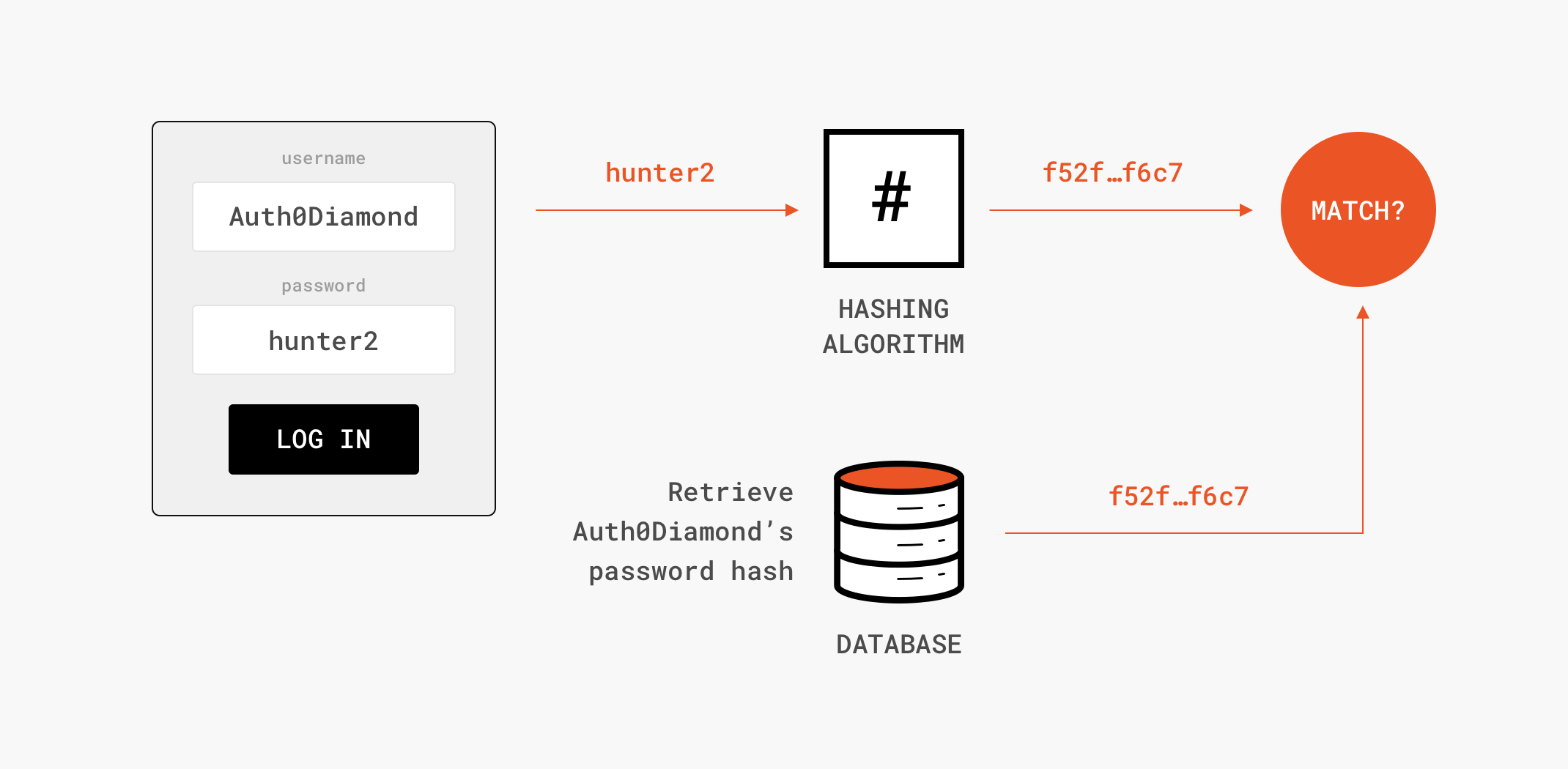
Data integrity check is a most common application of the hash functions. Information that has been tampered with could prove costly. On the other hand encryption is the mathematical process used to encode a message with an algorithm.
This means that the sender and the delivery of a message can be verified. This is an obvious case but the same conclusion applies to most encryption systems. Integrity involves maintaining the consistency and trustworthiness of data over its entire life cycle.
Cryptography Algorithms Cryptography algorithms are the means of altering data from a readable form to a protected form and back to the readable form. Integrity In the world of information security integrity refers to the accuracy and completeness of data. A cryptographic hash function is a mathematical function used in cryptography.
Data authenticity means that the initial message sender is who heshe claims to be. The information cannot be read without a key to decrypt it. This application provides assurance to the user about correctness of the data.
It deals with everything related to secure communications and data integrity. To maintain integrity data must not be changed in transit and steps must be taken to ensure that data cannot be altered by an unauthorized person or program. However cryptography is a broad term encompassing so much more than encryption.
I came across various definitions of what authenticity means in cryptography. Digital signatures can also provide for data integrity along with authentication and nonrepudiation. More generally cryptography is about constructing and analyzing protocols that prevent third.
Thus you may want to add a digital signature. Cryptography also aids in nonrepudiation. Typical hash functions take inputs of variable lengths to return outputs of a fixed length.
Interestingly when using public key cryptography it is not sufficient to sign then encrypt SE or to encrypt then sign ES. Integrity - Information cannot be altered.
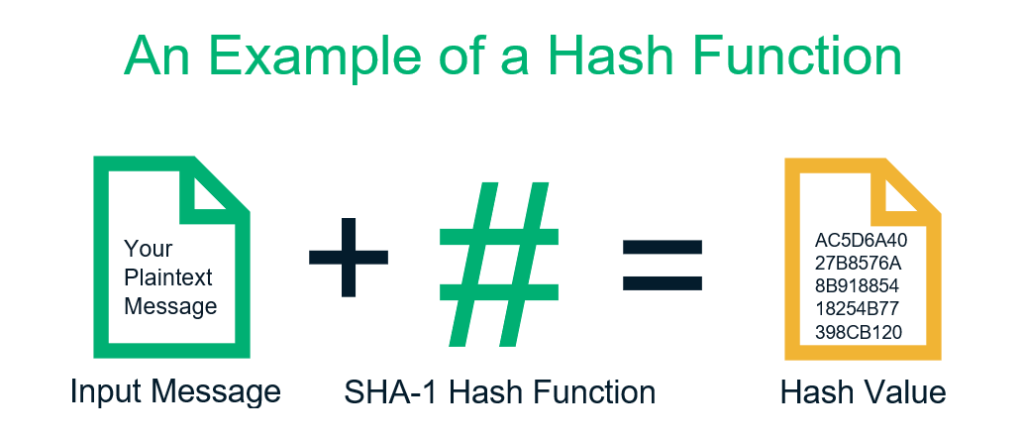
Hash Function In Cryptography How Does It Work Infosec Insights
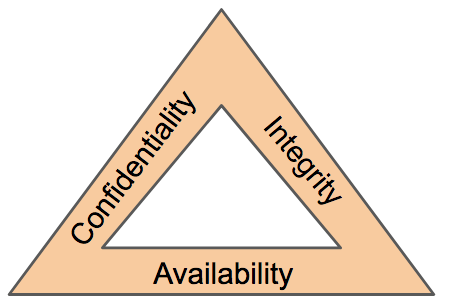
Confidentiality Integrity And Availability The Cia Triad Certmike

Part 1 Cryptography 1 Integrity Part 1 Cryptography 2 Data Integrity Integrity Detect Unauthorized Writing I E Modification Of Data Example Ppt Download

Cryptography 101 Data Integrity And Authenticated Encryption By Emily Williams Medium

Message Integrity Authentication And Non Repudiation Dev Community

The Cia Triad In Cryptography Geeksforgeeks
Security Mechanics Chapter 2 Basic Security Mechanics And Mechanisms Wireless Lan Security Networking Etutorials Org
What S The Difference Between Encryption Hashing Encoding And Obfuscation
What S The Difference Between Encryption Hashing Encoding And Obfuscation

The Cia Triad In Cryptography Geeksforgeeks

The Cia Triad In Cryptography Geeksforgeeks

Cryptography 101 Data Integrity And Authenticated Encryption By Emily Williams Medium

Confidentiality Integrity Availability Authentication Non Repudiation Security Goal Cia Youtube

Cryptography Vs Encryption Cryptography Cyber Security Program Cybersecurity Training

What Is Cryptography Definition Uses Study Com

Message Integrity Practical Networking Net

Chapter 2 Advanced Cryptography Part C Ppt Download
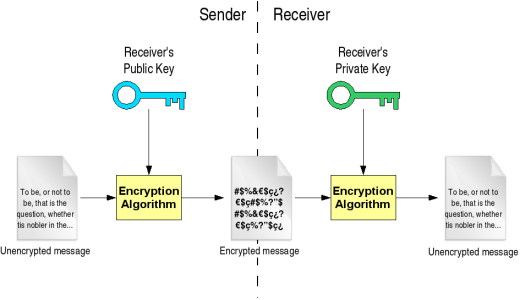
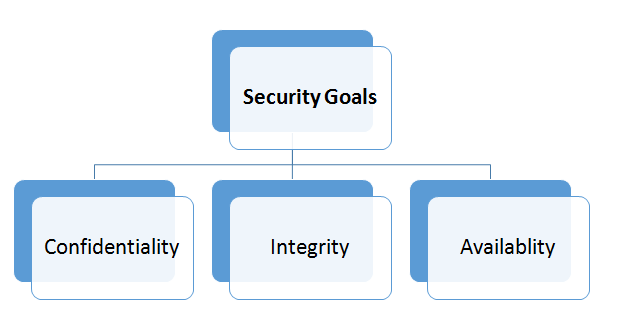
Post a Comment for "Definition Integrity In Cryptography"