Definition Of Diffusion Velocity
In the steady state the flame front produces a flow outward molecular diffusion establishes a bulk velocity component in the normal direction and oxygen plus a little nitrogen flows inward toward the centerline. The particle velocity is proportional to the density difference between the particle and the fluid and to the particle diameter d.
Diffusion velocity The relative mean molecular velocityof a selected gas undergoing diffusionin a gaseous atmosphere commonly taken as a nitrogenN2 atmosphere.

Definition of diffusion velocity. By definition the new coordinate Z is locally normal to the surface of the. 24 Similarly a diffusion force may be defined as Fdiff 3πµud Cc 25. Then the formula simplifies to.
In this form the convectiondiffusion equation combines. D is the diffusion coefficient. T is the absolute temperature.
μ is the mobility or the ratio of the particles terminal drift velocity to an applied force μ v d F. Therefore in terms of the velocity gradient a the scalar dissipation rate becomes showing that c 2increases as Z for small Z. The average velocity attained by charged particles eg.
In terms of the velocity gradient a the scalar dissipation rate. Diffusion is the kinetic process that leads to the homogenization or uniform mixing of the chemical components in a phase. Supply volume m3s Induction volume at Distance Discharge Velocity ms Velocity at distance ms.
K B is Boltzmanns constant. Golubkin Sizykh 89 and Ogami Akamatsu 165 identify the diffusion velocity by absorbing the diffusion term into the convection term in the vorticity equation. The net velocity at which these electrons drift is known as drift velocity.
The basic idea of the diffusion velocity method is to handle diffusion as a part of the convection process. Mobility of Charge Carrier- This is a property of conductor defined as the ratio of drift velocity to applied electric field in a conductor. The resulting derivations of species and mass conservation equations are straightforward.
1a. An additional component of advection for the particle. The diffusion current and drift current together are described by the driftdiffusion equation.
Two frequently used important special forms of. Only where fuel and oxidizer are mixed on the molecular level chemical reactions. 46 rows Fouriers law of conduction This definition of heat flux fits Maxwells original definition.
With definition of strain rate. Fluid mechanics The relative mean molecular velocity of a selected gas undergoing diffusion in a gaseous atmosphere commonly taken as a nitrogen N 2 atmosphere. Individual diffusion product Induction Ratio Primary Air Induced Air Temperature Measurements of Primary Air Discharge Air and Induced Air Room Air Induction Equation Induction Ratio Q Qx Qo C Vo Vx Qx Where.
Mixing takes place by convection and diffusion. Electrons in a material due to an electric field. Drift velocity can be defined as.
In the steady state the total volumetric rate of products is usually greater than the sum of the other two. A molecular phenomenon that depends upon the gaseous concentration as well as upon the pressure and temperature gradients present. Qo X C Vo Vx C.
Diffusion Velocity The diffusion velocity is defined as 0 D C J U. This equation is an early example of a fluctuation-dissipation relation. The SI unit of drift velocity is ms.
Counterflow diffusion flame Flamelet structure of diffusion flames. Drift velocity of charge carriers in a conductor depends upon two factors one is the intensity of applied electric field across the conductor and other is one property of the conductor called. To do that an artificial velocity field is defined to represent the diffusion process.
With z taken as the vertical coordinate the additional velocity component appears in the third term of advective flux. In a common situation the diffusion coefficient is constant there are no sources or sinks and the velocity field describes an incompressible flow ie it has zero divergence. Although mixing in a fluid liquid or gas may occur on many length scales as induced by macroscopic flow diffusive mixing in solids by contrast occurs only on the atomic or.
The diffusion velocity is a molecular phenomenon and depends upon the gaseous concentration as well as upon the pressureand temperaturegradients present. In both models the phenomena of diffusion are introduced by defining the absolute velocity of a chemical species to have a component due to diffusion called the diffusion velocity v.

Mhmt 14 Momentum Heat Mass Transfer Mass Transfer

Angular Acceleration Derivation Angular Acceleration Learning Science Angular
Http Faculty Poly Edu Rlevicky Handout2 3323 Pdf

Grahams Law Of Diffusion Gas Laws Chemistry Root Mean Square Problem And Solution
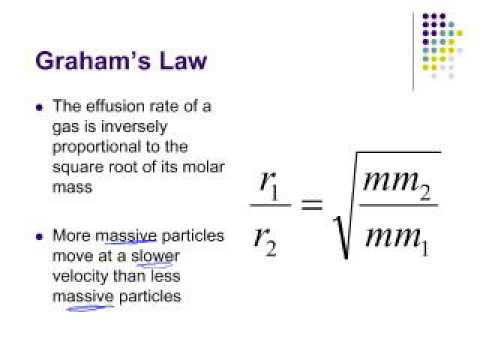
Effusion And Diffusion Youtube

Pin On Ems Studying And Training
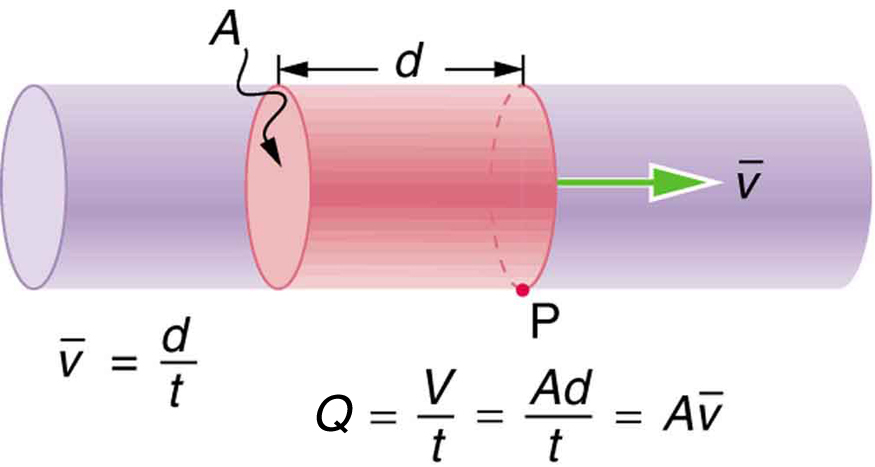
Flow Rate And Its Relation To Velocity College Physics
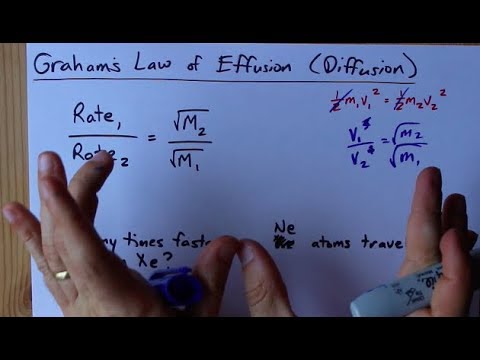
Graham S Law Of Effusion Diffusion Example Youtube

Average Speed And Average Velocity Definition Examples Diagrams

2222 Quantum Physics 2007 81 2 1 An Equation For The Matter Waves The Time Dependent Schrodinger Equation Classica Wave Equation Quantum Mechanics Physics
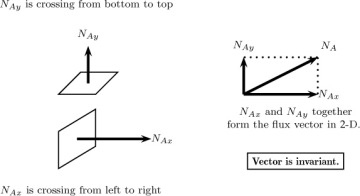
1 3 Flux Vector Introduction To Modeling Of Mass Transfer Processes Informit

Diffusion Factor An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Molecular Velocity An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Stem Engineering Rocket Calculations Stem Engineering Engineering Teaching

Molecular Velocity An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
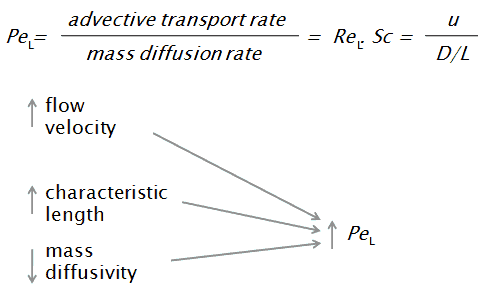
What Is Peclet Number Definition

Speed Velocity And Acceleration Acceleration Powerpoint Presentation Velocity
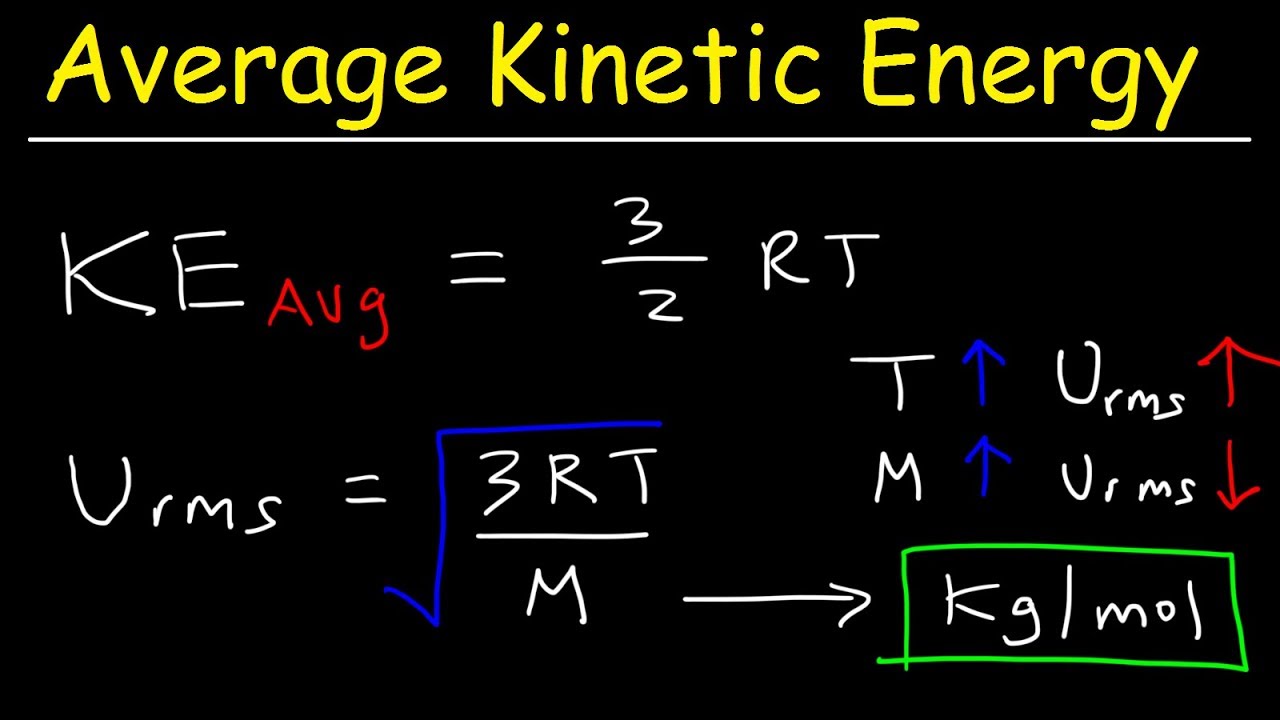
Average Kinetic Energy Of A Gas And Root Mean Square Velocity Practice Problems Chemistry Gas Laws Youtube
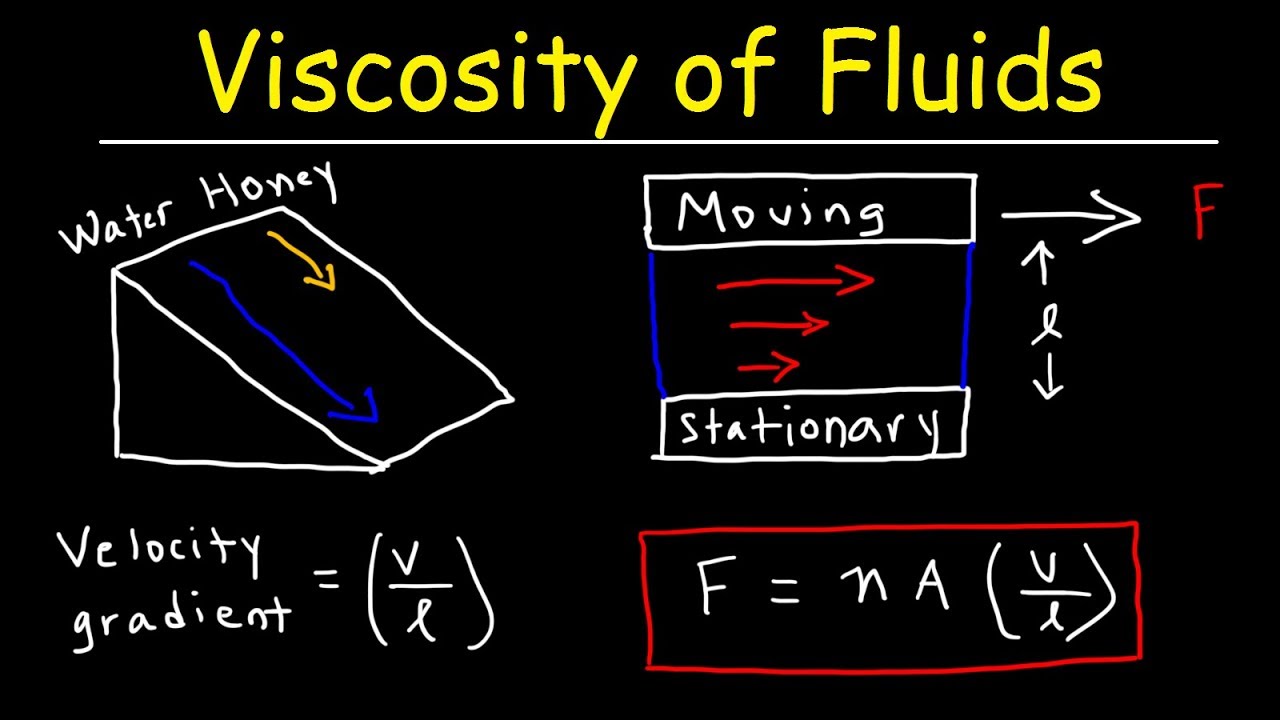
Viscosity Of Fluids Velocity Gradient Fluid Mechanics Physics Problems Youtube

Post a Comment for "Definition Of Diffusion Velocity"