Definition Of Mass Velocity In Fluid Mechanics
To learn various flow measurement techniques. Conservation of mass and momentum assuming incompressible inviscid and irrotational flow.

Fluid Mass Flow Rate And The Continuity Equation Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
From the equation we can see that mass flow rate depends on the density velocity and the area of cross-section of the fluid.

Definition of mass velocity in fluid mechanics. The quantity density times area times velocity has the dimensions of masstime and is called the mass flow rate. A substance that deforms continuous-ly when subjected to a shear stress. 0 By definition for irrotational flow.
Or 𝑄 1 𝑄 2. It is also called velocity field. Momentum of fluid per second at section 1 Mass x velocity.
Mas vəläsədē fluid mechanics The weight flow rate of a fluid divided by the cross-sectional area of the enclosing chamber or conduit. In simple words it is the movement of mass per unit time. Density or mass density of fluid is ratio of Mass of fluid m per unit Volume V SI unit of Density is Kgm3 Density of water at 4 277K is 1000 kgm3 Density Mass m Unit Volume V.
Fluid mechanics is the scienceand technology of flu-ids either at rest fluid statics or in motion fluid dynamics and their effects on boundaries such as solid surfaces or in-terfaces with other fluids. R V where xyzt is the velocity potential function. Define properties of fluids and classification of fluids.
V r constant The point at the center of rotation is called a singular point where velocity approaches to infinite. The relationship between volume flow and mass flow follows directly from the definition of density ρ m3 kg volume mass ρ 21 and m3 s s kg Q M volume flow mass flow ρ giving M Q ρ kgs 22 In any continuous duct or airway the mass flows passing through all cross sections along its length. Let us find the momentum of fluid at section 1.
ρ mass density of the fluid v Flow velocity of the mass elements A cross-sectional vector areasurface j m mass flux. Similarly Moment of momentum per second at section 2 ρ Q x V2 x r2. In fluid mechanics mean velocity of an incompressible fluid flow through a control surface S is defined as the velocity of a uniform fluid flow of the same fluid density that produces the same mass flow rate through S as the given fluid flow.
Mass flow rate is the rate of movement of a massive fluid through a unit area. Momentum of fluid per second at section 1 ρ Q x V1. Such that the components of.
Definition of a fluid. While not obvious in the basic equation Vn must also be measured relative to. In general including cases where the area is curved the equation becomes a surface integral.
A Provide an expression for the mass flux m based on ρV andδ. Mass velocity Mass current density or Mass flux Average velocity Volume flux Mass Velocity. Fluid Mechanics Objectives for the subject Fluid Mechanics To study fluid statics and fluid dynamics.
The formula for mass flow rate is given as follows. The above equation is only true for a flat plane area. Consider a steady incompressible boundary layer with thickness δx that de-velops on a flat plate with leading edge at x 0.
Conservation of mass requires 𝜌 1 𝑉 1 𝐴 1 𝜌 2 𝑉 2 𝐴 2. In this flow fluid mass rotates due to the conservation of angular momentum. The velocity profile is inversely proportional to the radius.
This parameter is defined such that when multiplied by the fluid density ρf and the cross-sectional area of the tube Ap it provides the rate of mass flow through the tube m Bergman et al 2011 that is the flow of a mass m through a surface per unit time t. For example lb hft2. V dA cs ρ ρn cs m.
V n dA NOTE. Moment of momentum per second at section 1 ρ Q x V1 x r1. Fluid Mechanics Problems for Qualifying Exam Fall 2014 1.
There is a vector identity prove it for yourself that states for any scalar. Outcomes for the subject Fluid Mechanics Learner will be able to. When evaluated along a line it is called a velocity profile.
For incompressible flow 𝜌 1 𝜌 2 we have 𝑉 1 𝐴 1 𝑉 2 𝐴 2. In continuum mechanics the flow velocity in fluid dynamics also macroscopic velocity in statistical mechanics or drift velocity in electromagnetism is a vector field used to mathematically describe the motion of a continuum. Velocity at a point on the are a across which fluid flows.
Note that only the normal component of velocity contributes to flow rate across a boundary. This quantity is an important parameter in determining the thrust produced by a propulsion system. Basic laws of fluid mechanics.
The length of the flow velocity vector is the flow speed and is a scalar. Based on a control volume analysis for the dashed box answer the following. R V 0 Therefore.
To study application of mass momentum and energy equations in fluid flow.

Mcat Physics Flashcard Continuity Of Volume Flux Illustration Fluid Mechanics Continuity Equation In The Flow Of An Idea Fluid Mechanics Physics Mechanic

Expression For Velocity Of Sound Wave In A Fluid Sound Waves Conservation Of Mass Waves

Cv Physiology Velocity Versus Flow Of Moving Blood

Role Of Mach Number In Compressible Flows Physics And Mathematics Basic Physics Astronomy Facts
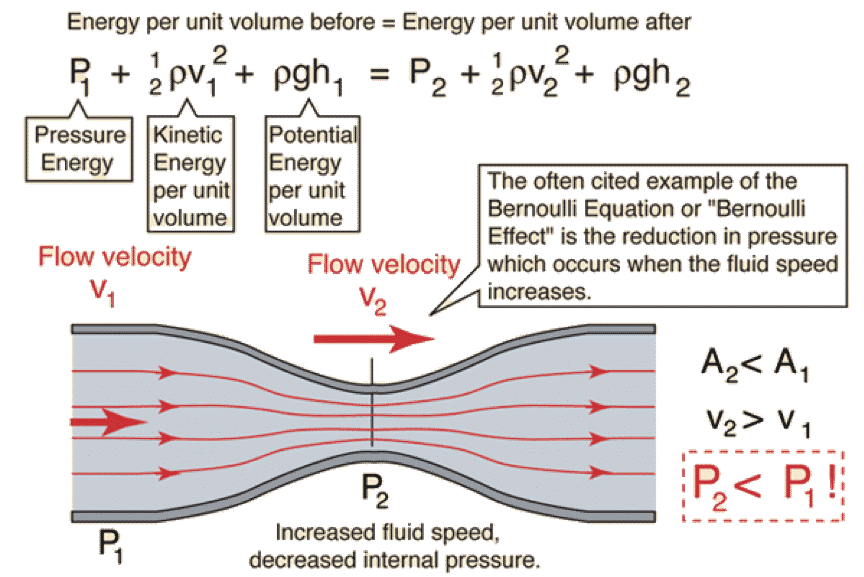
How To Measure Air Velocity And Flow Rate In Depth Guide
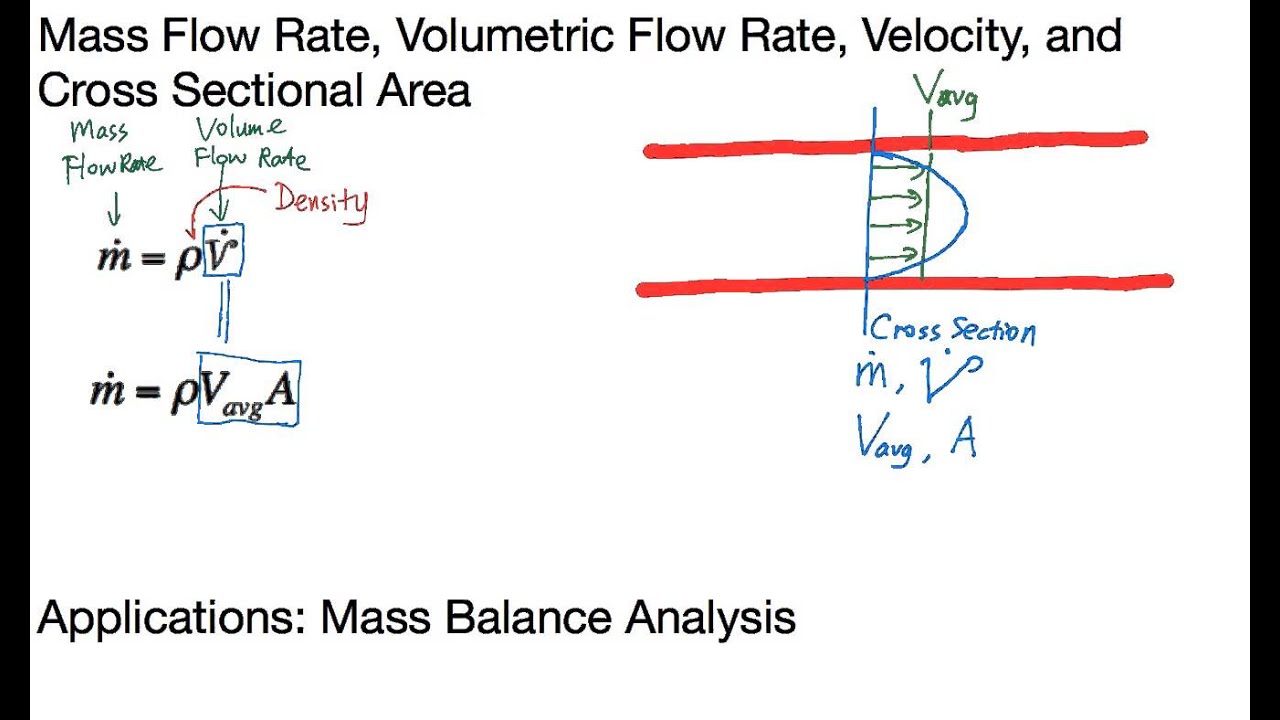
Mass Flow Rate Volume Flow Rate Velocity And Cross Sectional Area Youtube

Flow Rate And Its Relation To Velocity Physics
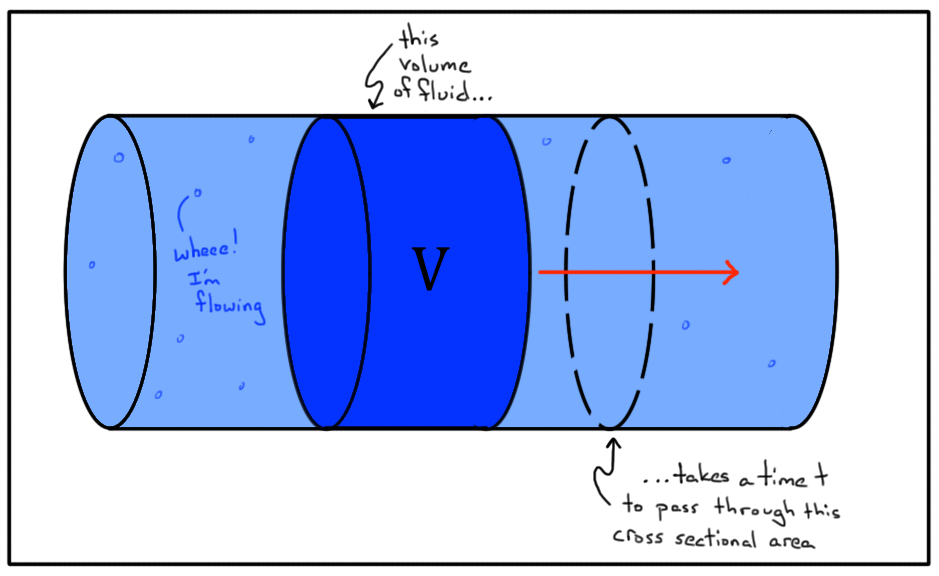
What Is Volume Flow Rate Article Fluids Khan Academy

Volume Flow Rate Mass Flow Rate Fluid Dynamics Physics Problems Youtube

Thermodynamic Calculation Of A Heat Of First Order Phase Transitions Fluid Mechanics Engineering Physics Books Fluid Mechanics
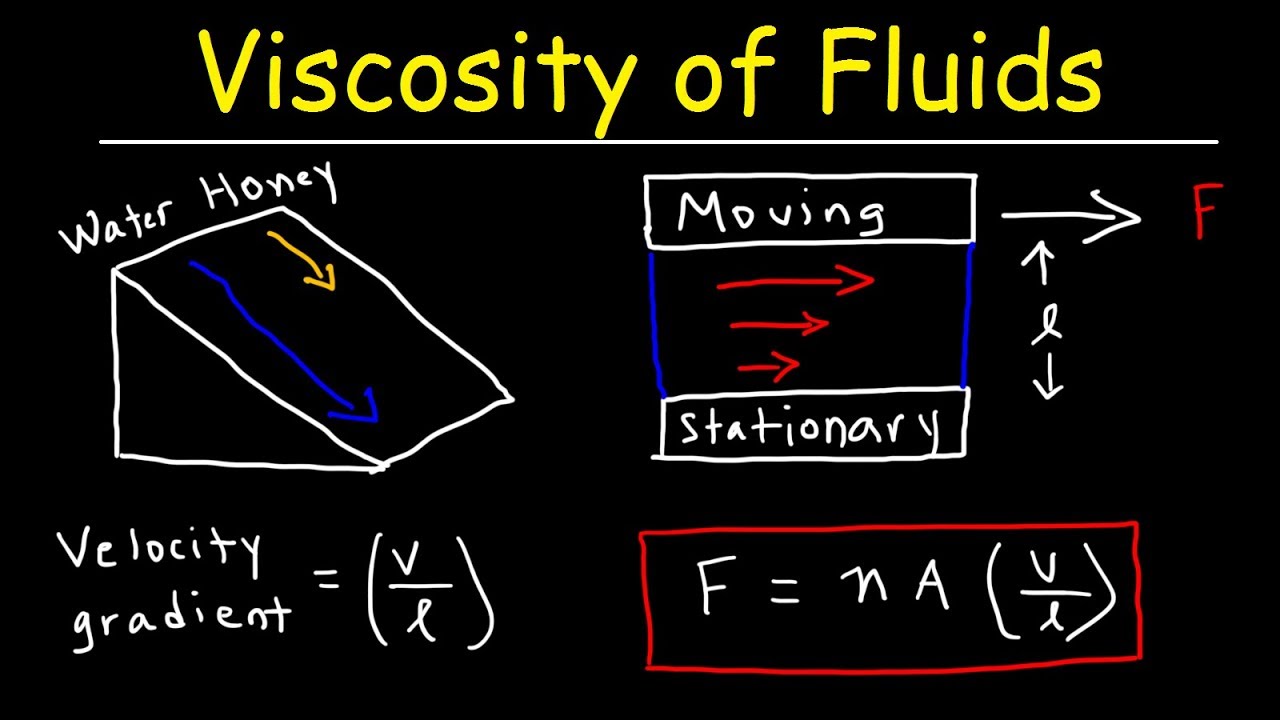
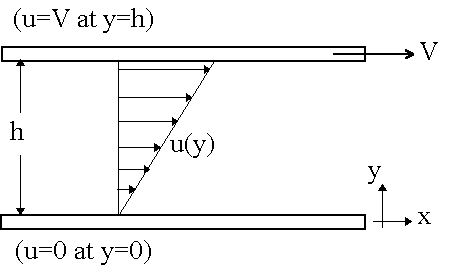
Viscosity Of Fluids Velocity Gradient Fluid Mechanics Physics Problems Youtube

Reynolds Number Reynolds Number Flow Definition Fluid Dynamics

Flow Rate And Its Relation To Velocity Physics

Conservation Of Energy Astronomy Facts Thermodynamics Physics Formulas
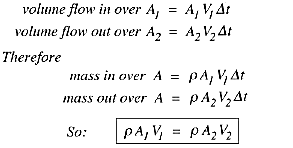

Post a Comment for "Definition Of Mass Velocity In Fluid Mechanics"