Definition Of X-ray Fluoroscopy
The beam is transmitted to a TV-like monitor so that the body part and its motion can be seen in detail. After the x-rays pass through the patient they are captured by a device called an image intensifier and converted into light.
Security Medical X Ray Differences Astrophysics Inc
Your doctor can view the monitor to perform certain procedures such as pain blocks or steroid injections.
Definition of x-ray fluoroscopy. An instrument used chiefly in industry and in medical diagnosis for observing the internal structure of opaque objects as the living body by means of the shadow cast by the object examined upon a fluorescent screen when placed between the screen and a source of X-rays. X-rays from the tube pass through the body and project the bones and organs as images on the screen. The study of moving body structures which are alike an X-ray movie is called as Fluoroscopy.
Fluoroscopy uses x-ray to produce real-time video images. Fluoroscopy is a kind of X-ray movie. Medical Definition of fluoroscope Entry 1 of 2.
An x-ray procedure that makes it possible to see internal organs in motion. The beam is diffused to a TV-like monitor in order to see in detail the body parts and also its motion. Fluoroscopy Imaging An x-ray imaging technique used to evaluate moving pulmonary and cardiac structures and help in needle localization of masses being biopsied Cons Fluoroscopy exposed Pts to more radiation than a standard film.
The axis of rotation of the C-arm is depicted as a dashed line in the illustration to the left. While an X-ray takes a single picture a fluoroscope takes X-rays and sends the images to a monitor. It can also look at other parts of your respiratory tract.
It uses the same technology as an x-ray in order to generate a working image for a doctor to interpret in the process of caring for a patient. Fluoroscopy as an imaging tool enables physicians to look at many body systems including the skeletal digestive urinary respiratory and reproductive systems. The light is then captured by a TV camera and displayed on a video monitor.
Use of magnification modes in fluoroscopy is usually associated with an increase in. Digital fluoroscopy DF is a digital x-ray imaging system that produces dynamicimagesobtained with an area x-ray beam. Fluoroscopy is a study of moving body structures--similar to an X-ray movie A continuous X-ray beam is passed through the body part being examined.
Examination by this method is. Fluoroscopy is a form of X-ray imaging guidance that helps your doctor to locate the internal injection site where an injection such as a steroid or joint injection is to be administered for pain relief. Small lesions can be overlooked there is no permanent record.
Fluoroscopy is an innovative technology that offers many similar benefits in reference to imaging as x-rays do. Early fluoroscopes consisted simply of an X-ray source and a fluorescent screen between which the patient was placed. An Introduction to Fluoroscopy Safety 7 the axis of rotation of the -arm that holds the x-ray source and detector which is typically close to the center of the patient.
The isocenter lies on the rotational axis between the source and detector. The patient is put into position so that the part to be viewed is placed between an x-ray tube and a fluorescent screen. Chest fluoroscopy is an imaging test that uses X-rays to look at how well your lungs are working.
Your respiratory tract includes your lungs nose throat trachea and bronchi. Computed tomography CT fluoroscopy and radiography conventional X-ray including mammography all use ionizing radiation to generate images of the body. Fluoroscopy or real-time projection X-ray imaging has been in clinical use since shortly after Roentgens discovery of X-rays.
Fluoroscopy is like GPS global positioning system navigation for the tip of an injection needle. An instrument for visual observation of the body by means of x-ray. Introduction to digital fluoroscopy Digital fluoroscopy components Analog and digital image characteristics Image digitization quantizationsampling Image processing Summary Fluoroscopic Analog Image Continuous brightness variation corresponding to differential x.
When the image was magnified by a factor of 25 Figure K the system further increased the x-ray tube voltage to 94 kV and used a tube current of 28 mA which increased the input air kerma to 61 mGyminute. Ionizing radiation is a form of. Here the body which needs to be examined receives X-ray beam.
The differencebetween conventional fluoroscopy and Digital fluoroscopy is the natureof the image and the manner in which it is digitized Advantages of Digital fluoroscopy over conventional fluoroscopy are. A fluoroscope is like a continuous X-ray providing live images to a TV screen.
The Importance Of Radiopaque Markers In Digital X Ray
Effect Of Changing X Ray Tube Voltage Kv Radiology Suny Upstate Medical University
Plain Radiography Springerlink
General Radiology X Rays And Fluoroscopy Pleasantonimaging Com

Conventional Radiography Special Subjects Merck Manuals Professional Edition
Dead Pixel Artifact Radiology Case Radiopaedia Org
C Arm X Ray Machines All You Needed To Know
X Rays Undergraduate Diagnostic Imaging Fundamentals
Plain Radiograph X Ray Insideradiology
Radiography X Ray Imaging Let S Talk Science

Conventional Radiography Special Subjects Merck Manuals Professional Edition

Radiographic Contrast Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org

Dacrocystography Patient Comfort Patient History Surgical Gloves
Assessment Of Cxr Positioning Views How To Read A Chest X Ray Part 4 Medzcool Youtube
What Is Fluoroscopy And How To Prepare Envision Radiology

How X Rays Work Radiology Student Nuclear Medicine X Ray
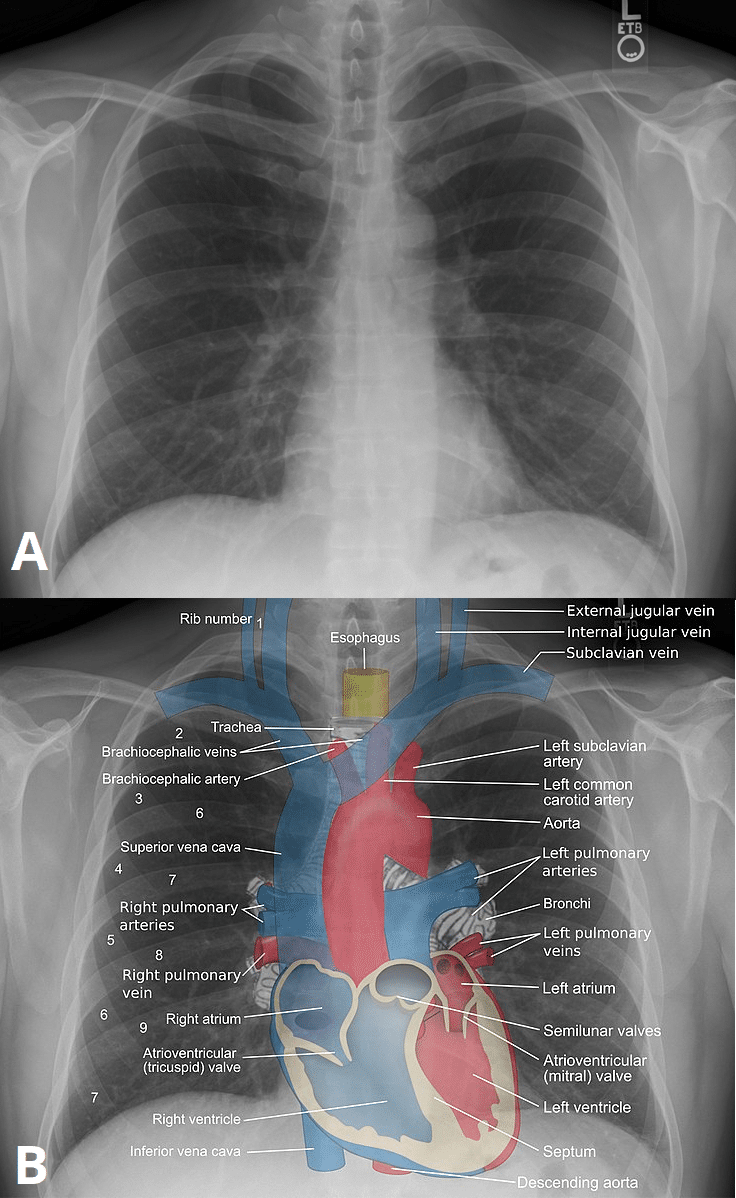
Plain Film X Ray Principles Interpretation Teachmeanatomy
X Rays Of The Extremities Johns Hopkins Medicine

Post a Comment for "Definition Of X-ray Fluoroscopy"