Short Definition For Vaccine
In stimulating the bodys adaptive immunity they help prevent sickness from an infectious diseaseWhen a sufficiently large percentage of a population has been. Bacille Calmette-Guérin Tuberculosis Vaccine.
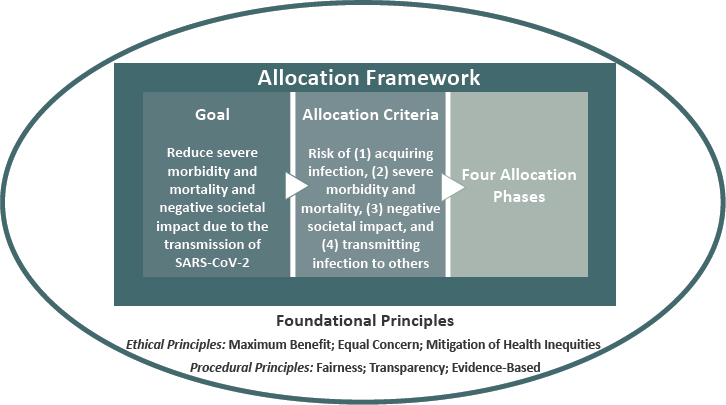
3 A Framework For Equitable Allocation Of Covid 19 Vaccine Framework For Equitable Allocation Of Covid 19 Vaccine The National Academies Press
It usually consists of a small amount of a killed weakened or otherwise modified version of a disease such as a virus or bacterium.

Short definition for vaccine. A vaccine typically contains an agent that resembles a disease-causing microorganism and is often made from weakened or killed forms of the microbe its toxins or one of its surface proteins. From Jenners book title came the use of the terms vaccine matter and vaccine virus for the cowpox inoculum the virus-containing material used in inoculations and vaccinations as a name for the inoculation procedure. French authors writing about Jenners work soon after his books publication used the word vaccine alone as a term for cowpox and vaccin a masculine derivative of vaccine as.
Anthrax vaccine a cell-free protein extract of cultures of Bacillus anthracis used for immunization against anthrax. Cell-Culture Inactivated Influenza Vaccine Trivalent Flucelvax DPT. Vaccines are substances that prevent the spread of disease.
Giving people vaccines can save millions of lives. This vaccine protects against. Vaccine suspension of weakened or killed microorganisms or toxins or of antibodies or lymphocytes that is administered to prevent disease.
As a result the body cannot defend itself. Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome AIDS. A preparation that is administered as by injection to stimulate the bodys immune response against a specific infectious agent or disease.
A traditional vaccine involves an injection either with a weakened form of the virus you are protecting against or a similar virus. Learn about the history effectiveness and types of vaccines. A suspension of attenuated or killed microorganisms viruses bacteria or rickettsiae administered for prevention amelioration or treatment of infectious diseases.
Updated on 19 July 2021. Either one can produce antibodies that remain in the system and. Vaccines contain a microorganism or virus in a weakened live or killed state or proteins or toxins from the organism.
The HPV vaccine became available in 2006. The introduction of vaccineinto the body to produce immunity to a specific disease. A vaccine is a substance introduced into someones body to prevent them from getting a specific disease.
The term vaccination comes from the Latin vaccacow and was coined when the first inoculations were given with organisms that caused the mild disease cowpox to produce immunity against smallpox. A vaccine is a biological preparation that provides active acquired immunity to a particular infectious disease. Vaccination is the administration of a vaccine to help the immune system develop protection from a disease.
It is given to people usually by injection to prevent them getting that disease. Today the word has the same meaning as inoculationand immunization. For example smallpox killed some 2 million people in 1967.
Vaccines like MMR and chickenpox are recommended for adults who have not had the diseases and vaccines including hepatitis A hepatitis B pneumococcus and meningococcus are recommended for sub-groups of the adult population. It uses your bodys natural defenses to build resistance to specific infections and makes your immune system stronger. Vaccination is a simple safe and effective way of protecting people against harmful diseases before they come into contact with them.
By 1979 the disease had disappeared. ˈvæksiːn C2 a substance that is put into the body of a person or animal to protect them from a disease by causing them to produce antibodies proteins that fight diseases. In 2018 the license was expanded to include people up to 45 years of age.
An antigenic preparation of a typically inactivated or attenuated see attenuated sense 2 pathogenic agent such as a bacterium or virus or one of its components or products such as a protein or toxin a trivalent. Vaccines work by stimulating the immune system to attack specific harmful agents. A vaccine containing partial cellular material as opposed to complete cells.
DPT vaccine- abbreviation for combination vaccine against diphtheria and pertussis whooping cough and tetanus toxoids. A medical condition where the immune system cannot function properly and protect the body from disease. Usually given in a series of injections in early childhood immunizing agent immunogen- any substance or organism that provokes an immune response produces immunity when introduced into the body.
A vaccine is a substance containing a harmless form of the germs that cause a particular disease.

Module 3 Mass Vaccination Campaigns Who Vaccine Safety Basics
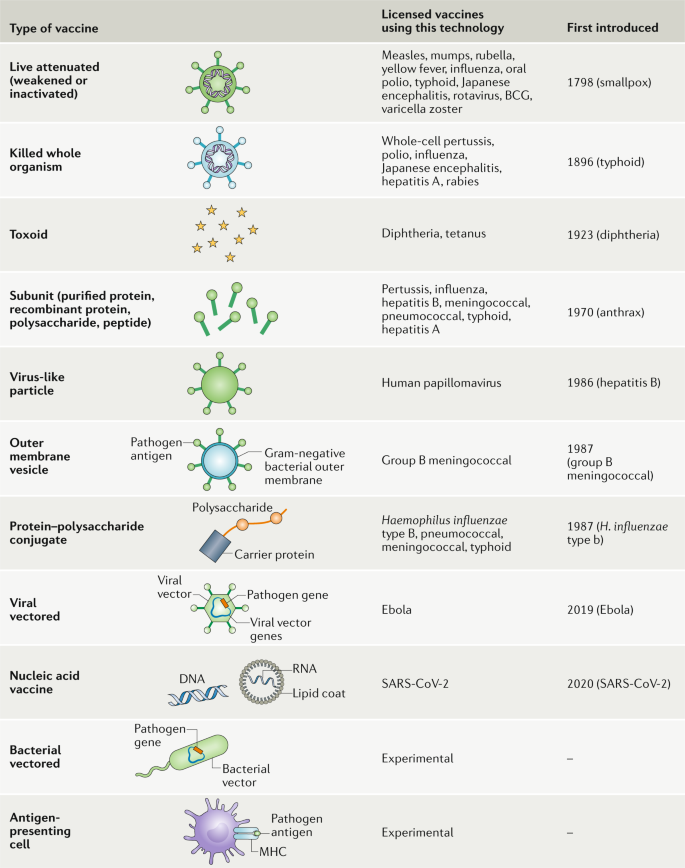
A Guide To Vaccinology From Basic Principles To New Developments Nature Reviews Immunology
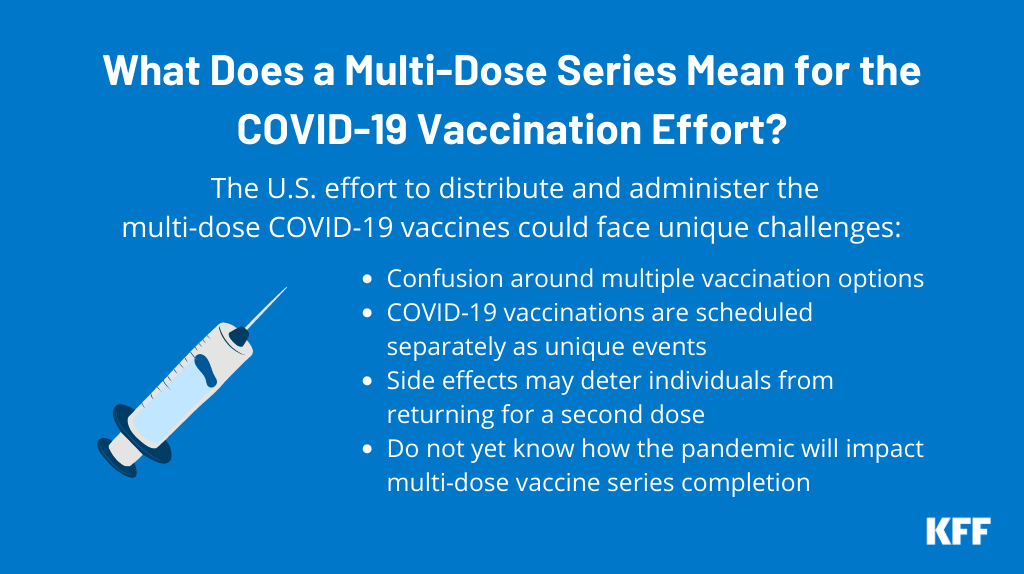
What Does A Multi Dose Series Mean For The Covid 19 Vaccination Effort Kff
-4.gif)
What Are The Different Types Of Vaccines

Explainer What Is A Vaccine Science News For Students
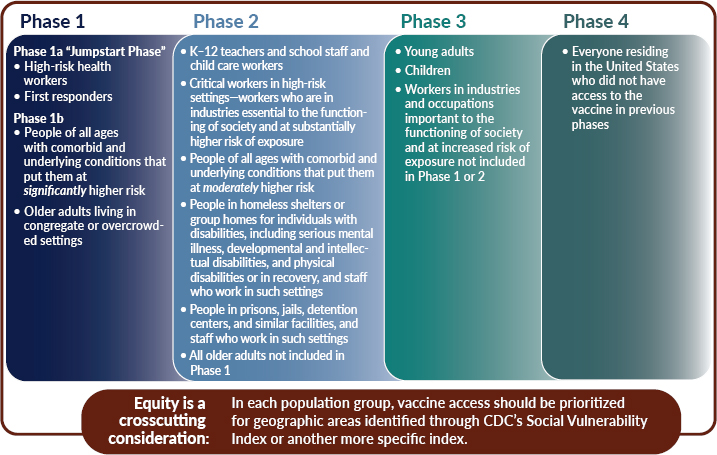
3 A Framework For Equitable Allocation Of Covid 19 Vaccine Framework For Equitable Allocation Of Covid 19 Vaccine The National Academies Press

Inoculation Medicine Britannica
Vaccination Importance Of Vaccines Vaccination And Immunization

Toxoid An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Defining Immunization Types Statistics And Resources Regis College Online

How Vaccines Work British Society For Immunology

Dna Vaccines Explained Biotech Primer Weekly

Vaccine Characteristics And Types Of Vaccine Online Biology Notes

How Vaccines Work British Society For Immunology

How Vaccines Work British Society For Immunology

Module 2 Types Of Vaccines Who Vaccine Safety Basics
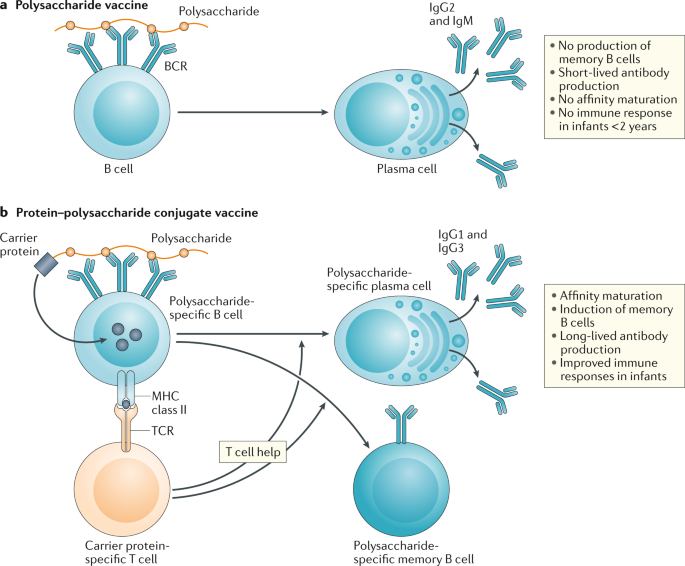
A Guide To Vaccinology From Basic Principles To New Developments Nature Reviews Immunology

Module 2 Subunit Vaccines Who Vaccine Safety Basics

Post a Comment for "Short Definition For Vaccine"