Definite Definition Of Neutron
Neutron stars are the collapsed cores of massive stars. Neutron - an elementary particle with 0 charge and mass about equal to a proton.

Unclear About Nuclear 2 1 1 Electrons Protons Neutrons And Isotopes Openlearn Open University St174 1
Neutron has the mass of 16750 X 10 -27 kg.

Definite definition of neutron. Neutron - an elementary particle with 0 charge and mass about equal to a proton. Neutropenia is a. Definition of Neutron Number.
Neutropenia is sometimes called agranulocytosis or granulocytopenia because neutrophils make up about 60 of WBCs and have granules inside their cell walls. Heres a comparison of a neutron stars typical. Show more Full Article.
Search the Dictionary for More Terms. Neutron definition an elementary particle having no charge mass slightly greater than that of a proton and spin of ½. Neutrons are in the nucleus the center of the atom.
The number of neutrons in an atom determines its isotope. Definition of neutron - Chemistry Dictionary. Nucleon - a constituent proton or.
Born from the explosive death of another larger stars these tiny objects pack quite a punch. A measure of the intensity of neutron radiation determined by the rate of flow of neutrons. Enters into the structure of the atomic nucleus.
A particlefound in the nucleusof an atom. Its mass is slightly bigger than the protons mass but higher than the electrons mass. What is a Neutron.
Nucleon - a constituent proton or neutron of an atomic nucleus. A neutron is the particle in the atomic nucleus with a mass of one and a charge of zero. Enters into the structure of the atomic nucleus.
Neutrophils are white blood cells WBCs produced in the bone marrow that ingest bacteria. Neutropenia Definition Neutropenia is an abnormally low level of neutrophils in the blood. They pack roughly the mass of our sun into a sphere with the diameter of a city.
Return to top of page. Thermal neutron any free neutron one that is not bound within an atomic nucleus that has an average energy of motion kinetic energy corresponding to the average energy of the particles of the ambient materials. Neutron stars are city-size stellar objects with a mass about 14 times that of the sun.
A dense celestial object that consists primarily of closely packed neutrons and that results from the collapse of a much larger stellar body See the full definition SINCE 1828. A neutron star is the collapsed core of a massive supergiant star which had a total mass of between 10 and 25 solar masses possibly more if the star was especially metal-rich. The neutron flux value is calculated as the neutron density n multiplied by neutron velocity v where n is the number of neutrons per cubic centimeter expressed as neutronscm3 and v is the distance the neutrons travel in 1 second expressed in centimeters per second or cmsec.
The number of neutrons in the nucleus of an atom equal to the mass number minus the atomic number of the atom. An electrically neutral subatomic particle in the baryon family having a mass of 1674 10 24 grams 1838 times that of the electron and slightly greater than that of the proton. Relatively slow and of low energy thermal neutrons exhibit properties such as large cross sections in fission that make them desirable in certain chain.
An uncharged elementary particle that has a mass nearly equal to that of the proton and is present in all known atomic nuclei except the hydrogen nucleus. A constituent of the nuclei of all atoms except those of hydrogen. 2019-05-22 by Nick Connor.
The total number of neutrons in the nucleus of an atom is called the neutron number of the atom and is given the symbol N. It is almost identical in massto a proton but carries no electric charge.

Nuclear Physics Students Britannica Kids Homework Help

Atoms And Molecules Counting Matter Molecules Atom Conservation Of Mass
Atomic Structure Boundless Microbiology
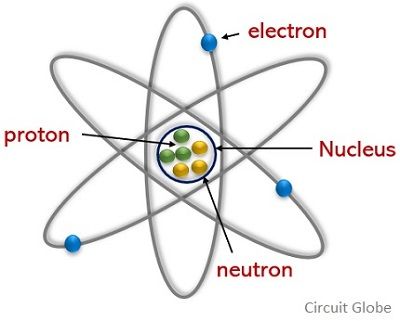
Difference Between Electron And Proton With Comparison Chart Circuit Globe

What Is The Basic Structure Of Atom Electrons Protons Neutrons Digital Kemistry Youtube

Atom Rutherford S Nuclear Model Britannica

Atomic Structure Boundless Microbiology

Amorphous Solid Easy Science Easy Science Flashcards Chemical Changes
The Standard Model Part 2 Enter The Atom By Simone Lilavois Medium

Basic Parts Of The Atom Protons Neutrons Electrons Nucleus Atom Matter Science Protons

Atomic Theory And Atoms Notes Studyblr Chemistry Studygram Notes Chemistry Notes Study Notes School Study Tips

What Is A Neutron And Its Charge Discovery And Mass Of A Neutron Neutrons Electron Configuration What Is Energy
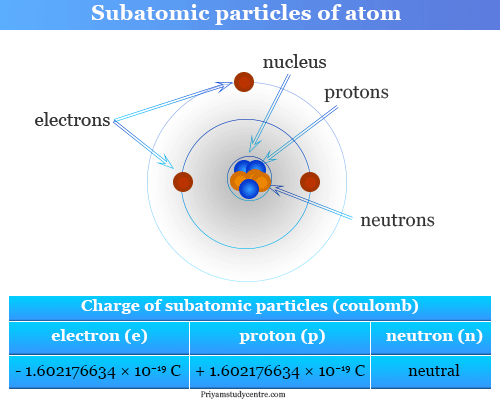
Elementary Particles Subatomic Particles List Mass Charge

Introduction To Atoms Ch 11 Flashcards Quizlet

Excess Reactant Easy Science Chemical Reactions Easy Science Excess

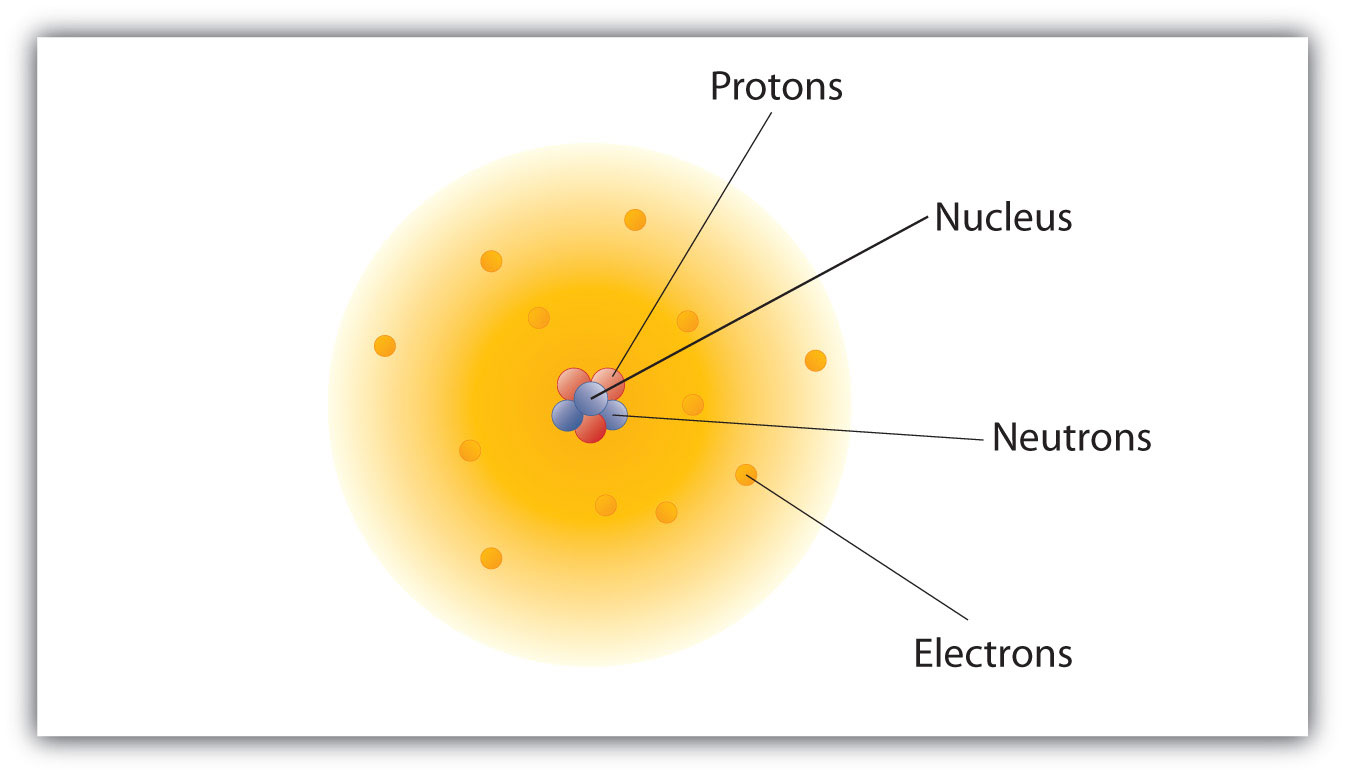

Post a Comment for "Definite Definition Of Neutron"