Definition Of Molecule For Class 6
RNA also acts as genetic material in some organisms as in some viruses and acts as messenger. Chemistry - meaning and importance.
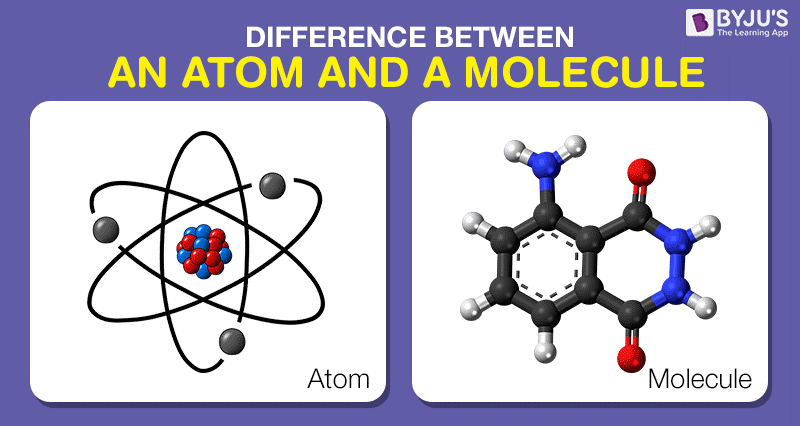
Difference Between Atom And Molecule In Tabular Form
The terms molecule compound and atom can be confusing.

Definition of molecule for class 6. ICSE Class 6 Chemistry Syllabus. Carbonyl - functional group consisting of a carbon atom double bonded to oxygen CO. Ores of iron such as haemetite Fe 2 O 3 magnetite Fe 3 O 4 siderite FeCO 3 and iron pyrites FeS 2 being magnetic can be.
A biomolecule or biological molecule is a loosely used term for molecules present in organisms that are essential to one or more typically biological processes such as cell division morphogenesis or development. Also ionic bonds have no definite shape. The forces which hold the atoms together in a molecule are called covalent bonds.
An ionic bond forms between a metal and a non-metal in which the non-metal attracts the electron from the other atom. A molecule is the smallest particle of a substance which has the properties of that substance and can exist in the free state. Glass water and air.
Ionic bonds are solid at room temperature. There are two types of molecules. ICSE Class 6 Chemistry Get sample papers syllabus textbook solutions revision notes test previous year question papers videos lectures online for ICSE Class 6 Chemistry on TopperLearning.
DNA acts as genetic material in most of the organisms. A more general name for this class. Learn more about the properties and structures of molecules in this article.
It is a member of the nonmetal group. In this process a large number of fibres from a cotton wool are drawn out and gently twisted such that the fibres gel together to form a yarn. Heres an explanation of what a molecule is with some examples of common molecules.
The syllabus consists of the course details of Class 6. Which of the ores mentioned can be concentrated by magnetic separation method. The rate of diffusion in liquids is higher than that of solids.
Fibre to Yarn. Furthermore ionic bonds are high in polarity. Molecules are made up of groups of atoms.
Liquids have fixed volume but no fixed shape. ICSE Chemistry Class 6 Syllabus. Devices used are takli Charaka and modern day machines.
Transparent Translucent and Opaque. A molecule is defined as the smallest unit of a compound that contains the chemical properties of the compound. Molecule a group of two or more atoms that form the smallest identifiable unit into which a pure substance can be divided and still retain the composition and chemical properties of that substance.
NCERT IN TEXT QUESTIONS 61. Describing the structure of an atom an atom is also sub-divided into smaller units. Carbon - Carbon is the name for the element with atomic number 6 and is represented by the symbol C.
Carbonate - an ion consisting of one carbon bonded to three oxygen atoms CO 32- or a compound containing this ion. Materials which allow light to pass through them completely are called Transparent objects. Class 6 Chemistry Sorting of Materials.
Proton electrons and neutrons are sub-particles of. Ores Which are magnetic in nature can be separated from non-magnetic gangue particles by magnetic separation method. CBSE Class 12 Biology Revision Notes Chapter 6 Molecular Basis of Inheritance DNA Deoxyribonucleic Acid and RNA Ribonucleic Acid are two types of nucleic acid found in living organisms.
Class 6 Chemistry Fibre to Fabric. Moreover they have high boiling and melting points. Liquids are difficult to compress as particles have less space between them to move.
Objects on the other side of Transparent objects can be seen clearly. A combination of atoms is called a molecule. Force of attraction between the particles is weaker than solids.
Development of Chemistry - A historical perspective. The process of making yarn from fibres is called Spinning. The syllabus consists of five themes - i Introduction to Chemistry ii Elements Compounds and Mixtures iii Matter iv Water and v Air and Atmosphere.
Transparent Translucent and Opaque. Water milk blood coffee etc. ICSE syllabus for Class 6 Chemistry prescribes the topics and concepts based on which students will be evaluated in the final examination.
Biomolecules include large macromolecules such as proteins carbohydrates lipids and nucleic acids as well as small molecules such as primary metabolites secondary metabolites and natural products. Students are advised to start preparing for their exam by going through Chemistry syllabus. Example of a liquid state of matter.

Molecule Definition Examples Structures Facts Britannica

Difference Between Molecules And Compounds In Tabular Form

Atoms Elements Molecules Compounds Poster Set Teaching Chemistry Chemistry Education Chemistry Classroom

Molecules And Atoms Pack Science Projects For Kids Atoms And Molecules For Kids Atom Activities

Selina Concise Chemistry Class 6 Icse Solutions Chapter 4 Elements Compounds Symbols And Formulae Ncert Books Chemistry Class Chemistry Basics Chemistry

Molecule And Molecules Of Elements Videos Concepts Compounds

Worksheet Counting Atoms Version B Counting Atoms Worksheet Chemistry Worksheets Counting Atoms

Polar And Nonpolar Molecules Covalent Bonding Molecules Chemistry Lessons

Important Questions Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 1 Basic Concepts Chemistry 2 11th Chemistry Basic Concepts Chemistry

Atoms And Molecules Difference Between Atom And Molecule Atomvsmolecule Youtube

Molecule Vs Atom Cengage Learning Molecules Teaching Science
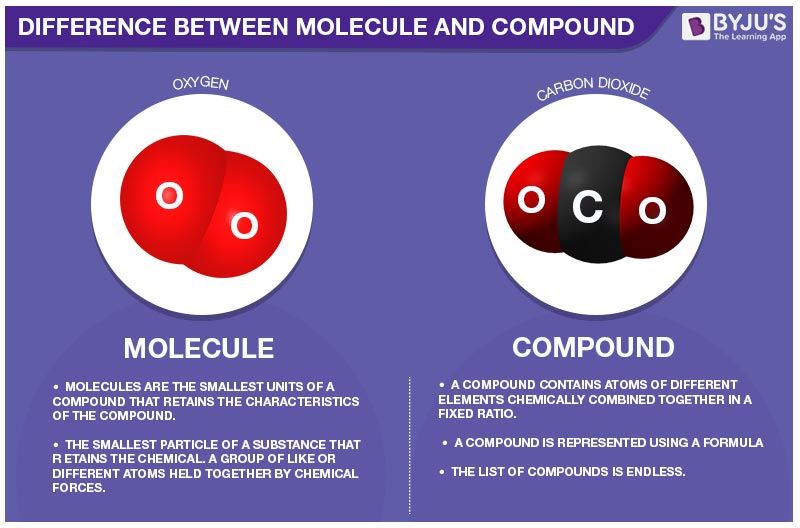
Difference Between Molecule And Compound In Tabular Form

Matter Atoms Elements Molecules And Compounds Anchor Posters Atoms And Molecules For Kids Molecules Science Poster

Difference Between Atoms And Molecules Atoms And Molecules Definition

What Are Atoms Molecules Definition Differences Video Lesson Transcript Study Com

Molecule Definition Examples Structures Facts Britannica

6 Main Types Of Chemical Reactions Google Search Chemistry Classroom Chemistry Lessons Chemical Reactions

Post a Comment for "Definition Of Molecule For Class 6"