Definition Of X-ray Film
A special photographic film with a sensitive emulsion layer that blackens in response to the light from intensifying screens. X-Ray Film A film base coated with an emulsion designed for use with x-rays.

Infmetry X Ray Film Mouse Pad Electronics Ray Film X Ray Computers Tablets And Accessories
Source Radiography - The origin of radiation.

Definition of x-ray film. X-ray film should not be used if outdated as it may fog and markedly compromise its diagnostic usefulness. X-rays are absorbed by many forms of matter including body tissues and are used in medicine and industry to produce images of internal structures. Any of the electromagnetic radiations that have an extremely short wavelength of less than 100 angstroms and have the properties of penetrating various thicknesses of all solids of producing secondary radiations by impinging on material bodies and of acting on photographic films and plates as light does.
An X-ray or much less commonly X-radiation is a penetrating form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation. The radiographic film is processed with chemicals to produce a visible manifest image which is then viewed on a light box catalogued and physically stored. Xray Film n 1.
An emulsion coating both sides of the film contains ting silver halide crystals that are sensitive to such things as visible light X-rays gamma rays heat moisture and pressure. A dental X-ray film that can be held in place by the teeth during radiography. Photographic film used to make X-ray pictures.
Most X-rays have a wavelength ranging from 10 picometers to 10 nanometers corresponding to frequencies in the range 30 petahertz to 30 exahertz 30 1015 Hz to 30 1018 Hz and energies in the range 124 eV to 124 keV. Nouns denoting man-made objects. A high-energy stream of electromagnetic radiation having a wavelength shorter than that of ultraviolet light but longer than that of a gamma ray.
An x-ray tube or a radioisotope. Radiography is an imaging technique using X-rays gamma rays or similar ionizing radiation and non-ionizing radiation to view the internal form of an objectApplications of radiography include medical radiography diagnostic and therapeutic and industrial radiographySimilar techniques are used in airport security where body scanners generally use backscatter X-ray. Bitewing - a dental X-ray film that can be held in place by the teeth during radiography.
How to pronounce x-ray film. The x-ray film is somewhat similar to photographic film in its basic composition. Geometric factors include the size of the area of origin of the radiation.
A film base coated with an emulsion designed for use with x-rays. The emulsion has silver halide crystals immersed in gelatin. Photographic film used to make X-ray pictures.
The X-ray film is the medium that record the image of part exposed with X-rays. Definition of x-ray film processing in the Medical Dictionary by The Free Dictionary. Single-emulsion filmhas the emulsion on one side of the cellulose base.
X-ray film - photographic film used to make X-ray pictures. X-ray film is a gelatin-covered polyester base. However unlike photographic film the light or radiation sensitive emulsion is usually coated on both sides of the base of X-ray film so that it can be used with intensifying screens.
Introduction X-ray films are the most important material used to decode the information carried by the attenuated x-ray beam when they are made to pass through the tissue They capture the invisible image into visible form. Autoradiography is a detection method in which X-ray or photographic film is exposed to emissions from radioisotopes on TLC plates to produce an image on the film. The x-ray film is composed of following.
X-RAY FILM noun Sense 1. Definition - The sharpness of features on a radiograph that correspond to boundaries from thickness or material density changes in the radiographed component. Photographic film film - photographic material consisting of a base of celluloid covered with a photographic emulsion.
X-rays after passing through the patient interact with the image receptor and a latent image an invisible change that represents the object that was radiographed forms in the film. After exposure exposure time depends on the amount of radioactivity per zone the film is developed to reveal the location of the areas of radioactivity as darkened spots or zones of varying optical density.

Pulmonary Plethora Causes Obv Left Heart Abnormalities Double Outlet Right Ven Human Anatomy And Physiology Nuclear Medicine Anatomy And Physiology
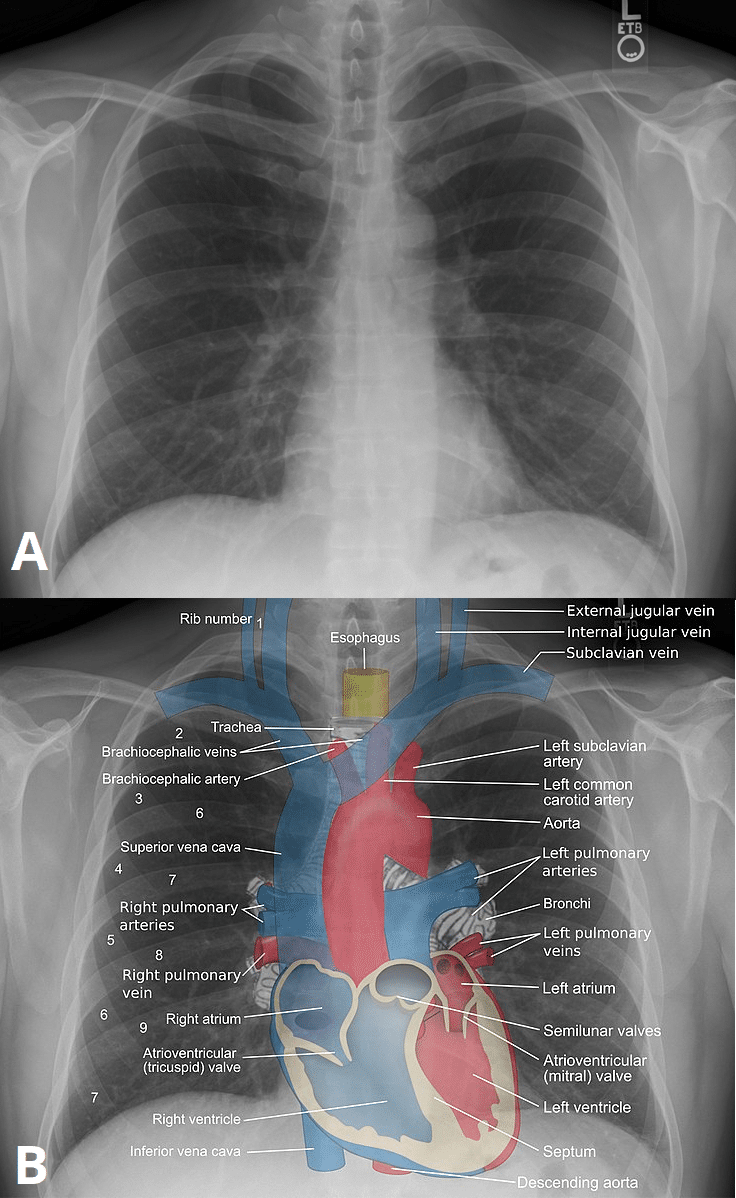
Plain Film X Ray Principles Interpretation Teachmeanatomy
Different Types Sizes Of X Ray Films

X Ray Artifacts Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org

X Rays Definition Block Diagram And Working Of X Ray Machine X Ray Radiology Schools Radiology Student

X Ray Films An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Chest X Ray Basic Interpretation X Ray Radiology Silhouette Sign
Shredding Is Not The Only Option For X Ray Film Destruction

How Do X Rays Work Independent Imaging

Radiographic Contrast Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org
Digital X Rays Vs Traditional X Rays The Differences Medical Imaging Experts
Plain Radiograph X Ray Insideradiology
Effect Of Changing X Ray Tube Voltage Kv Radiology Suny Upstate Medical University

How To Read Chest X Rays International Emergency Medicine Education Project

Buy Dentalfilm Eco 30 Self Developing X Ray Film Online On Dentalaaka Ray Film X Ray Development

X Ray Films An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/article/en/normal-chest-x-ray/eIIXNhFk2r9VNLRTkmISA_Screenshot_2019-02-21_at_10.07.34.png)
Normal Chest X Ray Anatomy Tutorial Kenhub

Pin By Jeremy Enfinger On Radiographic Anatomy Radiology Radiology Student Radiology Schools
Post a Comment for "Definition Of X-ray Film"