Definition Of Mass Defect In Chemistry
This additional mass is accounted for by binding energy that is released when a nucleus is formed. It is equal to the mass defect less the quantity of energy or mass released when a bound system is created.
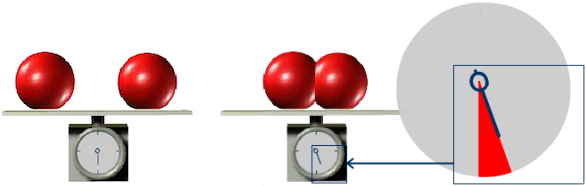
E Mc2 And Binding Energy From Einstein Light
In atomic mass The difference called the mass defect is accounted for during the combination of these particles by conversion into binding energy according to an equation in which the energy E released equals the product of the mass m consumed and the square of the velocity of light in vacuum c.

Definition of mass defect in chemistry. The mass defect may be calculated directly from emc2 equation. Mass Defect and Binding Energy Careful measurements have shown that the mass of a particular atom is always slightly less than the sum of the masses of the individual neutrons protons and electrons of which the atom consists. Mass defect Chemistry The difference in the mass of a polyatomic molecule and the sum of the masses of its constituent particlesie electrons protons and neutrons.
A nuclide AX has N neutrons and Z protons so that the difference in mass is derived as m Zmp Nmn mtot. The binding energy which is proportional to this mass difference is known as the mass defect. This mass is typically associated with the binding energy between nucleons.
This difference in the mass is called mass defect given by Delta mZm_pA-Zm_n-m_nuc Where Zm p is the total mass of the protons. The mass defect per Nucleon is called packing fraction. The observed atomic mass is always less than the sum of the masses of all constituent particles.
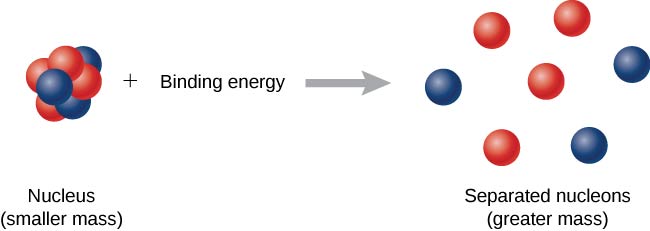
The difference between the mass of the atom and the sum of the masses of its parts is called the mass defect Δm. Binding energy is also known as separation energy. Up to 10 cash back Mass defect is associated with the binding energy of the nucleus.
Mass defect is the difference between the sum of the masses of all constituents and observed the atomic mass of an atom of an element. Mass loss is the sum of the mass of particles present in the nucleus of an atom and the difference between the actual mass of the nucleus. The missing mass is the energy released by the formation of the atomic nucleus.
A-Zm n is the total mass of the neutrons. The mass defect occurs because matter is converted into energy as per Einsteins E mc2 which is the energy that binds the nucleus together and overcomes the mutual repulsion between protons. The binding energy of a system can appear as extra mass which accounts for this difference.
The total mass of the nucleusm nuc is less than the sum of individual masses of neutrons and protons which in fact constitutes it. Nuclear binding energy is used to determine whether fission or fusion will be a favorable process. The actual atomic mass is less than the predicted mass calculated by adding the masses of nucleons.
Mass defect is known as the mass difference which means the sum of the total mass of the nucleus constituents. The protons and neutrons are more than that of the mass of the nucleus. This concept has been increasingly used in mass spectrometry over the years mainly due to the growing use of high resolution mass spectrometers capable of exact mass measurements in many application areas in analytical and bioanalytical chemistry.
Mass defect is the difference between the predicted mass and the actual mass of an atoms nucleus. Mass defect also called mass deficit is the difference between the mass of an object and the sum of the masses of its constituent particles. In physics and chemistry a mass defect refers to the difference in mass between an atom and the sum of the masses of the protons neutrons and electrons of the atom.
It is a fundamental property of the nucleus and the principle behind nuclear energy. Discovered by Albert Einstein in 1905 it can be explained using his formula E mc2 which describes the equivalence of energy and mass. Binding Energy of the Nucleus.
Mass defect is the difference between the actual atomic mass and the predicted mass calculated by adding the mass of protons and neutrons present in the nucleus. The mass defect of a nucleus represents the mass of the energy binding the nucleus and is the difference between the mass of a nucleus and the sum of the. Mass defect has also entered into the mass spectrometry terminology with the availability of high resolution mass spectrometry and has found application in mass spectral analysis.
M nuc is the mass of the nucleus. This decrease of the mass of the nucleus is called Mass Defect. Mass defect definition the amount by which the mass of an atomic nucleus differs from the sum of the masses of its constituent particles being the mass equivalent of the energy released in the formation of the nucleus.
The mass defect occurs because matter is converted into energy as per Einsteins E mc2 which is the energy that binds the nucleus together and overcomes the mutual repulsion between protons. Mass defect Chemistry The difference in the mass of a polyatomic molecule and the sum of the masses of its constituent particlesie electrons protons and neutrons. Thus BE m c2 Zmp Nmn mtotc2.
Mass defect is defined as the difference between a compounds exact mass and its nominal mass.
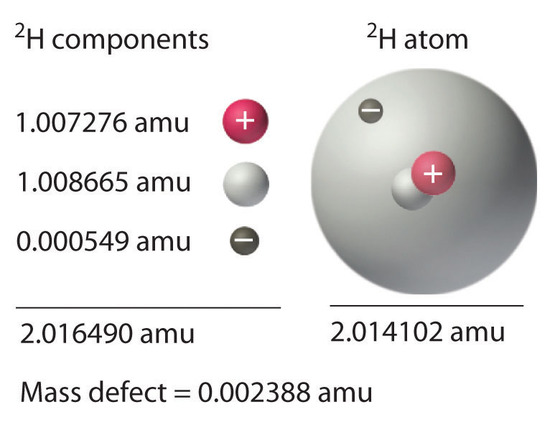
21 6 Energy Changes In Nuclear Reactions Chemistry Libretexts
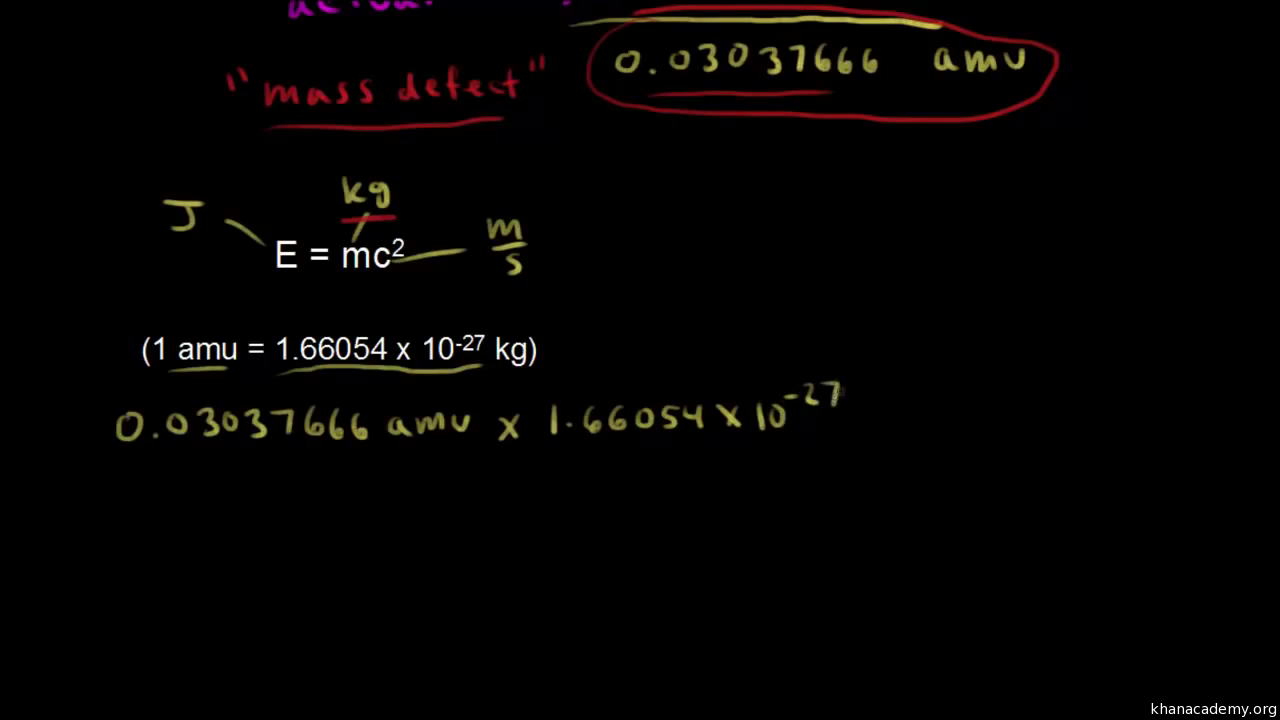
Mass Defect And Binding Energy Video Khan Academy

Nuclear Binding Energy Per Nucleon Mass Defect Problems Nuclear Chemistry Youtube

Mass Defect And Binding Energy Video Khan Academy

Nuclear Physics Definition Law Of Radioactive Decay Applications

Mass Defect Binding Energy 1 Of 7 An Explanation Youtube

Mass Defect Easy Science Easy Science Neutrons Beta Particle

Mass Defect And Binding Energy Ib Physics Youtube
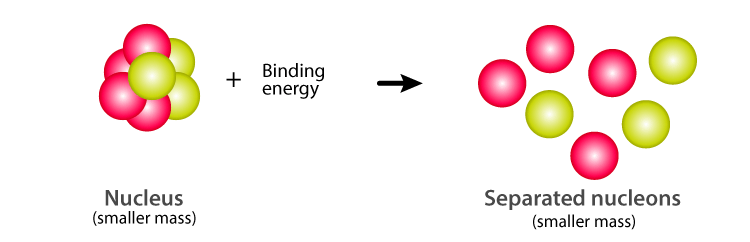
Nuclear Binding Energy Definition Formula Explanation

Mass Defect Binding Energy 1 Of 7 An Explanation Youtube

Important Questions For Cbse Class 12 Physics Mass Defect And Binding Energy

Lecture 1 2 C 2015 Calculate The Mass Defect And The Binding Energy Per Nucleon For A Particular Isotope Calculate The Mass Defect And The Binding Ppt Download
10 3 Nuclear Binding Energy Physics Libretexts

A Nucleus Is More Than Just Mass Ppt Video Online Download
Ppt 26 1 Properties Of Nucleus 26 2 Binding Energy And Mass Defect Powerpoint Presentation Id 1596224

Properties Of Nucleus 26 2 Binding Energy And Mass Defect Unit 26 Nucleus Is Defined As The Central Core Of An Atom That Is Positively Charged Ppt Download

Isotopes Mass Defect E 2 Mc Isotopes Thanks

Properties Of Nucleus 26 2 Binding Energy And Mass Defect Unit 26 Nucleus Is Defined As The Central Core Of An Atom That Is Positively Charged Ppt Download

Ppt 26 1 Properties Of Nucleus 26 2 Binding Energy And Mass Defect Powerpoint Presentation Id 1596224
Post a Comment for "Definition Of Mass Defect In Chemistry"