Definition Of Prokaryotic Organism
The size of a prokaryotic cell can range between 02 to 10 microns. A microscopic single-celled organism which has neither a distinct nucleus with a membrane nor other specialized organelles including the bacteria and cyanobacteria.

Difference Between Prokaryotic Cells And Eukaryotic Cells With Comparison Chart And Explanation Of Organelles Bio Differences
Being or characteristic of a prokaryote.

Definition of prokaryotic organism. Microorganisms are broadly characterized as prokaryotes and eukaryotes where both the classes differ from each other in their characteristic structure shape and the type of microorganisms they contain. Bacteria and Archaea are the two domains of life that are prokaryotes. However organisms with prokaryotic cells are very abundant and make up much of Earths biomass.
Prokaryotes are single-celled organisms that are the earliest and most primitive forms of life on earth. Prokaryotic cells are single-celled microorganisms known to be the earliest on earth. Many also have polysaccharide capsules.
Prokaryotic cells are simple cells that do not have a true nucleus or other cell organelles. Prokaryotic definition is - of relating to or being a typically unicellular organism as of the domains Bacteria and Archaea lacking a distinct nucleus and membrane-bound organelles. Prokaryotic cells range in diameter from 0150 µm.
Made of a single cell. As organized in the Three Domain System prokaryotes include bacteria and archaeans. Prokaryote is a Latin word which when broken into two half means pro before and kary nut.
Any of a wide variety of one-celled organisms that lack a distinct cell nucleus or other structures bound by a membrane and that have DNA that is not organized into chromosomes. A prokaryotic cell consists of a single membrane and therefore all the reactions occur within the cytoplasm. A teaspoon full of rich soil may contain billions of them.
Prokaryote also spelled procaryote any organism that lacks a distinct nucleus and other organelles due to the absence of internal membranes. Kingdom Monera includes the prokaryotic cells. Prokaryotic definition of or relating to a prokaryote a cellular organism that has no nuclear membrane and no organelles in the cytoplasm except ribosomesAccording to one book the key to evolution is symbiotic invasionssuch as mitochondria and other organelles invading prokaryotic cells to create eukaryotic cells.
What are Prokaryotic Cells. Prokaryotes reproduce asexually are the most primitive and ancient known forms. Prokaryotes are organisms made up of cells that lack a cell nucleus or any membrane-encased organelles.
The word prokaryote comes from the Greek πρό pro before and κάρυον karyon nut or kernel. In the two-empire system arising from the work of Édouard Chatton prokaryotes were classified within the empire Prokaryota. Organisms with prokaryotic cells are called prokaryotes and they are generally single-celled microorganisms.
Bacteria are among the best-known prokaryotic organisms. Prokaryotes are unicellular organisms that consist of a single prokaryotic cell. Prokaryotes include Bacteria and Archaea.
Prokaryotic cell refers to the cell which is unicellular ie. Organisms whose cells have no nucleus or membrane-bound organelle eg. Prokaryotic cells are single-celled entities that are primitive in structure and function as they lack a membrane-bound nucleus and other organelles.
Some prokaryotes such as cyanobacteria are. Organisms within the domains Bacteria and Archaea are based on the prokaryotic cell while all other forms of life are eukaryotic. Prokaryotes lack a distinct cell nucleus and their DNA is not organized into chromosomes.
The term prokaryote is derived from two Greek words pro meaning before and karyon meaning nucleus. This means the genetic material DNA in prokaryotes is not bound within a nucleus. The photosynthetic prokaryotes include cyanobacteria that perform photosynthesis.
A prokaryotic cell is a type of cell that does not have a true nucleus or membrane-bound organelles. These organisms can be free-living or can be found in the gut of animals. All prokaryotes have plasma membranes cytoplasm ribosomes a cell wall DNA and lack membrane-bound organelles.
A prokaryote is a typically unicellular organism that lacks a nuclear membrane-enclosed nucleus. Dictionary of Unfamiliar Words by Diagram Group Copyright. Prokaryotes are single-celled organisms of the domains Bacteria and Archaea.
They also lack the internal structures bound by membranes called organelles such as mitochondria. Any of a wide variety of one-celled organisms of the kingdom Monera or Prokaryota that are the most primitive and ancient known forms of life. But in the three-domain system based upon molecular analysis.
The lack of internal membranes in prokaryotes distinguishes them from eukaryotes. Prokaryotic cells are microorganisms that are known to be the earliest on earth.
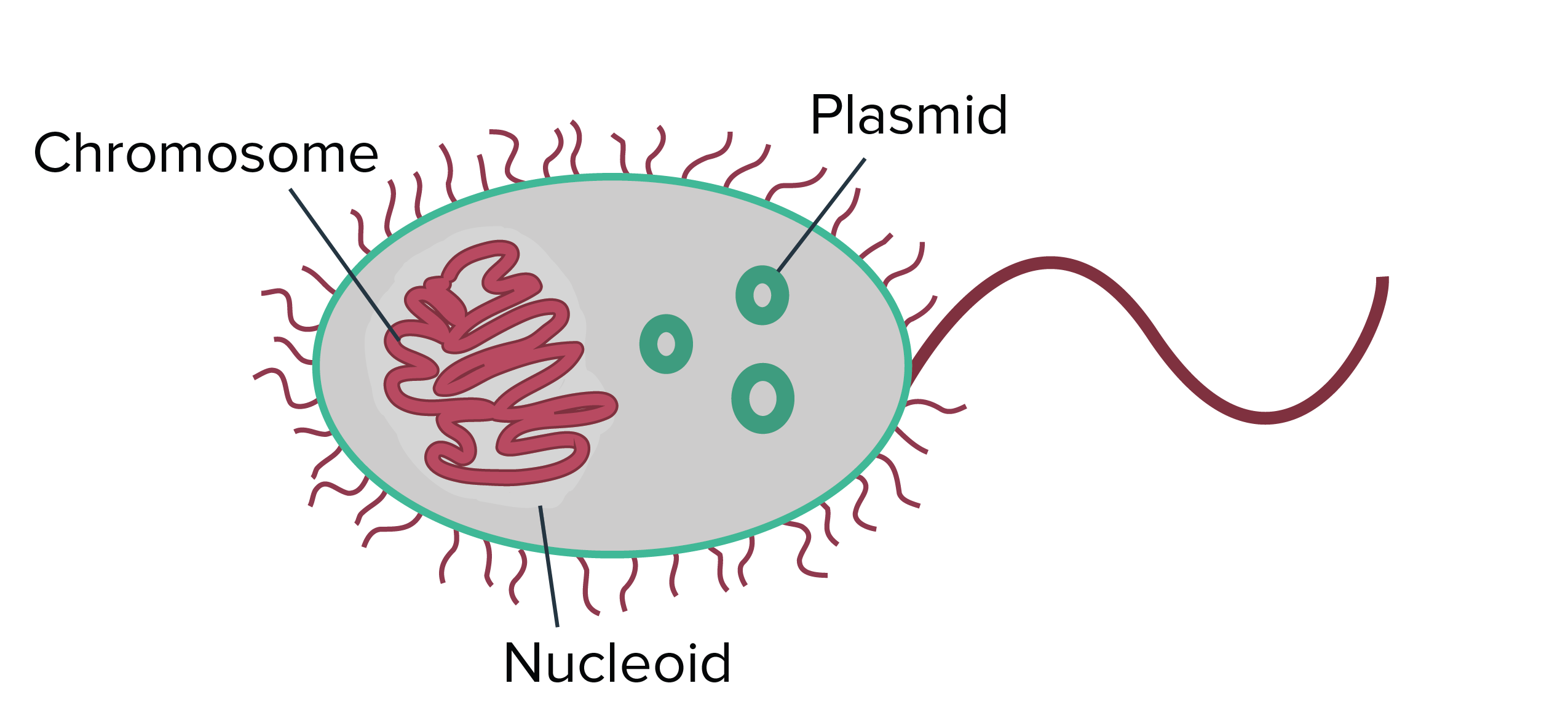
Prokaryote Structure Article Khan Academy
Why Is The Prokaryotic Cell Primitive Quora

Prokaryotic Cell Definition Examples Structure Biology Dictionary

Cells Definition Overview Expii
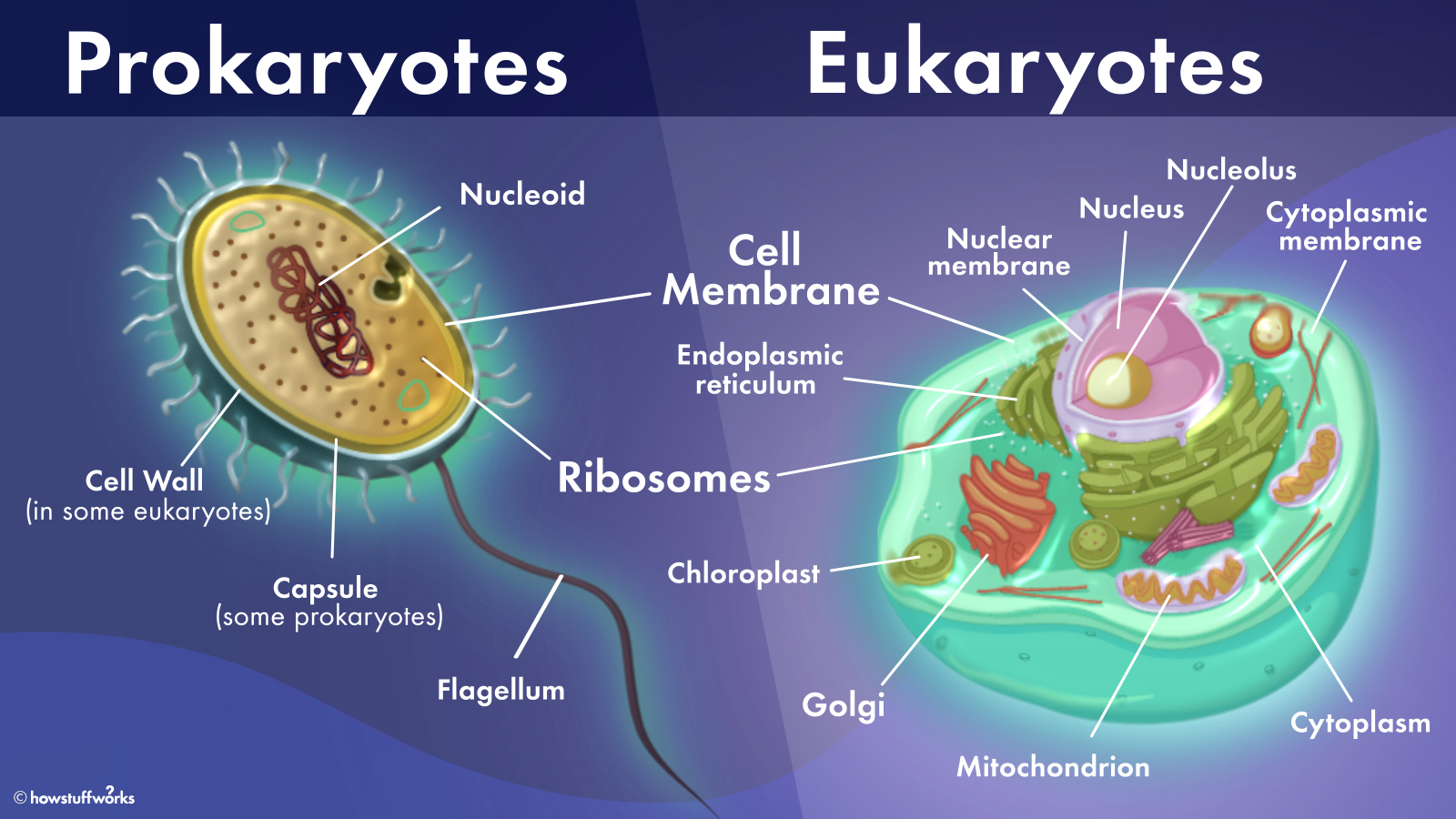
What S The Difference Between Prokaryotic And Eukaryotic Cells Howstuffworks

Prokaryotic Cell Definition Examples Diagrams
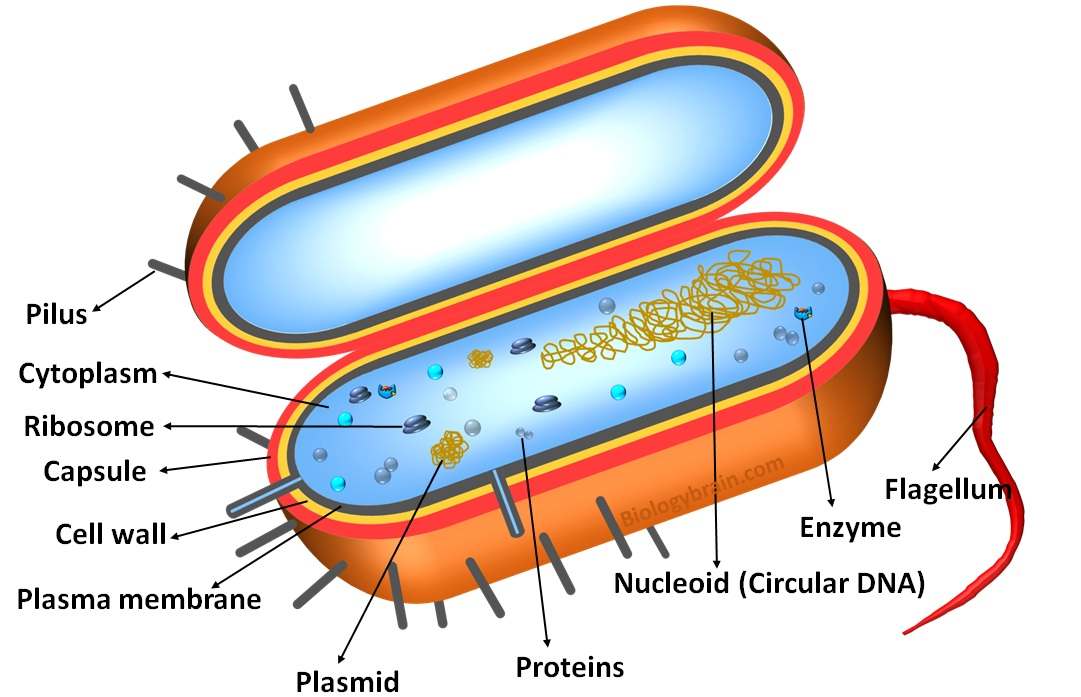
Labeled Prokaryotic Cell Diagram Definition Parts And Function Biology Brain

Prokaryotic Cell Definition Examples Structure Biology Dictionary

Prokaryotic Cells Definition Lesson For Kids Study Com

Prokaryotic Cell Components Examples With Questions And Videos
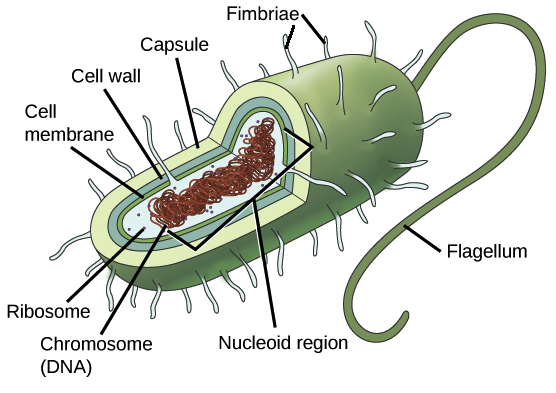
Prokaryotic Cells Article Khan Academy
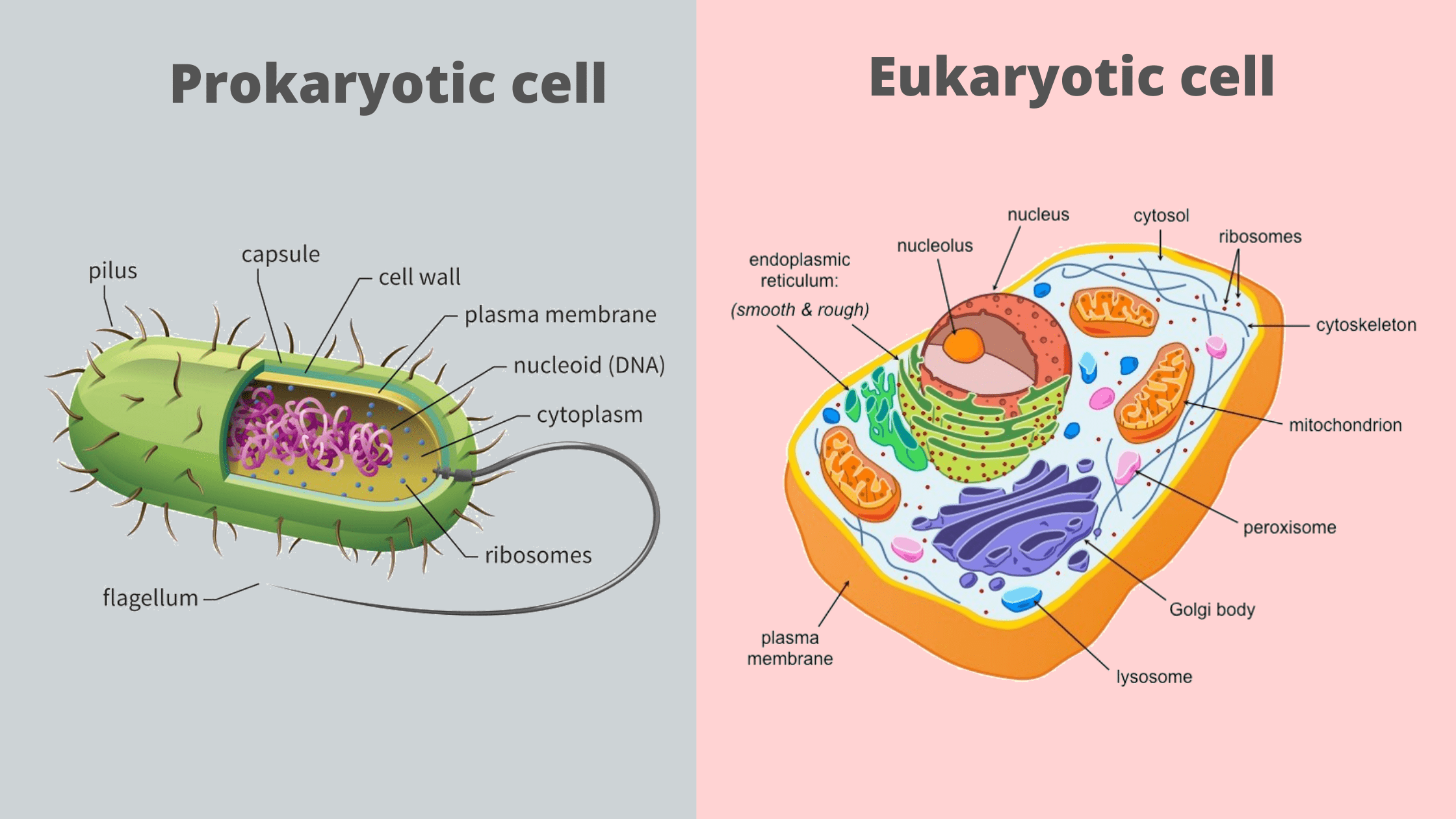
Prokaryotic Cell And Eukaryotic Cell
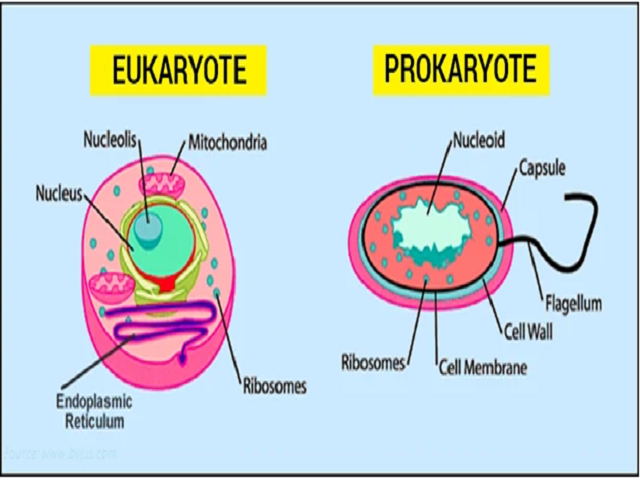
What Is The Difference Between Prokaryotic And Eukaryotic Cells
Prokaryotic Cells Characteristics Structure Division Examples
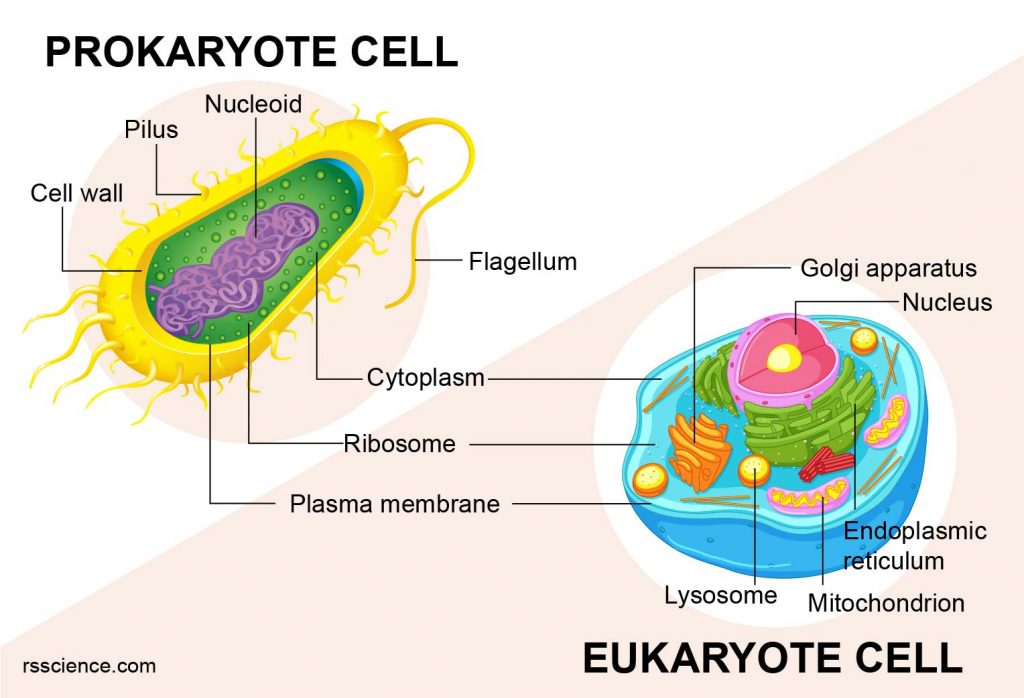
Eukaryotes And Prokaryotes What Are The Similarities Differences And Examples Rs Science

Prokaryotic Cell Definition Examples Structure Biology Dictionary
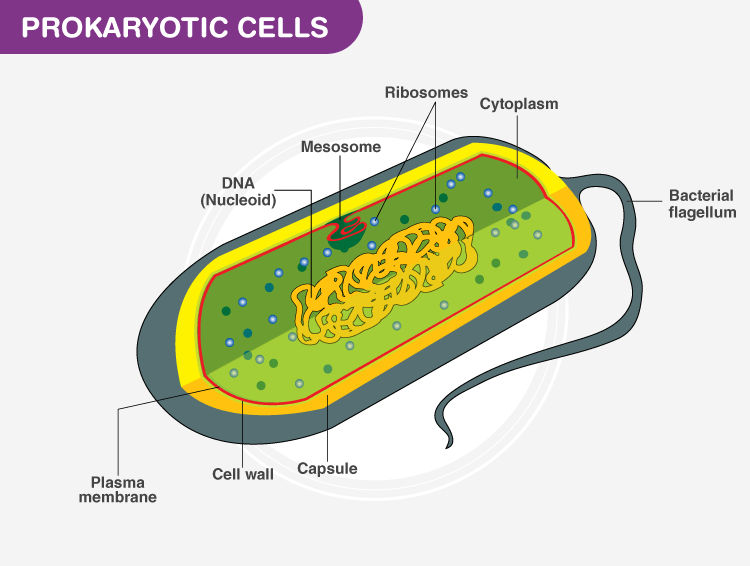
Prokaryotic Cells Definition Structure Characteristics And Examples
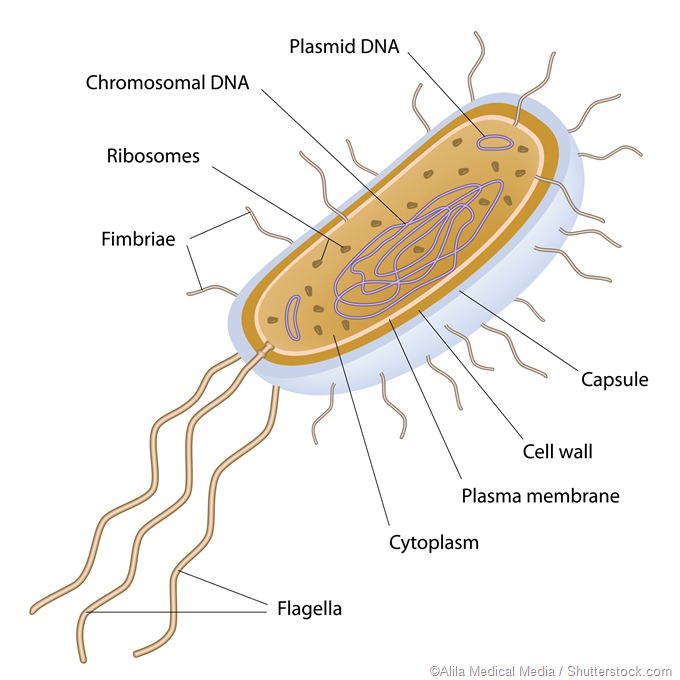
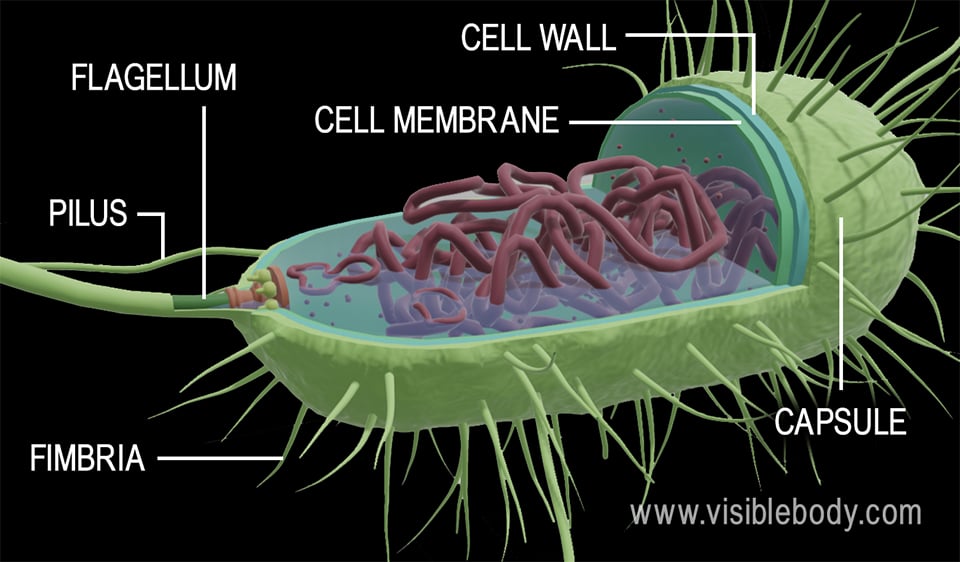
Post a Comment for "Definition Of Prokaryotic Organism"