Definition Of Rna Biology
RNA stands for ribonucleic acid which is a long single-stranded chain of cells that processes protein. Leave a Comment Microbiology By Supriya N.

Protein Production A Simple Summary Of Transcription And Translation Transcription And Translation Protein Synthesis Transcription
To read these blueprints the double-helical DNA is unzipped to expose the individual strands and an enzyme translates them into a mobile intermediate message called ribonucleic acid RNA.

Definition of rna biology. Any of a class of single-stranded molecules transcribed from DNA in the cell nucleus or in the mitochondrion or chloroplast containing along the strand a linear sequence of nucleotide bases that is complementary to the DNA strand from which it is transcribed. Generally it helps to exchange the hereditary information encoded by DNA into proteins. Tightly packed into every cell nucleus which measures just 10 microns in diameter is a three-meter long double-stranded DNA instruction manual on how to build and maintain a human body.
The nucleic acid of living cell having ribose sugar in its nucleotides and perform multiple vital roles in the coding decoding regulation and expression of genes is called Ribonucleic acid or RNA. Transfer RNA is an RNA type that acts as the intermediary element and plays a significant role in the loading and transferring amino acids to the site of protein synthesis ie. MRNA is involved in the transcription of DNA while tRNA has an important role in the translation component of protein synthesis.
A nitrogenous base a five-carbon sugar and a phosphate group. Ribosomal ribonucleic acid rRNA is the RNA component of ribosomes the molecular machines that catalyze protein synthesis. Ribonucleic acid is a biopolymer used to code decode regulate and express genes.
Ribosomal RNA constitute over sixty percent of the ribosome by weight and are crucial for all its functions from binding to mRNA and recruiting tRNA to catalyzing the formation of a peptide bond between two amino acids. Messenger ribonucleic acids mRNAs transfer the information from DNA to the cell machinery that makes proteins. A nucleic acid that is an essential component of all cells composed of a long.
Ribonucleic acid or RNA is an essential biological macromolecule. And that is the nucleic acid information molecule that transfers information from the genome into proteins by translation. RNA is the acronym for ribonucleic acid.
All the RNA in cells are themselves copies of DNA sequences contained in the genes of a cells chromosomes. During protein synthesis an organelle called a ribosome moves along the mRNA reads its base sequence and uses the genetic code to translate. A type of RNA distinguished by its length and abundance functioning in protein synthesis as a component of ribosomes.
Messenger ribonucleuc acid or mRNA for short plays a vital role in human biology specifically in a process known as protein synthesis. In order for each cell to maintain its structure and perform all of its functions it must. MRNA is a single-stranded molecule that carries genetic code from DNA in a cells nucleus to ribosomes the cells protein-making machinery.
The three-dimensional structure of RNA is critical to its stability and function allowing the ribose sugar and the. Messenger RNA mRNA is a single-stranded RNA molecule that is complementary to one of the DNA strands of a gene. RNA codes for amino acid.
RNA typically is a single-stranded biopolymer. Forms of RNA include messenger RNA mRNA transfer RNA tRNA and ribosomal RNA rRNA. Like DNA it can bind with great specificity to either DNA or another RNA through complementary base pairing.
The composition of the RNA molecule is identical with that of DNA except for the. Any of various nucleic acids that contain ribose and uracil as structural components and are associated with the control of cellular chemical activities compare messenger rna ribosomal rna transfer rna. The t-RNA first decodes the information or the nucleotide sequences carried by the m-RNA.
RNA or ribonucleic acid is a nucleic acid that is similar in structure to DNA but different in subtle ways. This intermediate message is called messenger RNA mRNA and it. RNA is a unique polymer.
It can also bind specific proteins or small molecules and remarkably RNA can catalyze chemical reactions including joining amino acids to make proteins. Messenger RNA mRNA transfer RNA tRNA and ribosomal RNA rRNA are the three major types of RNA. The cell uses RNA for a number of different tasks one of which is called messenger RNA or mRNA.
The mRNA is an RNA version of the gene that leaves the cell nucleus and moves to the cytoplasm where proteins are made. RNA is a single-stranded nucleic acid that is composed of three main elements. Rna definition ribonucleic acid.
However the presence of self-complementary sequences in the RNA strand leads to intrachain base-pairing and folding of the ribonucleotide chain into complex structural forms consisting of bulges and helices.

Pin On The Ingredients Of Life
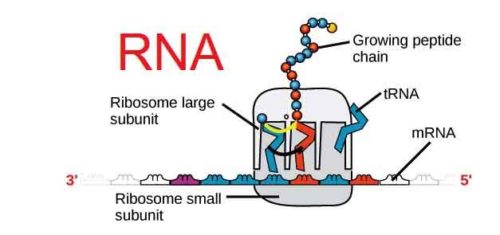
Rna Definition Types Structure And Functions Biology Edu Care

Illustration About The Central Dogma Of Molecular Biology Dna Replication Transcription And Trans Transcription And Translation Central Dogma Dna Replication

Eukaryotic Rna Differences And Processing Prokaryotes Dna Transcription Molecular Biology

Rna Splicing Definition Process Mechanism Types Errors Uses Rna Splicing Notes Process Biology Notes
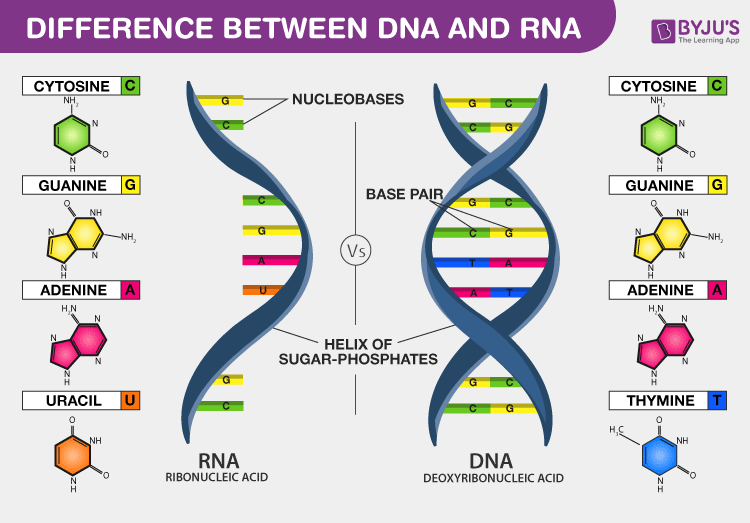
Dna Vs Rna Introduction And Differences Between Dna And Rna

Intron Definition Function And Structure Biology Dictionary Prokaryotes Dna Sequence Rna Polymerase
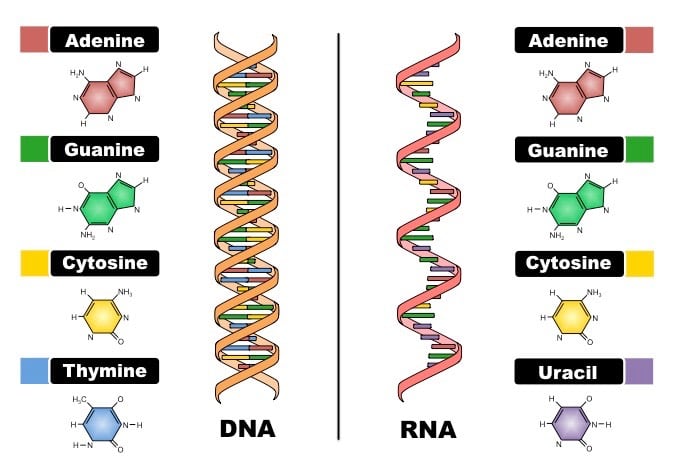
Types Of Rna And How To Extract Or Purchase It Biochain Institute Inc
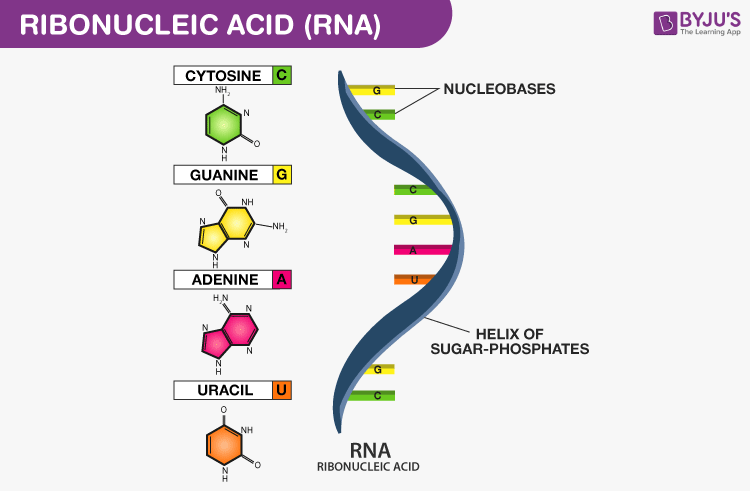
Rna Structure Functions And Types Of Rna
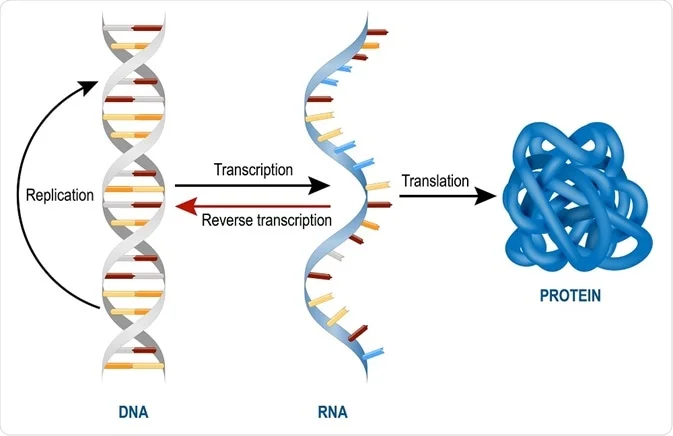
Types Of Rna Mrna Rrna And Trna
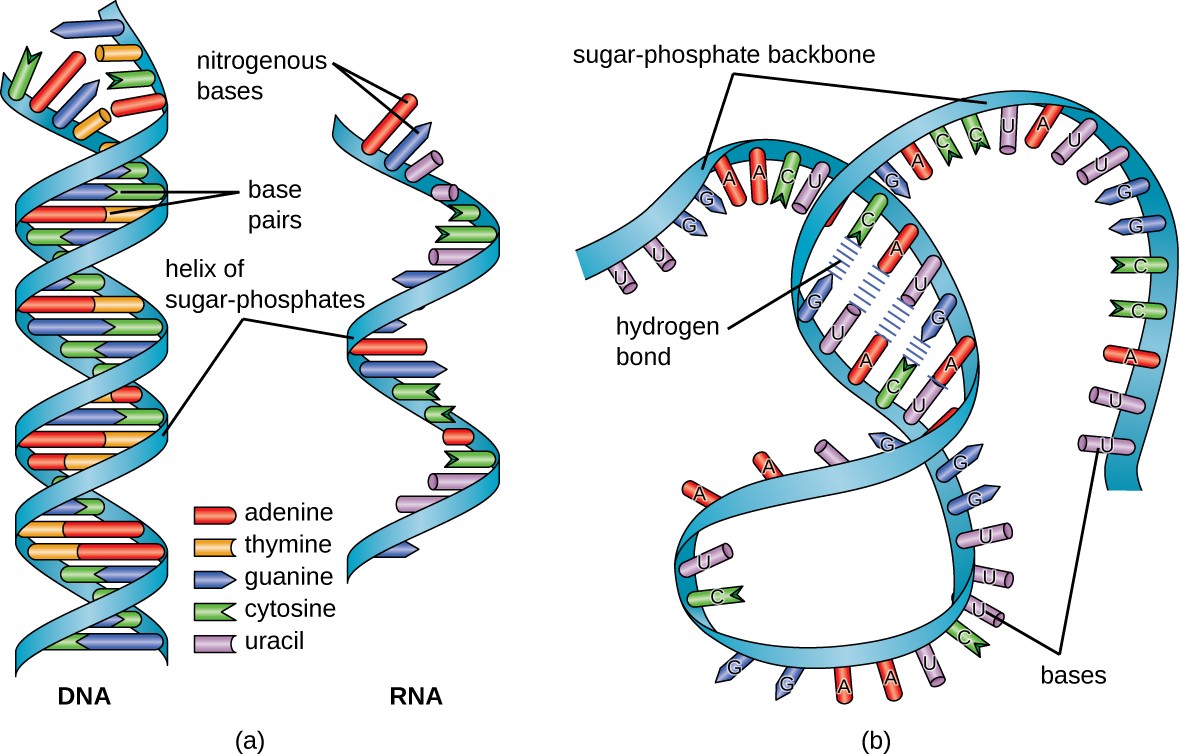
Structure And Function Of Rna Microbiology

15 Differences Between Transcription And Translation Transcription And Translation Transcription Gene Expression

Point Mutation Definition Types Examples Biology Dictionary Point Mutation Mutation Transcription And Translation

Dna And Rna Reading And Card Sort In 2020 Study Biology Biology Classroom Biology Lessons




Post a Comment for "Definition Of Rna Biology"