Definition Of Linear Kinetic Energy
If an object has a velocity or speed v v then its kinetic energy is. Kinetic energy is the measure of the work an object can do by the virtue of its motion.

Forms Of Energy Motion Heat Light Sound Potential Energy Kinetic Energy Energy
But interestingly enough its the object weighing less that will do more damage for a given momentum.

Definition of linear kinetic energy. The linear impulse momentum relations for a particle and conservation of linear momentum. The kinetic energy of a rotating body can be compared to the linear kinetic energy and described in terms of the angular velocity. What is the potential energy.
The kinetic energy of an object is the energy it possesses because of its motion. The extended objects complete kinetic energy is described as the sum of the translational kinetic energy of the centre of mass and rotational kinetic energy of the centre of mass. Kinetic energy is a form of energy that an object or a particle has by reason of its motion.
By definition LET is a positive quantity. Here I is the rotational mass or moment of inertia of a rotating object and ω is the angular speed. The kinetic energy K is 12mv2 and the momentum P is mv so the ratio of kinetic energy to momentum KP v2 and v 2KP 2 2510 5 ms.
A river flowing at a certain speed. Note that the equation is still valid when the object is not travelling in a straight line. Kinetic Energy Kinetic energy is energyof motion.
Definition Of Linear Kinetic Energy. Definition of Kinetic energy. Em0 c 2 which we refer to as the rest energy.
Energy associated with motion Examples of Kinetic energy in a Sentence Recent Examples on the Web The Kinetic energy transferred by the asteroid to the rock soil and air jiggles the molecules to temperatures that exceed the surface of the sun. If work which transfers energy is done on an object by applying a net force the object speeds up and thereby gains kinetic energy. The relativistic expression for kinetic energy leads directly to the famous massenergy relation E mc2.
The rotational kinetic energy is represented in the following manner for a. It is identical to the retarding force acting on a charged ionizing particle travelling through the matter. Kinetic energy is a property of a moving object or particle and depends not only on its motion but also on its mass.
If something is moving it has kinetic energy. It is the term. Kinetic energy is the energy of motion Kinetic energy is the easiest form of energy to think about.
The linear momentum of a particle or system of particles The angular momentum of a particle or system of particles. The mass m Pv 105 2 kg. It describes the action of radiation into matter.
The extended object s complete kinetic energy is described as the sum of the translational kinetic energy of the centre of mass and rotational kinetic energy of the centre of mass. Kinetic Energy Definition. K 2 1 m v 2.
Emγc22Kmc This equation has the form of kinetic energy plus potential energy equals total energy. K equals one half m v squared. If its moving faster it has more kinetic energy.
If kinetic energy is the energy of motion then naturally the kinetic energy of an object at rest should be zero. This is called linear kinetic energy. The kinetic energy of a particle or system of particles.
In dosimetry linear energy transfer LET is the amount of energy that an ionizing particle transfers to the material traversed per unit distance. Kinetic energy is the energy an object has due to its motion 17. The SI unit for energy is the joule newton x meter in accordance with the basic definition of energy as the capacity for doing work.
Kinetic Energy Equation KEfrac12mv2 Kinetic Energy Units. The SI unit of kinetic energy is J. And it is the square of the velocity in the kinetic.
It is given by KER 1 2Iω2. The kinetic energy of a rotating object is analogous to linear kinetic energy. The kinetic energy of an object is directly proportional to how much damage it will inflict when it strikes something.
The SI unit of kinetic energy is Joules which is equal to kg-m 2 s-2. This chapter generalizes linear momentum and kinetic energy two key dynamic concepts so that the conservation laws of linear momentum and energy hold for particle speeds up to the speed of light. Now lets rewrite the equation involving the kinetic energy.
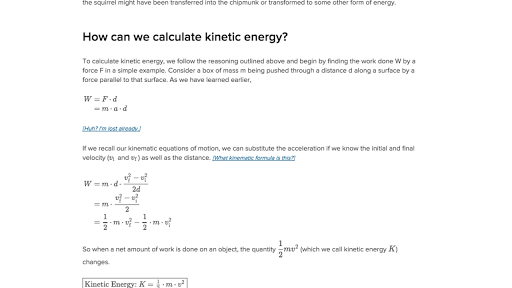
A standard relationship that can also be used is that K P22m so m P22K which is. Therefore we dont need the second term and an objects kinetic energy is just K ½mv2 Derivation using calculus but now we dont need to assume anything about the acceleration.
Kinetic Energy Linear And Rotational Isaac Physics

Derivation Of Kinetic Energy Detailed Kinetic Energy Derivation

Kinetic Energy Equation Proof And Explanation Youtube

Kinetic Energy And The Work Energy Theorem College Physics Openstax In 2020 College Physics Physics Physics Concepts
Kinetic Energy Linear And Rotational Isaac Physics
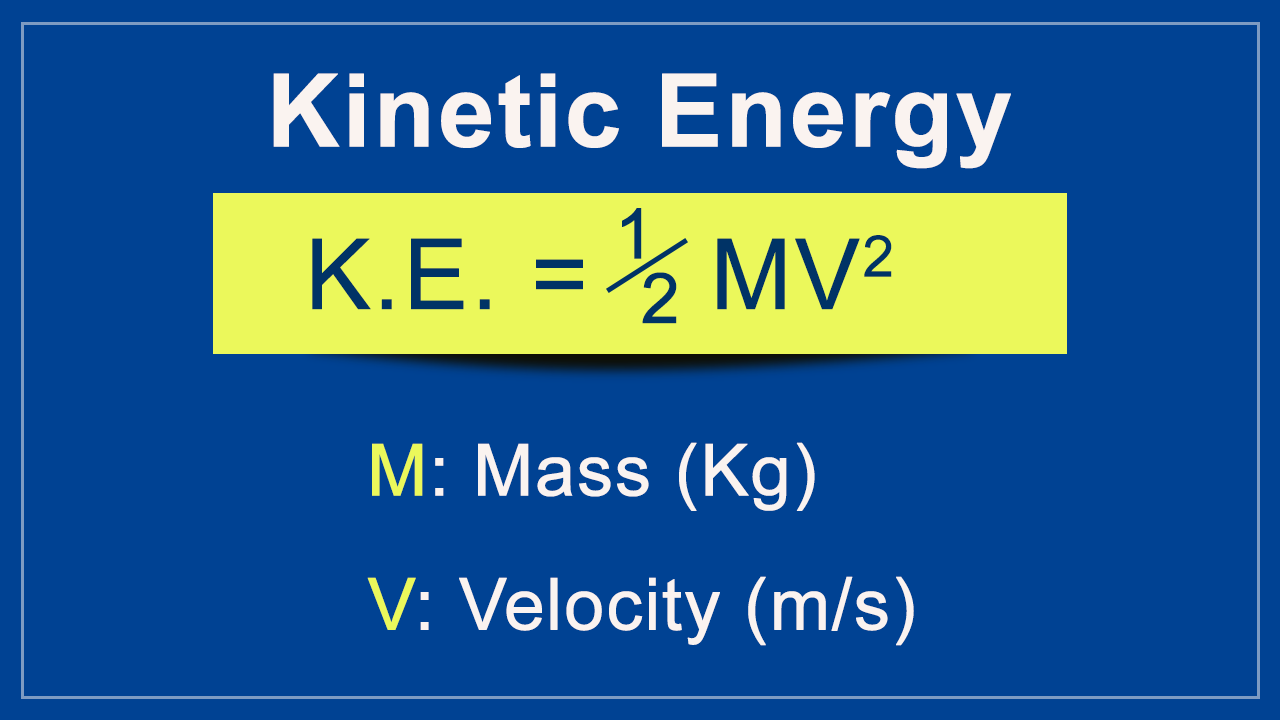
Kinetic Energy Formula Science Struck
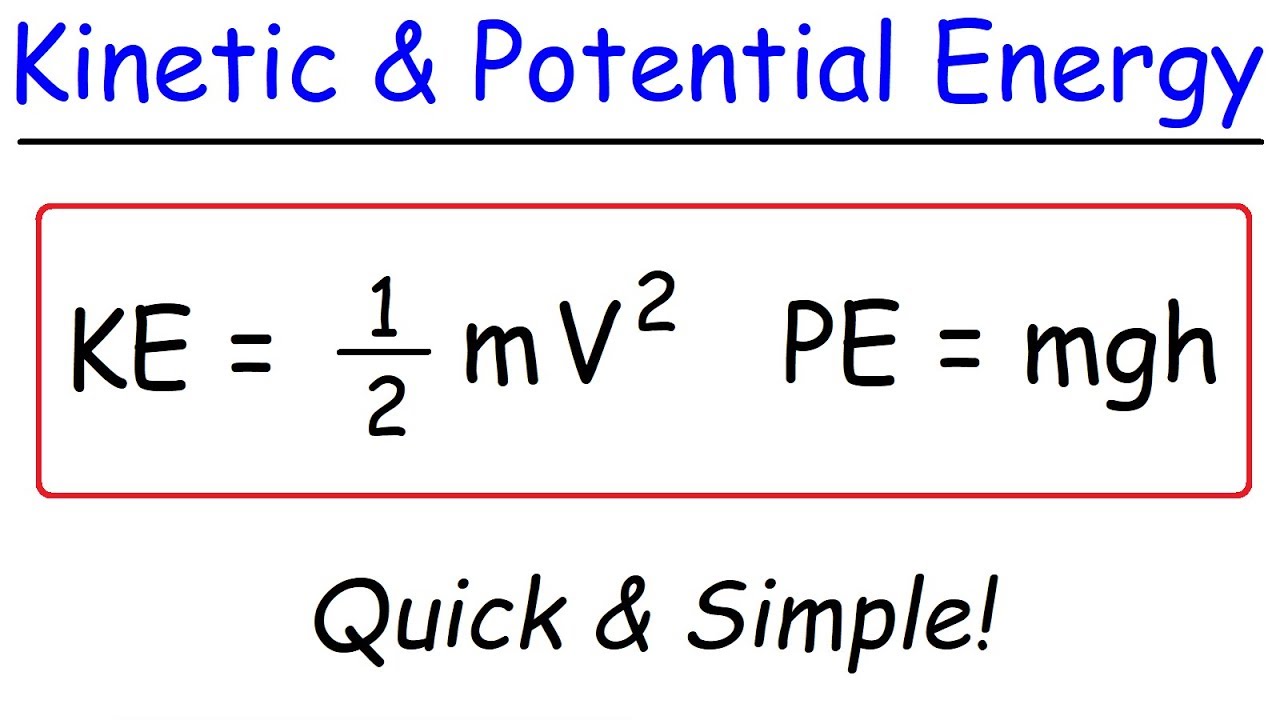
Kinetic Energy And Potential Energy Youtube
Kinetic Energy Linear And Rotational Isaac Physics

5 Examples Of Kinetic Energy In Everyday Life

Angular And Linear Velocity Explained With 4 Terrific Examples Physics Angular Velocity

Tetryonics 18 01 Photo Electron Kinetic Energies Science Illustration Quantum Mechanics Linear Momentum
Rotational Kinetic Energy Review Article Khan Academy
What Is Kinetic Energy Article Khan Academy

Kinetic Energy Formula Science Struck

Definition Of Circular Motion Cbse Digital Education Circular Motion Linear Momentum Circular

Rotational Kinetic Energy An Object Rotating About Some Axis With An Angular Speed Has Rotational Kinetic Energy Even Though It May Not Have Ppt Download
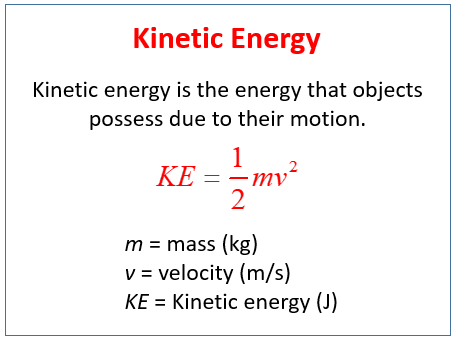
Kinetic Energy Examples Video Lessons Examples Step By Step Solutions
Kinetic Energy Review Article Khan Academy





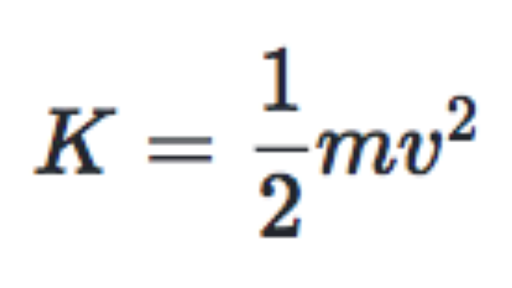
Post a Comment for "Definition Of Linear Kinetic Energy"