Definition Of Nuclear Magnetic Resonance
1 Nuclear magnetic resonance is defined as a condition when the frequency of the rotating magnetic field becomes equal to the frequency of the processing nucleus. It does so by recording the magnetic spectral patterns given off by the nuclei within a samples atoms.
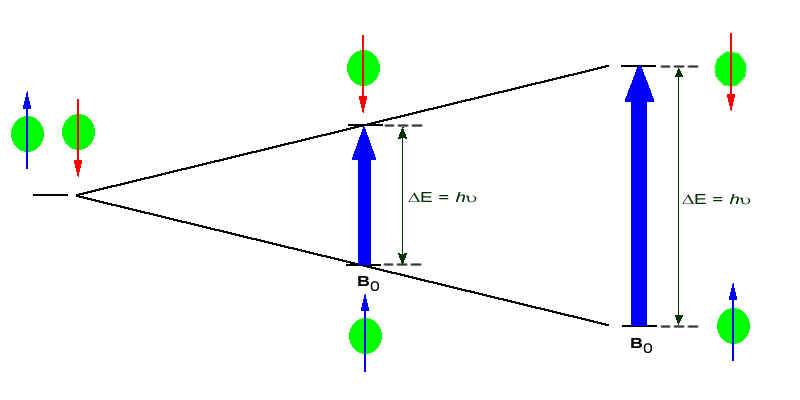
13 0 Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy Chemistry Libretexts
Nuclear magnetic resonance In the absence of atomic motion in rigid lattices crystals NMR makes it possible to determine molecular structures not observable by other means.
Definition of nuclear magnetic resonance. Definition Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy or NMR is a process used to find out information about a compounds magnetic properties. The selective absorption of electromagnetic radiation by an atomic nucleus in the presence of a strong static magnetic field. See also electron spin resonance.
Used in research and in medicine to monitor tissue metabolism and to distinguish between normal and abnormal cells. This phenomenon was first observed in 1946 by the physicists Felix Bloch and Edward M. Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy is a powerful analytical technique used to characterize organic molecules by identifying carbon-hydrogen frameworks within molecules.
In many solids even at low temperatures there occur atomic diffusion and rotation of groups of atoms. On the other hand however there exist some restrictions. Nuclear magnetic resonance a phenomenon exhibited by many atomic nuclei.
Nuclear magnetic resonance NMR spectroscopy is the study of molecules by recording the interaction of radiofrequency Rf electromagnetic radiations with. By applying an external magnetic field to a solution in a constant radio frequency field it is possible to determine the structure of an unknown compound. Nuclear magnetic resonance is a physical phenomenon in which nuclei in a magnetic field absorb and re-emit electromagnetic radiation.
Of all the spectroscopic methods it is the only one for which a complete analysis and interpretation of the entire spectrum is normally expected. Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy most commonly known as NMR spectroscopy or magnetic resonance spectroscopy MRS is a spectroscopic technique to. When placed in a constant magnetic field the nuclei absorb electromagnetic radiation at a few characteristic frequencies.
Using NMR researchers can determine the molecular structure of a compound. Nuclear magnetic resonance NMR selective absorption of very high-frequency radio waves by certain atomic nuclei that are subjected to an appropriately strong stationary magnetic field. It also can be applied successfully to investigate amorphous alloys1 For thin tapes no complications occur due to skin effects.
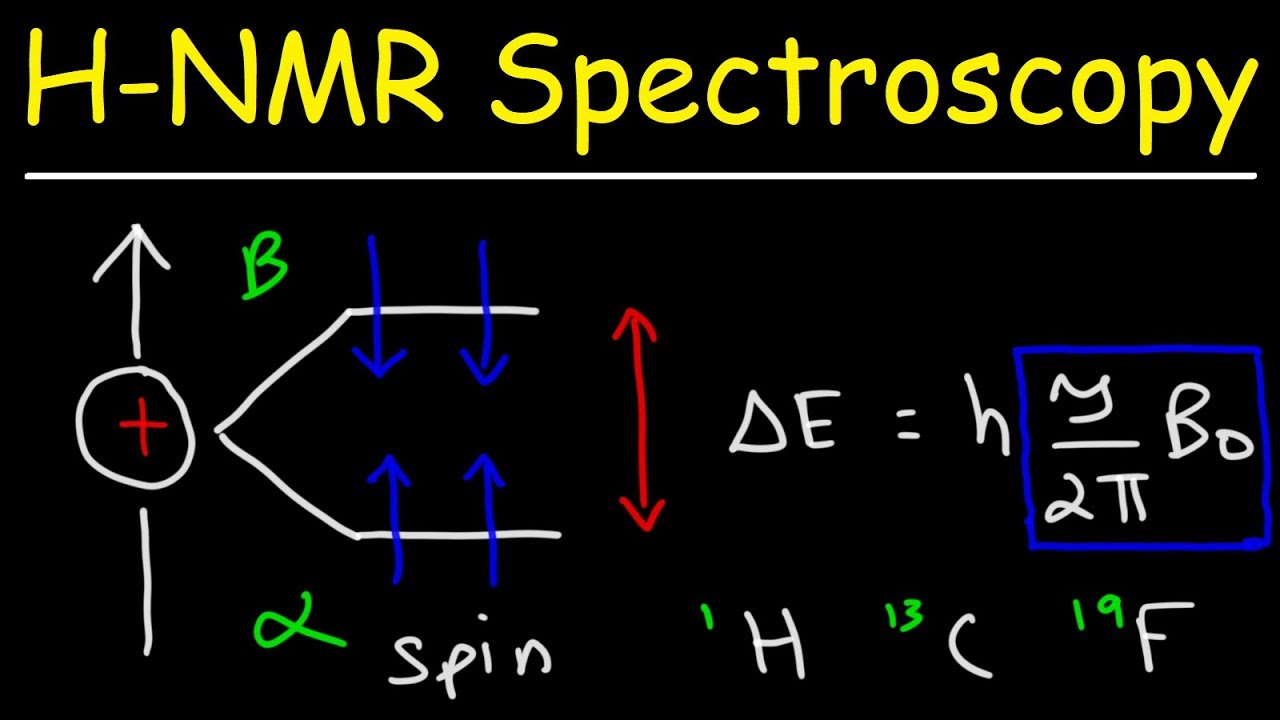
2 If ratio frequency energy and a magnetic field are simultaneously applied to the nucleus a condition as given by the equation v үH 0 2π is met. A technique for determining the magnetic moments of nuclei by subjecting a substance to high-frequency radiation and a large magnetic field. The technique is used as a method of determining structure.
Because certain atoms absorb specific frequencies nuclear magnetic resonance is used to analyze substances in spectroscopy and to examine soft body tissues in magnetic resonance imaging MRI. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance NMR yields information about the structure and electronic properties of metals and alloys. The absorption of energy exhibited by particles as atomic nuclei or electrons in a static magnetic field when the particles are exposed to electromagnetic radiation of certain frequencies abbreviation MR see nuclear magnetic resonance More from.
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance When the nuclear magnetic moment associated with a nuclear spin is placed in an external magnetic field the different spin states. Nuclear magnetic resonance in British English. These movements affect the shape of the NMR absorption peak.
Over the past fifty years nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy commonly referred to as nmr has become the preeminent technique for determining the structure of organic compounds. Nuclear magnetic resonance definition is - the magnetic resonance of an atomic nucleus. Chemical analysis that uses such resonance especially to study molecular structure.
The absorption of energy as specific frequencies of radio waves by the nuclei of atoms that are placed within a strong magnetic field.
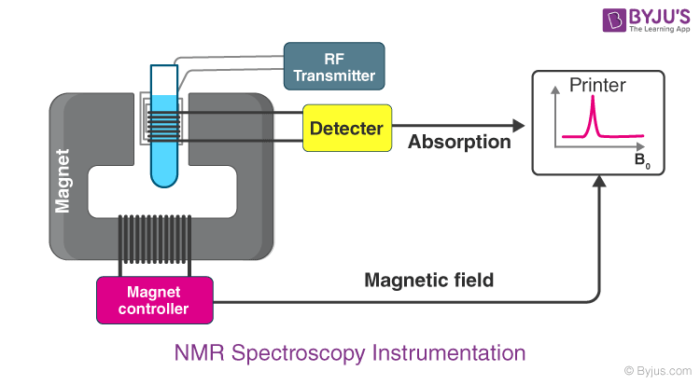
Nmr Spectroscopy Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Principle Working Chemical Shift Instrumentation Applications
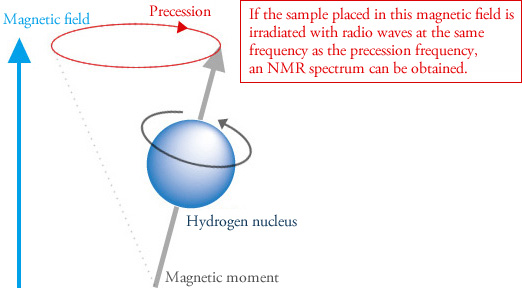
Nmr Basic Knowledge Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectrometer Nmr Products Jeol

Chemical Compound Proton Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy Britannica
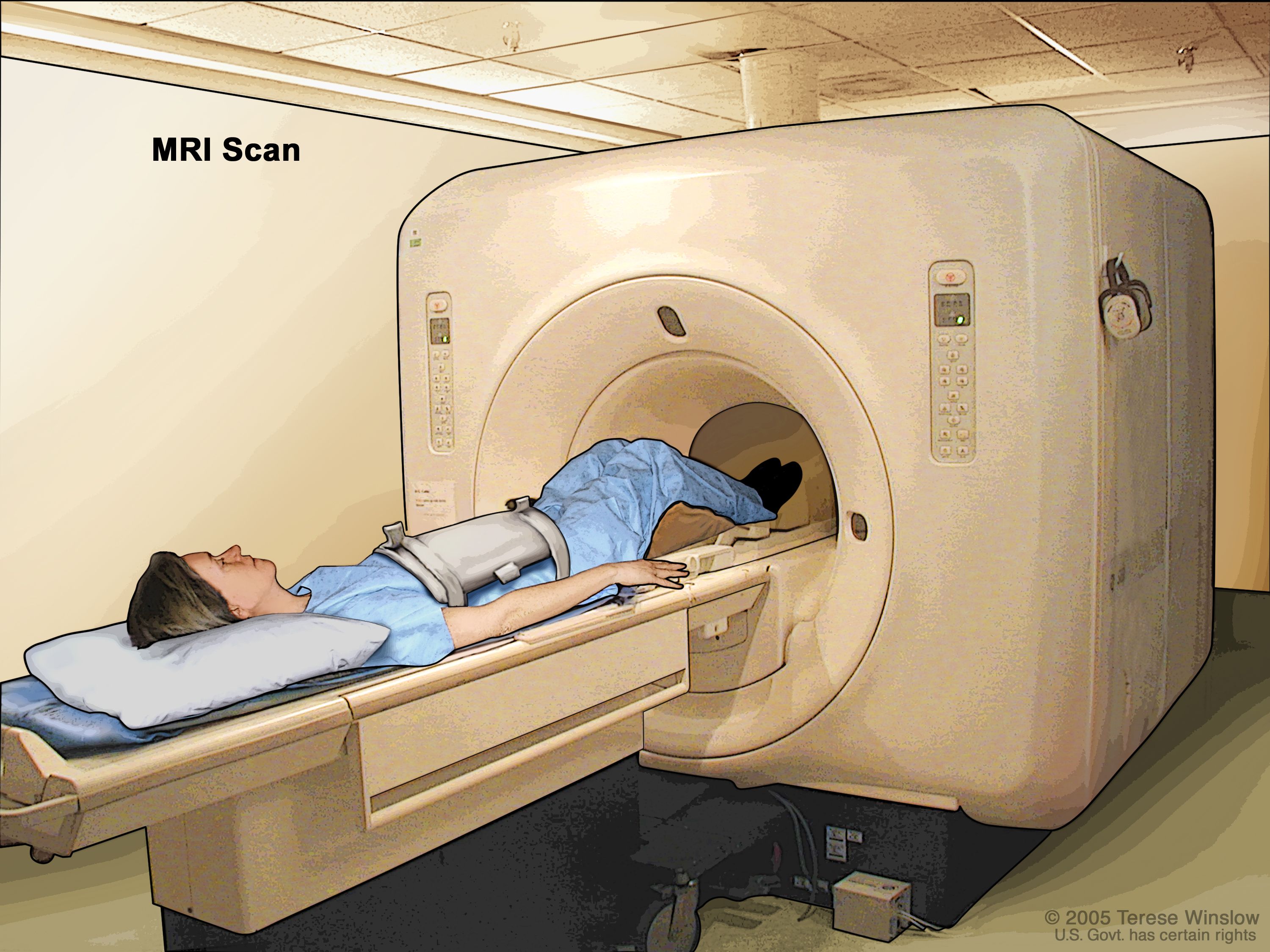
Definition Of Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Imaging Nci Dictionary Of Cancer Terms National Cancer Institute
Basic Introduction To Nmr Spectroscopy Youtube
Organic Spectroscopy International Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy Nmr Spectroscopy

Nmr Basic Knowledge Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectrometer Nmr Products Jeol
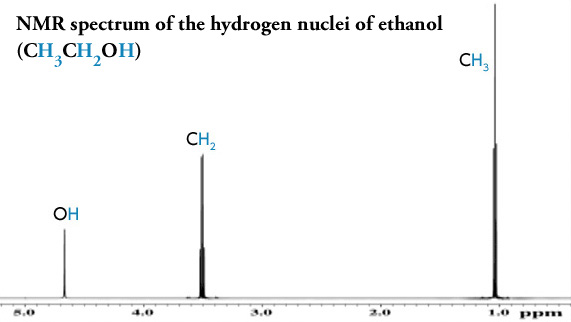
Nmr Basic Knowledge Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectrometer Nmr Products Jeol

Ppt Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Nmr Spectroscopy Powerpoint Presentation Id 673634
Introduction To Proton Nmr Chemistry Libretexts

Nmr Spectroscopy Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Biology Dictionary
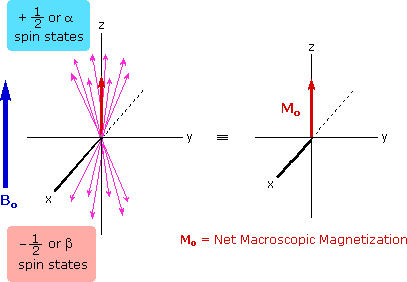

Post a Comment for "Definition Of Nuclear Magnetic Resonance"