Definition Of Spectral Noise Density
The noise spectral density of an ADC can be defined easily as the full-scale signal power of an ADC less the noise power spread across 1-Hz bandwidth unit increments. Therefore the power of white noise is infinite.

Spectral Density An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
1 where k is the level of the white current or voltage noise.

Definition of spectral noise density. Noise power densities defined as the power spectral density of the fluctuations of a quantity such as an optical power or phase where the frequency argument refers to a noise frequency rather than to an optical frequency In the following both types of quantities are discussed. Therefore white noise cannot exist. N 24kTR Rules of thumb for 300 K.
This explains the term white noise in analogy to white light. In statistical signal processing and physics the spectral density power spectral density PSD or energy spectral density ESD is a positive real function of a frequency variable associated with a stationary stochastic process or a deterministic function of time which has dimensions of power per hertz Hz or energy per hertz. Example 422 Moving Average.
The general equation which describes the voltage or current noise spectral density in the 1f region is eninkFC Eq. Noise Spectral Density or Noise Density N o is a measurement of the noise power per Hertz. Generally human sensitivity peaks just below 10 Hz for 230 V filament lamps.
Clarification needed The symbol ℒ is called a capital or uppercase script L. The units of power spectral density are power per hertz. Analog Devices Matt Duff describes how to conver.
The spectral density of a white noise sequence is therefore constant for all ω 1 2 1 2 which means that every frequency ω contributes equally to the overall spectrum. Power spectral density A standard definition often used in electronics is the peak-peak amplitude in a 10 Hz to 100 kHz bandwidth. 1 kΩ 407 nVHz 4 nVHz 50 Ω 091 nVHz 1 nVHz k Boltzmann constant 13810-23JK.
G X fA Signal power is the integral of PSD over all frequency space. The IEEE defines phase noise as ℒf S φ f2 where the phase instability S φ f is the one-sided spectral density of a signals phase deviation. The noise spectral density of an ADC can be defined easily as the full-scale signal power of an ADC less the noise power spread across 1 Hz bandwidth unit increments.
In particular noise power spectral density ie the power from random and deterministic EMI sources can help you identify which EMI and noise sources in your design contribute to noise measured at specific points in space. A changing FFT sampling depth. When the two signals are equal the cross spectral density reduces to the Fourier transform of an autocorrelation function according to the WienerKhinchin.
This is effectively what is done when testing for EMC certification. Electrically a physical resistor at temperature T A is equivalent to. Therefore a plot of power spectral density obtained from amplitude voltage measurements requires that the voltage measurements be squared.
For discretely sampled signals in the time domain the DFT algorithm would be used to determine the cross spectral density. Cross spectral density definition. Such a definition provides a single value that can be compared across products but since it is an integrated value it does not provide any information on how the noise is distributed across the frequencies.
In a previous article we discussed that the noise power spectral density PSD specifies the average power of noise at different frequencies within the bandwidth of interest. White Noise White noise is a CT stochastic process whose PSD is constant. 40 nVrtHz sqrt10k 157 5 uVrms.
For white noise which is constant with respect to frequency we can simply divide the total noise power by the bandwidth of the system. It only spreads the noise across different unit bandwidths of frequency. 2EXAdf No real physical process may have infinite signal power.
The equation in the video should be. People experience a subjective response to lamp flicker. A changing FFT sampling depth does not alter an ADCs spectral noise density.
Although S φ f is a one-sided function it represents the double-sideband spectral density of phase fluctuation. Spectrum is flat up to THz frequencies at room temperature. In this article well see that PSD is the main tool that allows us to examine the effect of a noise source on the output of a linear time-invariant LTI system.
Mathematically cross spectral density is defined using a Fourier transform of a convolution between the two signals. The spectral density of voltage fluctuations produced by an arc furnace is approximately in inverse proportion to the square root of the frequency. The spectral density is the distribution of total variance over frequency.

Spectral Density An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Using Power Spectral Density Psd To Characterize Noise Technical Articles

Use Noise Spectral Density To Evaluate Adcs In Software Defined Systems Analog Devices

Signal Integrity Analysis Of Usb 3 0 Data Bus Usb External Hard Drive Analysis

Use Noise Spectral Density To Evaluate Adcs In Software Defined Systems Analog Devices
Tutorial On Power Spectral Density Calculations

Spectral Density An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Using Power Spectral Density Psd To Characterize Noise Technical Articles
Understanding Signal To Noise Ratio And Noise Spectral Density In High Speed Data Converters Ti Com Video

Spectral Density An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Using Power Spectral Density Psd To Characterize Noise Technical Articles

Visualizing The Periodic Table Visualoop Physics Concepts Periodic Table Map Puzzle

7 2 Power Spectral Density White Noise Youtube

Noise Spectral Density A New Adc Metric Analog Devices

Using Power Spectral Density Psd To Characterize Noise Technical Articles

Spectral Density An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
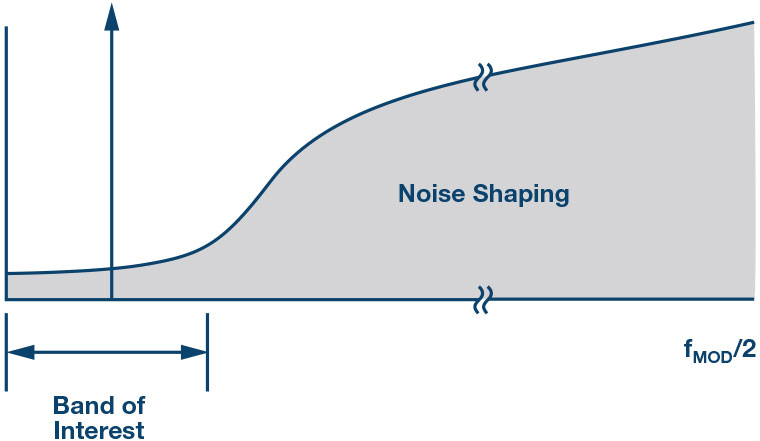
Noise Spectral Density A New Adc Metric Analog Devices

Noise Spectral Density A New Adc Metric Analog Devices

Spectral Density An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Post a Comment for "Definition Of Spectral Noise Density"