Definition Of Utility Theory
Utility is a term in economics that refers to the total satisfaction received from consuming a good or service. Economists use an abstract measure for the amount of.
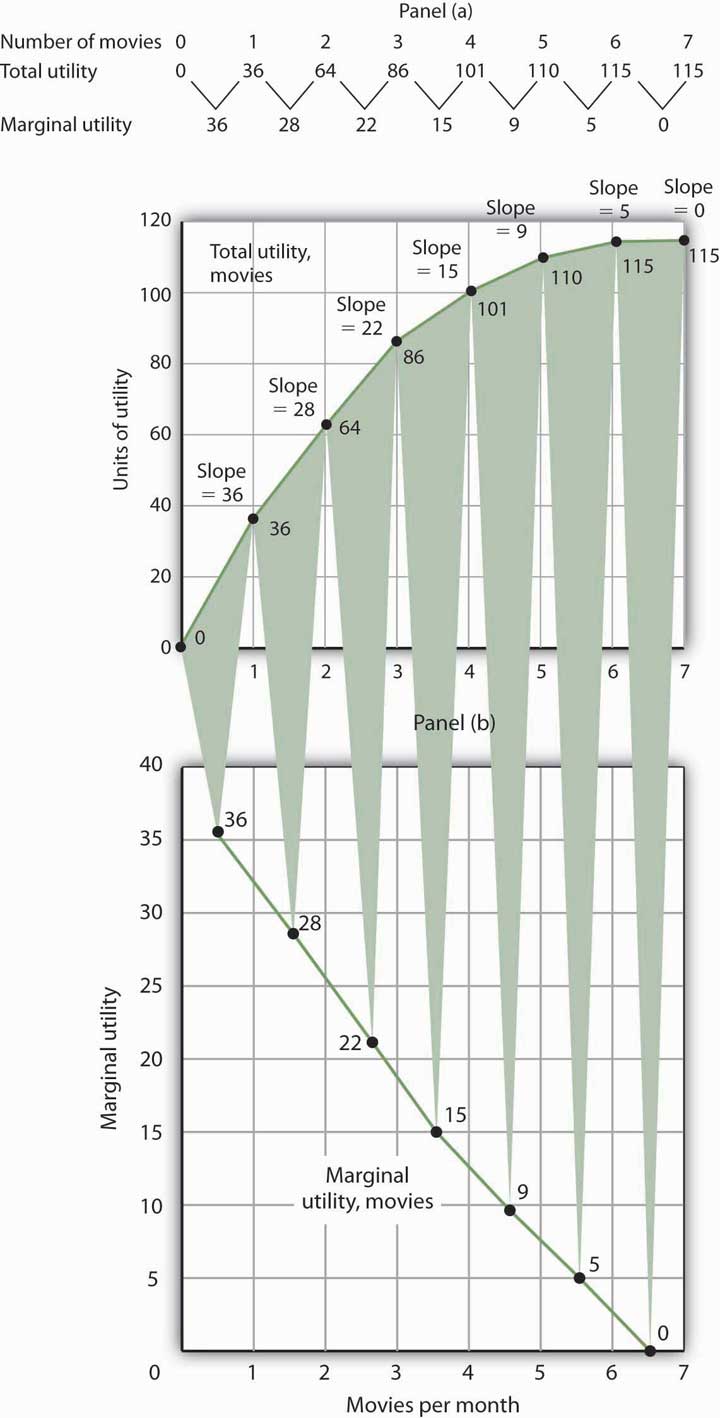
7 1 The Concept Of Utility Principles Of Economics
Though not fully articulated until the 19 th century proto-utilitarian positions can be discerned throughout the history of ethical theory.

Definition of utility theory. Economic theories based on rational choice usually assume that consumers will strive. This means that the higher the utility level the higher the item will be prioritized in the consumers budget. The theorys main concern is the representation of individual attitudes toward risk.
A utility function is a real valued function ux such that. Marginal utility is the increase in total utility obtained by consuming one more unit of a good service or activity. Total utility is a conceptual measure of the number of units of utility a consumer gains from consuming a good service or activity.
Utility theory is a positive theory Theory that seeks to explain an individuals observed behavior and choices. See also expected utility decision theory 6. Expected utility theory is a special instance of the theory of choice under objective and subjective uncertainty.
The only issue is whether. Utility theory is formally elegant and has been an enormously fruitful source of research programs in individual and group decision making related to commercial markets social and political relations bargaining conflict resolution gaming and scarce resource allocation in practically all areas. It advises choosing the action or event with the maximum expected utility.
In the field of economics utility u is a measure of how much benefit consumers derive from certain goods or services. Psychology Definition of UTILITY THEORY. In classical economics expected utility theory is often used as a descriptive theorythat is a theory of how people do make decisionsor as a predictive theorythat is a theory that while it may not accurately model the psychological mechanisms of.
That seeks to explain the individuals observed behavior and choices. It is the only moral framework that. Utility theory is an economic hypothesis that postulates the fact that consumers make purchase decisions based in the degree of utility or satisfaction they obtain from a given item.
Utility is the amount of satisfaction that you will get from the consumption of a product or service. 1 This is an ordinal utility function. Expected utility refers to the utility of an entity or aggregate economy over a future period of time given unknowable circumstances.
Utilitarianism holds that the most ethical choice is the one that will produce the greatest good for the greatest number. Utilitarianism is one of the most powerful and persuasive approaches to normative ethics in the history of philosophy. A measure of the total benefit or disadvantage attaching to each of a set of alternative courses of action b.
As a consumer consumes more and more of a good or service its marginal utility falls. The distinction between normative and positive aspects of a theory is very important in the discipline of economics. The exact numerical values and difference between them are completely irrelevant.
Utilitarianism is an ethical theory that determines right from wrong by focusing on outcomes. U x is greater or less that. With regard to making decisions any normative theory of utility which tries to depict rational or optimal choice behavior.
From a finance standpoint it refers to how much benefit investors obtain from portfolio performance. Its usage has evolved significantly over time. In expected utility theory under objective uncertainty or risk the probabilities are a primitive concept representing the objective uncertainty.
Within economics the concept of utility is used to model worth or value. It is a form of consequentialism. Expected utility theory is used as a tool for analyzing.
Transaction Utility Theory ABSTRACT - The basic premise of this paper is that a consumers behavior depends not just on the value of goods and services available relative to their respective prices but also on the consumers perception of the quality of the financial terms of the teal. Expected utility is a theory in economics that estimates the utility of an action when the outcome is uncertain. The term was introduced initially as a measure of pleasure or happiness within the theory of utilitarianism by moral philosophers such as Jeremy Bentham and John Stuart Mill.
Choice theory derives a utility function which simplifies how choices can be described.

Utility Maximization Slope Of The Indifference Curve Is Tangent To The Budget Constraint Indifference Curve Indifference Economics
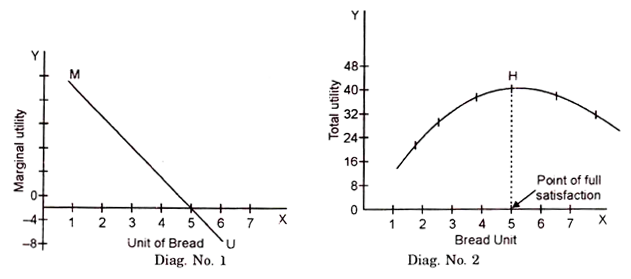
Utility Meaning Characteristics And Types Economics

Cardinal And Ordinal Utility In 2021 Cardinal Indifference Curve Business And Economics
Utility Definition Economics Measure Of Satisfaction
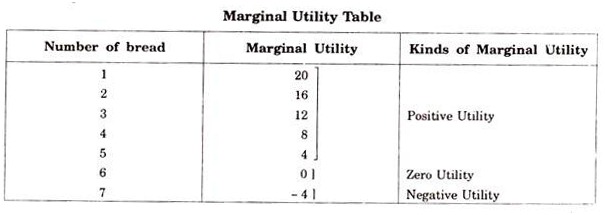
Utility Meaning Characteristics And Types Economics

The Expected Utility Theorem Is The Guiding Principle Behind Modern Risk Management Techniques Understanding Th Theorems Management Techniques Risk Management
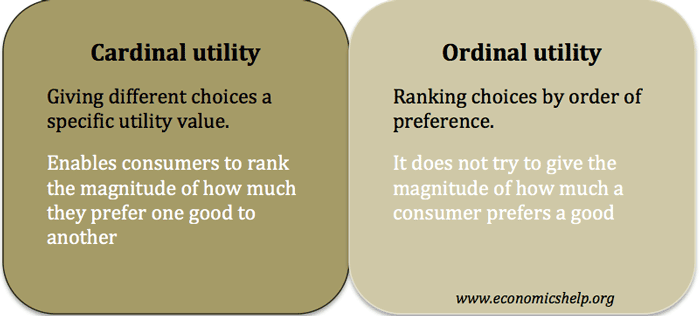
Cardinal And Ordinal Utility Economics Help

What Is Utility Several Definitions And Some Examples

Indifference Curves Different Combinations Of The Two Goods The Same Level Of Utility Is Derived From Consump Indifference Curve Indifference Teaching Tools
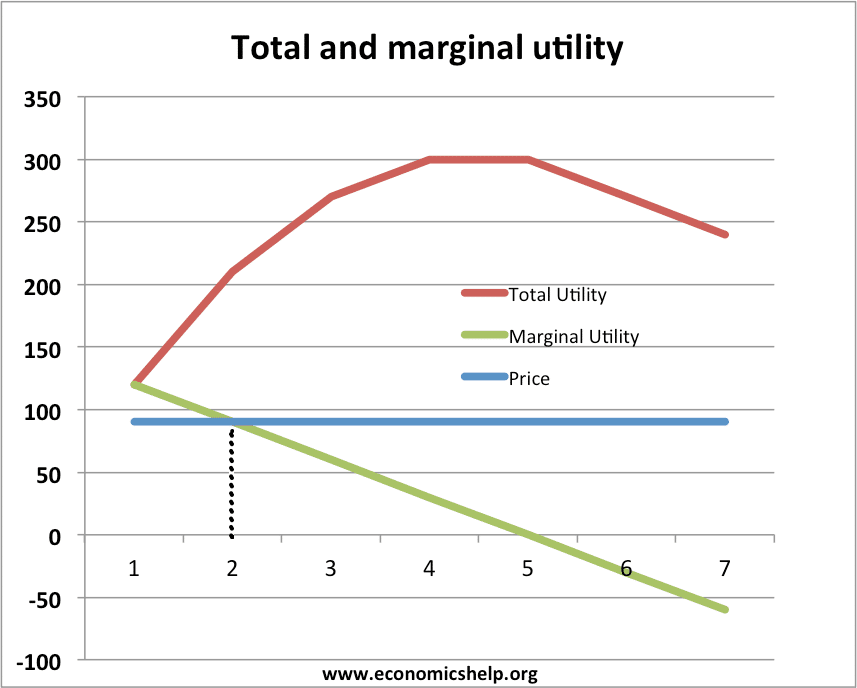
Utility Maximisation Economics Help

What Is Utility Function Definition And Explanation Basic Concepts Choice Theory Indifference Curve

What Is Utility Several Definitions And Some Examples

Marginal Utility Economics Britannica

What Is Marginal Utility Definition Theory Formula Example Video Lesson Transcript Study Com

What Is Utility Function Definition And Explanation Basic Concepts Choice Theory Indifference Curve
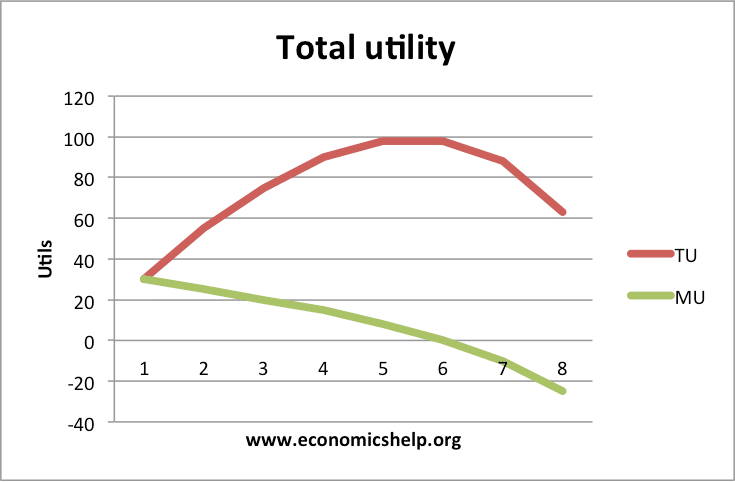



Post a Comment for "Definition Of Utility Theory"