Definition Entity Integrity Constraint
The principal end of the constraint. The definition for a referential integrity constraint specifies the following information.
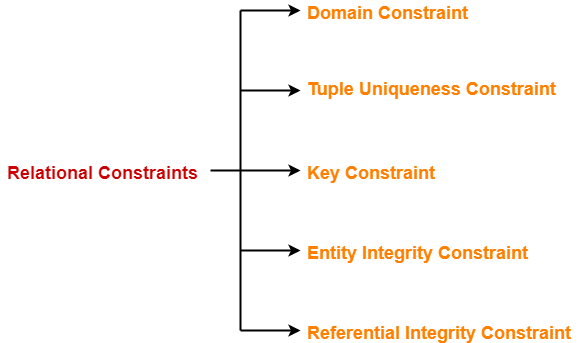
Constraints In Dbms Types Of Constraints In Dbms Gate Vidyalay
The entity constraints are primary key foreign key unique.

Definition entity integrity constraint. Integrity is usually expressed in terms of constraints which are consistency rules that the database is not permitted to violate. Entity integrity is an integrity rule which states that every table must have a primary key and that the column or columns chosen to be the primary key should be unique and not null. Finally your definition of data integrity is similarly wrong.
The only way to enforce entity integrity is with unique indexes or unique constraints that are NOT NULL which happens to be the definition of a primary key. A table can contain a null value other than the primary key field. Entity integrity is the concept that every row in a table be unique.
Although most relational databases do not specifically dictate that a table needs to have a Primary Key it is good practice to design a. Referential integrity concerns the concept of a foreign key. Primary Key Constraint When this constraint is associated with the column of a table it will not allow NULL values into the column and it will maintain unique values as part of the table.
A referential integrity constraint is defined as part of an association between two entity types. The constraints available in SQL are Foreign Key Not Null Unique Check. These constraints are given within one table.
INTEGRITY CONSTRAINTS OVER RELATION Database integrity refers to the validity and consistency of stored data. Entity Integrity constraint uniquely identifies each row in table. Entity means any place thing or person in database.
Entity Integrity constraints says that no primary key can take NULL value since using primary key we identify each tuple uniquely in a relation. Entity integrity An entity is any person place or thing to be recorded in a database. An entity represents a real world object.
Entity integrity specifies that the Primary Keys on every instance of an entity must be kept must be unique and must have values other than NULL. Emp_Id Name Address Pincode Passport_Number Salary. This is because the primary key value is used to identify individual rows in relation and if the primary key has a null value then we cant identify those rows.
Entity Integrity constraint uniquely identifies each row in table. A referential constraint is the rule that the nonnull values of a foreign key are valid only if they also appear as values of a parent key. Defining the parent key is called entity integrity.
For example Let us take example of table Employee having columns. There are primarily two types of integrity constraints that help us in ensuring the uniqueness of each row namely UNIQUE constraint and PRIMARY KEY constraint. Each table represents an entity and each row in a table is the instance of entity.
Entity Integrity Constraint is used to ensure the uniqueness of each record or row in the data table. Entity Integrity Constraint. Primary key assures the entity integrity constraint is applied to a table.
Entity object the definition of the entity constraint is used to detect associations between tables create the specified key constraints in the database and ensure that data in. Integrity Constraints are used to apply business rules for the database tables. Entity constraints.
Constraints may apply to each attribute or they may apply to relationships between tables. The entity integrity constraint states that primary key value cant be null. The referential integrity rule states that any foreign-key value can only be in one of two states.
For example if order is an entity the orders table represents the idea of an order and each row in the table represents a specific order. Constraints can be defined in two ways 1 The constraints can be specified immediately after the column definition. An entity type whose entity key is referenced by the dependent end.
An entity integrity constraint is used to identifyrecognize the row or record of a table uniquely. Each table represents an entity and each row of a table represents an instance of that entity. The table that contains the parent key is called the parent table of the referential constraint and the table that contains the foreign key is a.
Each table represents an entity and each row in a table is the instance of entity. An entity represents a real world object.

Entity Framework A Referential Integrity Constraint Violation On Many To Many Relationship Stack Overflow
Chapter 9 Integrity Rules And Constraints Database Design 2nd Edition

Integrity Constraints In Dbms W3spoint W3schools

Entity Integrity Rule And Constraints Check And Foreign Key In Sql Youtube
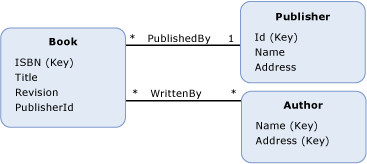
Referential Integrity Constraint Ado Net Microsoft Docs
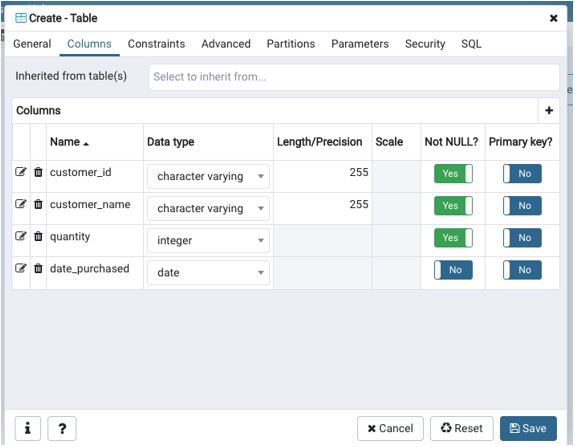
Integrity Constraints In Dbms Types Of Integrity Constraints In Dbms

Define Referential Integrity Concept Relational Constraints And Database Analysis Database Design Analysis Relational Database
Chapter 9 Integrity Rules And Constraints Database Design 2nd Edition
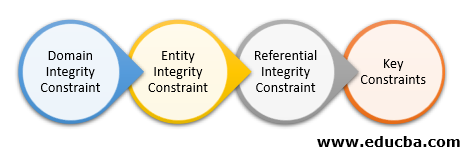
Integrity Constraints In Dbms Types Of Integrity Constraints In Dbms
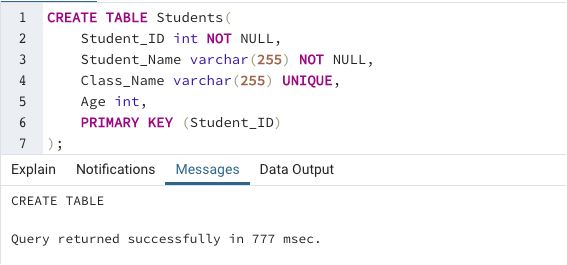
Integrity Constraints In Dbms Types Of Integrity Constraints In Dbms

Dbms In Hindi Join Dependency Hindi Tutorials Point Dbms Hindi Tutorial

Entity Integrity Rule And Constraints Check And Foreign Key In Sql Youtube

Mysql 11 Entity Integrity Youtube

What Is Referential Integrity Database Guide





Post a Comment for "Definition Entity Integrity Constraint"