What Is Vaccine Give Example
Remember you are far more likely to be seriously injured by a vaccine-preventable disease than by a vaccine. Moderna COVID-19 vaccine.

Module 2 Subunit Vaccines Who Vaccine Safety Basics
This vaccine is authorized for people age 18 and older.

What is vaccine give example. A vaccine is a medical product. It requires two injections given 28 days apart. Exposure to the disease organism can occur through infection with the actual disease resulting in natural immunity or introduction of a killed or weakened form of the disease organism through vaccination vaccine-induced immunity.
Inactivated vaccines produce immune responses in different ways than live attenuated vaccines. Examples include IPV polio vaccine hepatitis A vaccine rabies vaccine and most influenza vaccines. They are considered an intermediate phase between the inactivated and attenuated vaccines.
For most vaccines a weakened form of the disease germ is injected into your body. JanssenJohnson Johnson COVID-19 vaccine. For some Muslim fundamentalists for example opposition to the polio vaccine in Afghanistan Nigeria and Pakistan has had much more to do with social and political issues rather than theological issues.
A vaccine or immunization is a way to build your bodys natural immunity to a disease before you get sick. For example inactivated vaccines for influenza are currently available as subunit rather than whole viral vaccines in the US. In the process of making these vaccines the toxins are weakened so.
A vaccine can lessen. An example is how having an egg allergy that has caused breathing problems in the past is a precaution for flu vaccination because most flu vaccines are made through an egg-based process. The Moderna COVID-19 vaccine is 94 effective in preventing the COVID-19 virus with symptoms.
Vaccines though they are designed to protect from disease can cause side effects just as any medication can. Its the illness and all the symptoms of the disease. Other examples of diseases for which vaccines have been developed include mumps measles typhoid fever cholera plague tuberculosis tularemia pneumococcal infection tetanus influenza yellow fever hepatitis A hepatitis B some types of encephalitis and typhusalthough some of those vaccines are less than 100 percent effective or are used only in populations at high risk.
Hepatitis A given by injection in two doses Influenza given as a flu shot annually. Often multiple doses are necessary to build up andor maintain immunity. Many vaccine-preventable diseases can even result in death.
For example the tetanus toxoid is derived from the tetanospasmin produced by Clostridium tetani. The second dose can be given up to six weeks after the first dose if needed. This keeps you from getting and spreading the disease.
Live attenuated vaccines can in rare cases cause infection of the. It takes time before protection reaches its maximum level a few weeks after the second dose. For a one-dose vaccine people will have built maximum immunity against COVID-19 a few weeks after getting vaccinated.
Some have even believed that the polio vaccination effort was a conspiracy to sterilize Muslims in the area. Toxoid vaccines prevent diseases caused by bacteria that produce toxins poisons in the body. Among these are the many inactivated vaccines also known as whole-killed vaccines that protect against the following diseases.
On the other hand tetanus is caused by the bodys reaction to the toxin produced by the tetanus bacteria and so the vaccine contains inactivated tetanus toxin. These yeast cells are then able to produce one of the surface proteins from the hepatitis B virus and this is purified and used as the active ingredient in the vaccine. The inactivated polio vaccine is an example of this type of vaccine.
For some vaccines that have been in use for a much longer period of time we have a better idea of which antibody levels correlate with protection For example health care and lab workers who handle blood samples often have their hepatitis B antibody levels checked to show that they are immune to hepatitis B. For two-dose vaccines vaccines only give partial protection after the first dose and the second dose increases that protection. For example to make thehepatitis B vaccine part of the DNA from the hepatitis B virus is inserted into the DNA of yeast cells.
Toxoids are used as vaccines because they induce an immune response to the original toxin or increase the response to another antigen since the toxoid markers and toxin markers are preserved. For example measles is the result of the bodys reaction to the whole virus and so the vaccine contains a weakened form of the virus. For example tetanus can cause extreme pain muscle spasms lockjaw and blood clots measles can cause encephalitis an infection of the brain and blindness.
Some vaccines are associated with fever rash and achiness. For example the inactivated poliovirus vaccine does not produce sterilizing immunity and is 90 percent or more effective. Most side effects from vaccination are mild such as soreness swelling or redness at the injection site.
Some vaccines contain inactivated but previously virulent micro-organisms that have been destroyed with chemicals heat or radiation ghosts with intact but empty bacterial cell envelopes. Either way if an immune person comes into contact with that disease in the future their immune system will.

Why A Covid 19 Vaccine That S Only 50 Effective Could Still Help Stop The Pandemic Shots Health News Npr

Module 2 Types Of Vaccines Who Vaccine Safety Basics

Bacterial Vaccine An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

California County Requires Employers To Ascertain Vaccination Status
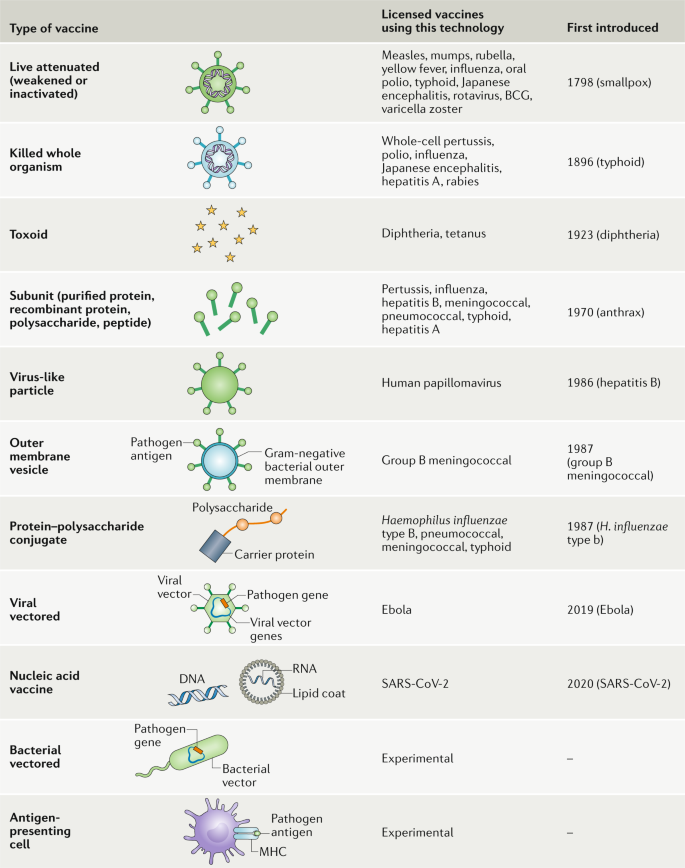
A Guide To Vaccinology From Basic Principles To New Developments Nature Reviews Immunology

How Vaccines Work British Society For Immunology

Coronavirus Vaccination Cards A Target Of Scams The Washington Post

Vaccination Cards Will Be Issued To Everyone Getting Covid 19 Vaccine Health Officials Say Abc11 Raleigh Durham
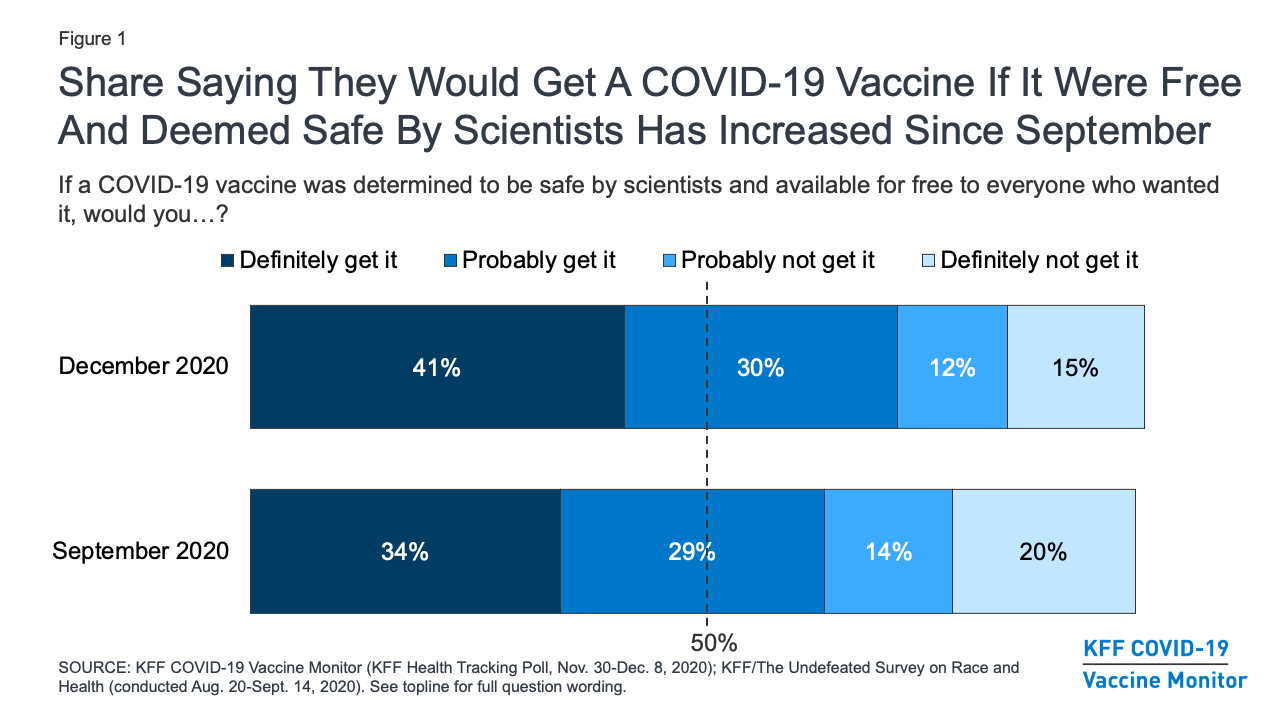
Kff Covid 19 Vaccine Monitor December 2020 Kff

Vaccine Science Safety National Foundation For Infectious Diseases

Covid 19 Vaccine Card Is Not An Immunity Passport Here S The Difference Cnet
Vaccinations And Booster Shots Adults Need Piedmont Healthcare
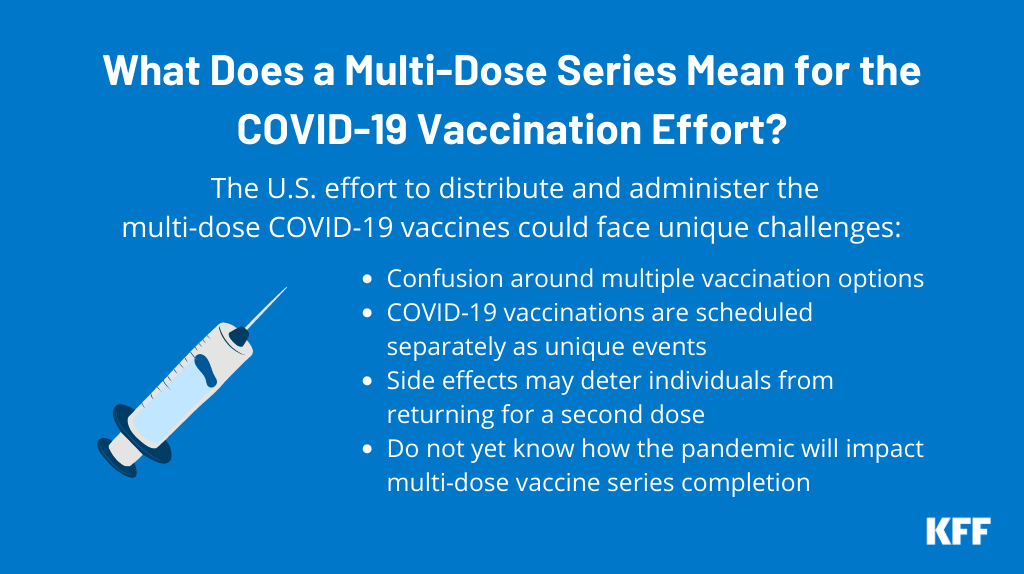
What Does A Multi Dose Series Mean For The Covid 19 Vaccination Effort Kff
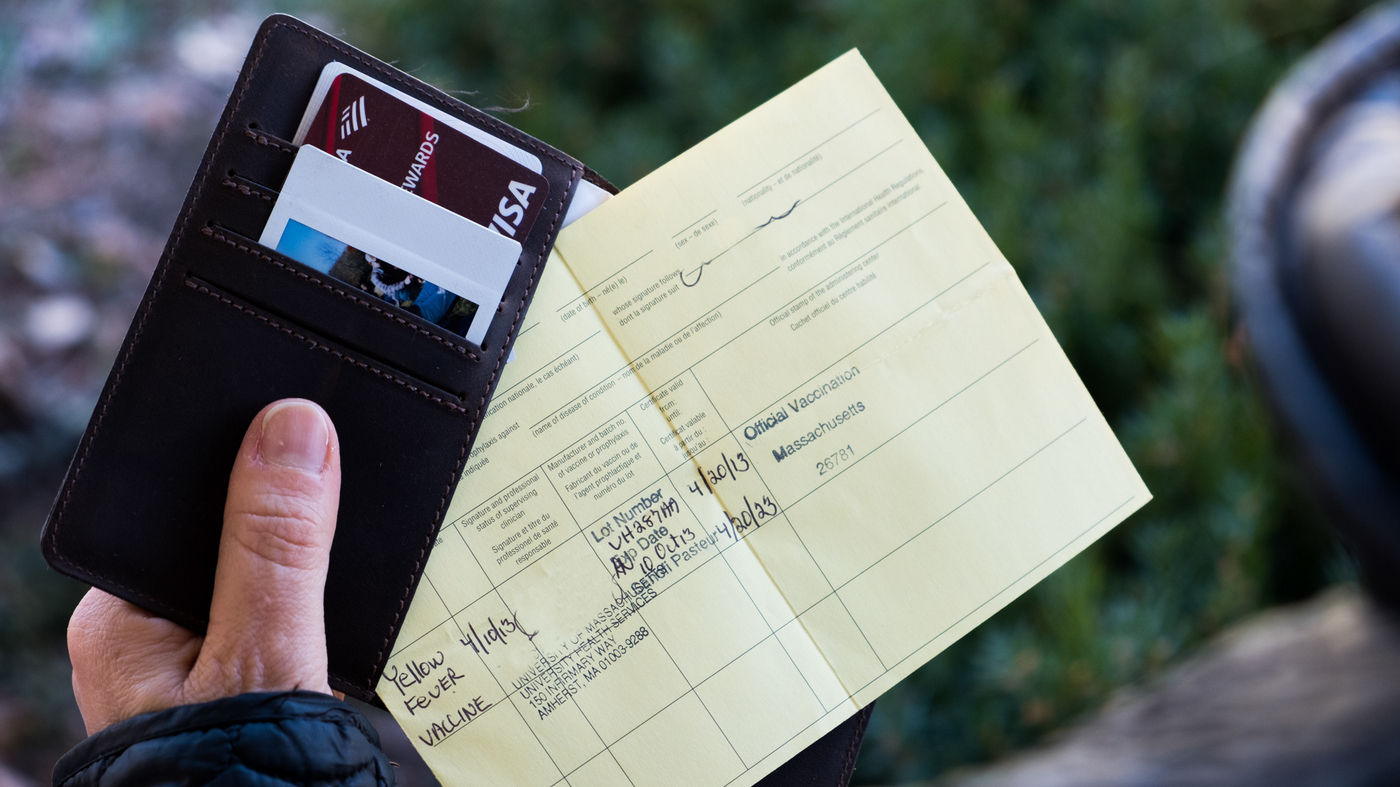

Vaccine Passport Debate Goes Back To 1897 Plague Vaccine Goats And Soda Npr

Gelatine In Vaccines Vaccine Knowledge
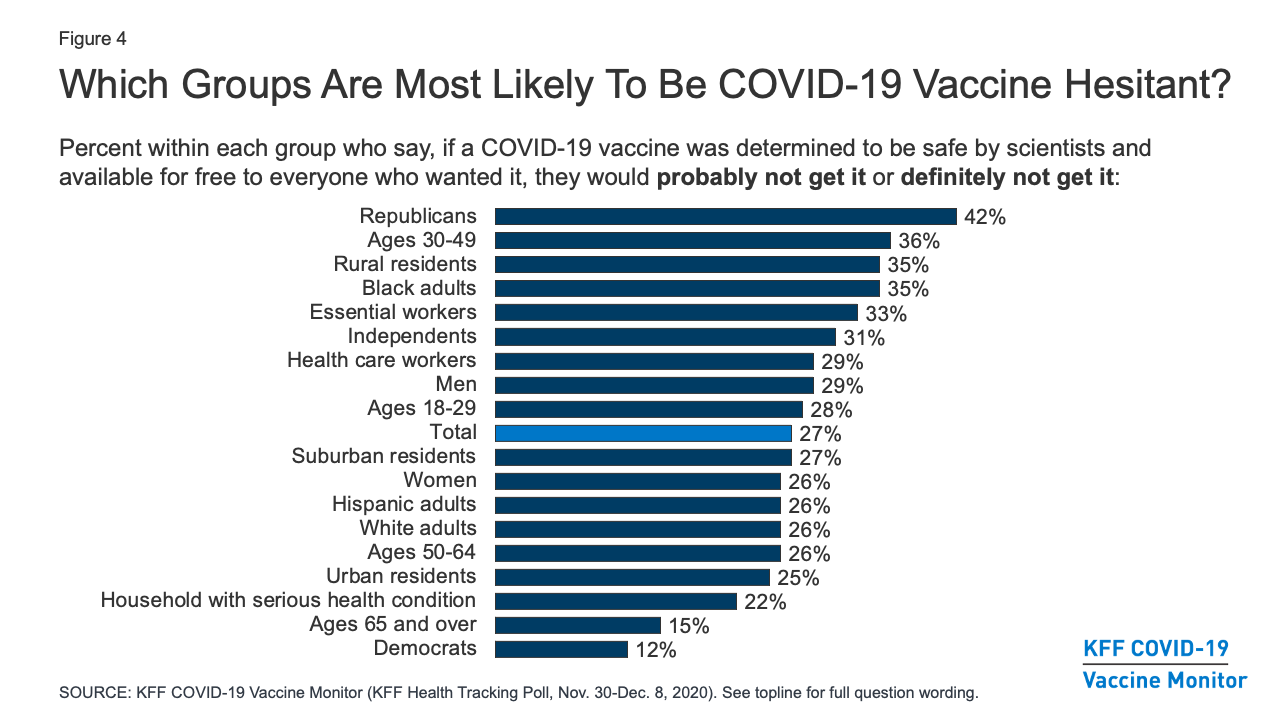
Kff Covid 19 Vaccine Monitor December 2020 Kff

Vaccine Science Safety National Foundation For Infectious Diseases
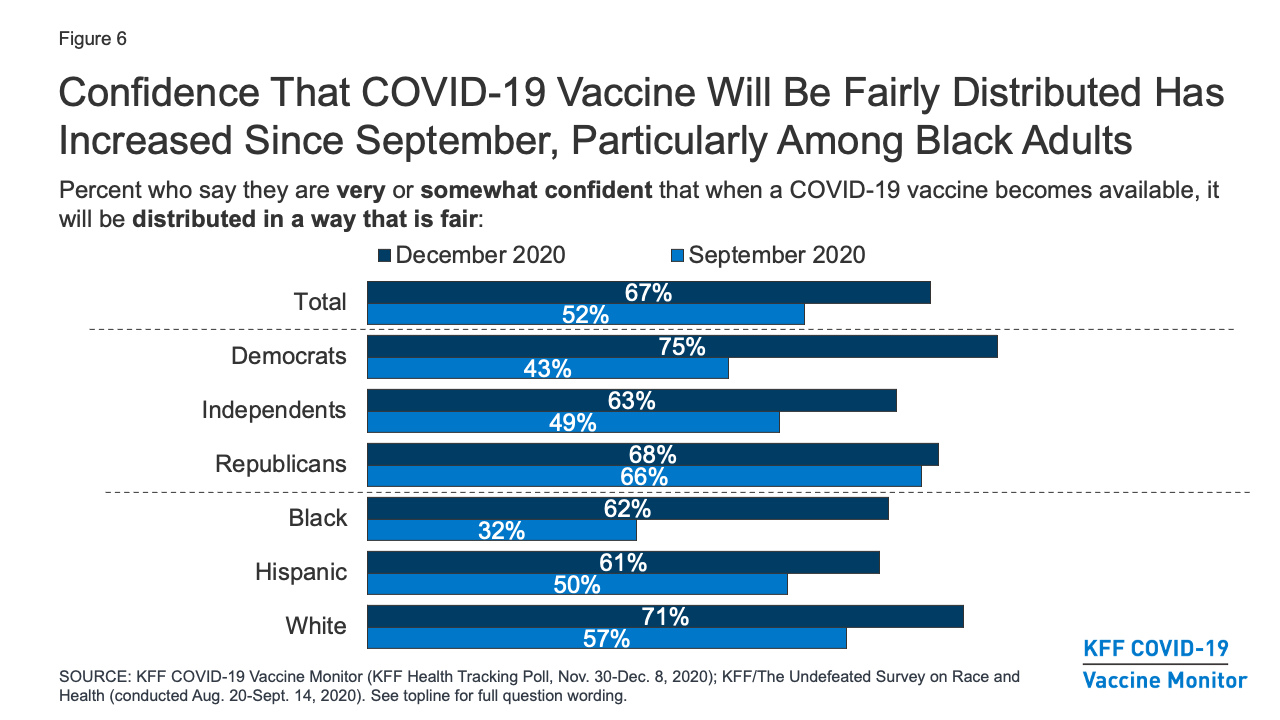
Kff Covid 19 Vaccine Monitor December 2020 Kff
Got Vaccinated Here S Why You May Want To Keep That To Yourself
Post a Comment for "What Is Vaccine Give Example"