Definition Of Immunity Short
The next time that an individual encounters that same antigen the immune system is primed to destroy it quickly. Antibodies are proteins that bind to and help attack pathogens such as bacteria and viruses.

Some Early Trends In Immunology Trends In Immunology
The quality or state of being immune especially.
Definition of immunity short. Synonyms Frequently Asked Questions About immunity Example Sentences Learn More About immunity. This means rejecting infections clearing up dust which gets in the lungs and killing cancer cells. Short- and Long-Term Cell Memory Whenever T cells and B cells are activated some become memory cells.
Typically antibodies are produced by white blood cells in response to infection. Knowledge of the genetic. The immune system keeps a record of every germ microbe it has ever defeated so it can recognise and destroy the microbe quickly if it enters the body again.
Immune system is a network ofcells tissues and organs that worktogether to defend the body against attacksby foreign invaders. In biology immunity is the capability of multicellular organisms to resist harmful microorganisms. Its discovery was one of the major achievements of 20th century science gradually emerging in the 1920s and then.
This process has a prominent genetic component. The immune system is a network of biological processes that protects an organism from diseases. Passive immunity develops after you receive antibodies from someone or somewhere else.
This type of immunity is short-lived because it doesnt. The World Health Organization for reasons unknown has suddenly changed its definition of a core conception of immunology. It detects and responds to a wide variety of pathogens from viruses to parasitic worms as well as cancer cells and objects such as wood splinters distinguishing them from the organisms own healthy tissue.
The condition of being immune. They are a key component of the human immune system. These components are called autoantigens or self-antigens and typically consist of proteins or proteins complexed to nucleic acids.
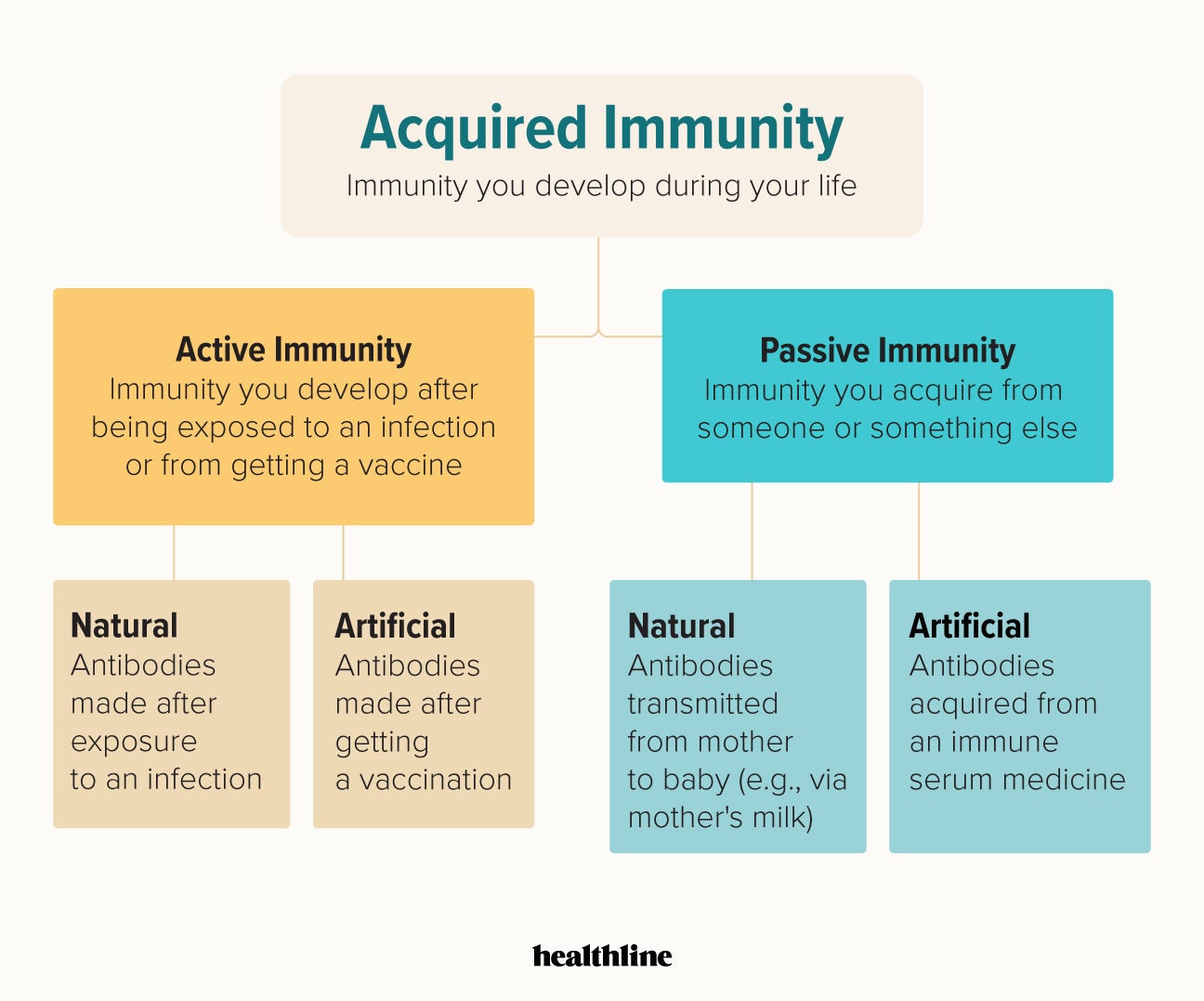
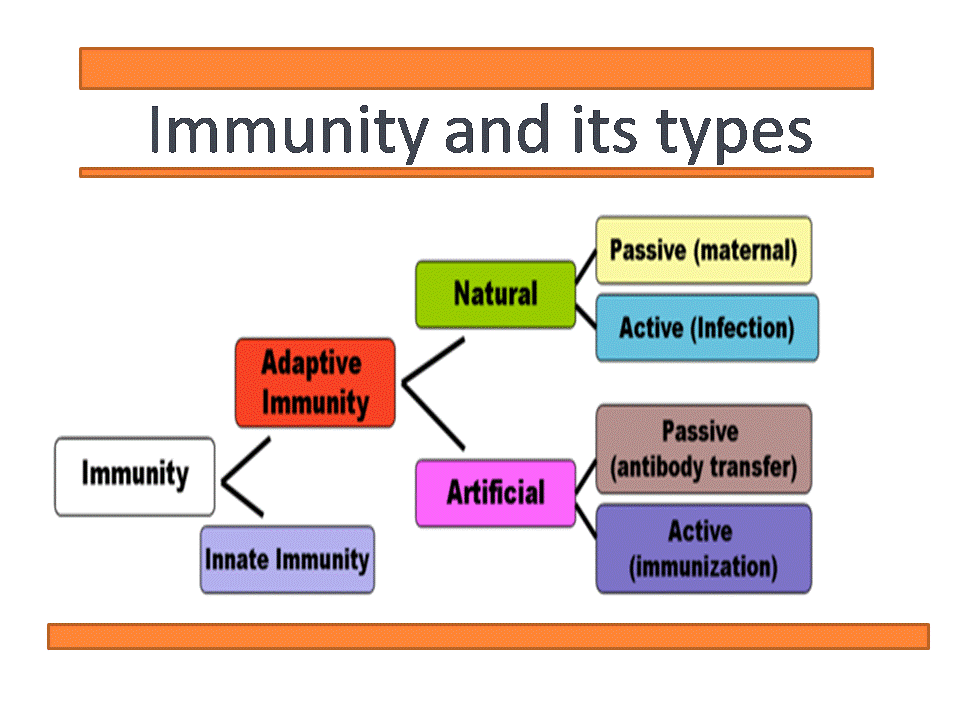
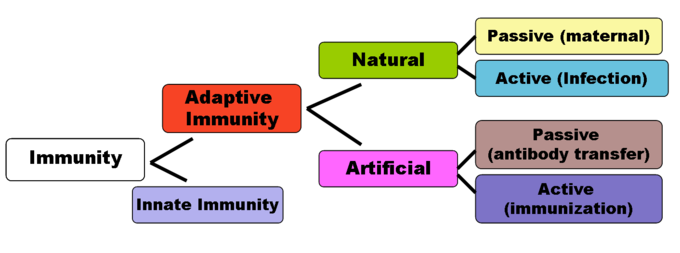
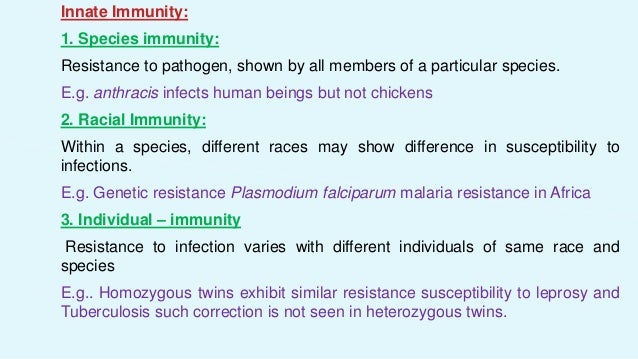
Immunity is of two types. Immunity is usually provided by the bodys own immune system which is determined by the action of ones genes. Because the humanbody provides an ideal environment formany microbes they try to break in.
The protection against infectious disease conferred either by the immune responsegenerated by immunization or previous infection or by other nonimmunologic factors. Definition of Autoimmunity Autoimmunity is the presence of antibodies which are made by B lymphocytes and T lymphocytes directed against normal components of a person autoantigens. The immune system is a complex network of cells and proteins that defends the body against infection.
Immunity is the ability of the body to defend itself from foreign bodies. A reduction in the risk of infection with a specific communicable disease such as measles or influenza that occurs when a significant proportion of the population has become immune to infection as because of previous exposure or vaccination so that susceptible individuals are much less likely to come in contact with infected individuals. These are primarilymicrobesgermstiny infection-causingorganismssuch as bacteria virusesparasites and fungi.
Acquired immunity - immunity to a particular disease that is not innate but has been acquired during life. Immunity involves both specific and nonspecific components. Passive immunity provides short-term protection against infection.
It may also be brought about by having had a disease or infection in the past and recovering from it. Antibodies are proteins produced by the body to neutralize or destroy toxins or disease-carrying organisms. Immunity is the ability of an individual to recognize the self molecules that make up ones own body and to distinguish them from such nonself molecules as those found in infectious microorganisms and toxins.
Other components of the immune system adapt themselves to each new disease encountered and can generate pathogen. Immunity to a disease is achieved through the presence of antibodies to that disease in a persons system. The nonspecific components act as barriers or eliminators of a wide range of pathogens irrespective of their antigenic make-up.
WHO supports achieving herd immunity through vaccination not by allowing a disease to spread through any segment of. Resistance of the body to infection by a disease-causing agent such as a bacterium or virus. It isthe immune systems job to keep them outor failing that to seek out.
Innate immunity protects the host against infection but has. Immunity can be acquired by the development of antibodies after an attack of an infectious disease or by a pregnant mother passing antibodies through the placenta to a fetus or by vaccination. Herd immunity also known as population immunity is the indirect protection from an infectious disease that happens when a population is immune either through vaccination or immunity developed through previous infection.
Immunity that occurs naturally as a result of a persons genetic constitution or physiology and does not arise from a previous infection or vaccinationgenetic immunity inherent immunity native immunity. A condition of being able to resist a particular disease especially through preventing development of a pathogenic microorganism or by counteracting the effects of its products see also active immunity passive immunity. When the percentage of people vaccinated against.
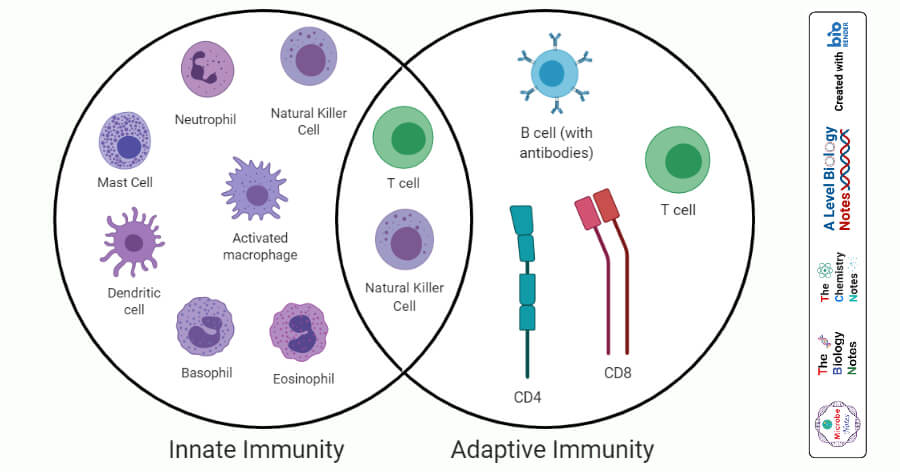
29 Differences Between Innate Immunity And Adaptive Immunity Microbe Notes

Immunity Cell Mediated Immunity Dr Ahrsia V F

Immunity An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

13 52 Immunity Biology Libretexts

Types Of Immune Responses Innate And Adaptive Humoral Vs Cell Mediated Video Khan Academy

Immunity An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Immunity Definition And Types Of Immunity Immunity Is

Immunity An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Barrier Defenses And The Innate Immune Response Anatomy And Physiology Ii

Immunity Details Definition And Types Of Immunity
Immunity And Its Types Innate And Acquired Immunity Online Biology Notes
11 12c Artificial Immunity Biology Libretexts

Immunity It S A Big Word Right Now But What Does It Mean And Why Is It Confusing Everyone Trust Transparency Center

Immune System Structure And Functions

Acquired Immunity What Is It And How Do You Get It



Post a Comment for "Definition Of Immunity Short"