Definition Of Speed Physics
Speed is defined as The rate of change of position of an object in any direction. The rate at which something moves is done or acts 3.

Angular And Linear Velocity Explained With 4 Terrific Examples Physics Angular Velocity
Speed is often described simply as the distance traveled per unit of.

Definition of speed physics. Speed in Physics Formula. Speed is defined as the distance moved by an object or particle in a particular period of time. Since speed only refers to the magnitude and not the direction it is a scalar quantity.
The formula is rather straightforward. V s t constant Speed is inversely proportional to time when distance is constant. It tells us how fast or slow an object is moving.
The time rate of change of position of the object in any direction is called speed of the object. Speed is a scalar quantity that refers to how fast an object is moving Speed can be thought of as the rate at which an object covers distance. Higher speed means an object is moving faster.
The definition of Speed in Physics is the distance covered by an object in unit time. Wave speed is the distance the wave travels in a given amount of time such as the number of meters it travels per second. Speed is a scalar quantity as it has only direction and no magnitude.
When something moves in a circular path at a constant speed and returns to its starting point its average velocity is zero but its average speed is found by dividing the circumference of the circle by the time taken to move around the circle. Speed Formula in Physics Its SI unit is ms. If it isnt moving at all it has zero speed.
Distance is measured in meters and time in seconds hence ms is the unit for speed. In other words the rate at which the object is moving is called speed. In science and physics the standard unit of measure for speed is generally meters per second or ms.
The equation that represents the wave speed is given as follows. For example if a car covers a distance of 10 km in 1 hour then the speed of the car is 10kmhour and 2778 meters per second. The measurement of speed can reflect two different scalar quantities.
It doesnt have a direction. It is thus a scalar quantity. Average speed is not the magnitude of the average velocity.
The car may be travelling at 50 mph at this moment but it may slow down or speed up during the next hour. Speed is given by the formula sdt where s is the speed d is the distance covered by the object and t is the. Put another way speed is a measure of distance traveled over a certain amount of time.
In SI system speed is measured in ms Meters Second. Average speed is the total distance traveled divided by the elapsed time. V 1 t s constant Combining these two rules together gives the definition of speed in symbolic form.
Speed according to its technical definition is a scalar quantity that indicates the rate of motion distance per time. 70 rows Speed is directly proportional to distance when time is constant. Since there is no directional component speed must be a scalar quantity.
In everyday use and in kinematics the speed commonly referred to as v of an object is the magnitude of the rate of change of its position with time or the magnitude of the change of its position per unit of time. The path covered by a body object in a given time is called speed of the object. Instantaneous Speed - The speed of an object at a given moment.
Out of the three terms the definition of speed in physics is the closest to the laymans understanding of it. Lower speed means it is moving slower. Speed is the scalar Quantity.
If an ocean wave crest travels a distance of 30 m in 10 seconds then the speed of the ocean wave is 3 ms. Speed is the rate at which an objects position changes measured in meters per second. General Physics physicsa scalar measure of the rate of movement of a body expressed either as the distance travelled divided by the time taken average speed or the rate of change of position with respect to time at a particular point instantaneous speed.
Speed Time Graphs - Physics Speed. A fast-moving object has a high speed and covers a relatively large distance in a short amount of time. Speed is measured as the ratio of distance to the time in which the distance was covered.
Unit time may be a second an hour a day or a year. SI unit of speed is meter per second abbreviated as ms. Speed is a physical measurement quantity that measures how far an object has traveled in a given amount of time.
Instantaneous speed is a scalar quantity as it has no direction specified. Speed distance travelled time taken. For measuring distance direction is not necessary path can be measured in any direction hence speed is not represented by any specific direction.
Speed in general terms is defined as the rate of change of the distance covered by an object in unit time. Instantaneous speed is the magnitude of the instantaneous velocity. Its units are length and time.
Speed is the scalar quantity that is the magnitude of the velocity vector. In physics you can calculate average speed by taking the total distance travelled and dividing it by the total time required to travel that distance.

Pin By Shaheen Iqbal On Physics Class Ix And X Physics What Is Velocity Class

1d Equations Lambda Waves Speed Velocity Hertz Physics Learning Targets Equations

Angular Displacement Velocity Acceleration Physics Mechanics Engineering Science Physics

Force And Motion Word Wall Force Potential Energy Word Wall

A 3 Page Worksheet That Covers Acceleration Types Of Acceleration And Interpreting Acceleration On Graphs Through A Acceleration Worksheets Physics Concepts

Definitions Directions Velocity

Speed And Velocity Best Concept Physics Online Learn Physics What Is Velocity

Flash Cards For Motion Graphs Motion Graphs Physical Science Physics

Difference Between Distance And Displacement Physics Notes Physics Study Materials

Speed Vs Velocity Student And Teacher Handout Velocity Speed Velocity Acceleration Physical Science

Energy Definition And Types Physics Education Quotes For Teachers Online Tutoring

This Image Shows How Speed Can Go To Velocity And How Velocity Can Go To Acceleration It Shows How Speed Relates To Accel Ap Calculus Physics Lessons Calculus

Speed Distance And Time Activity In 2021 Speed Lesson Time Activities Physics Experiments High School

Physics Class 9 10 Centripetal Force Centripetal Force Ch 7 Circularm In 2021 Centripetal Force Physics Constant Speed
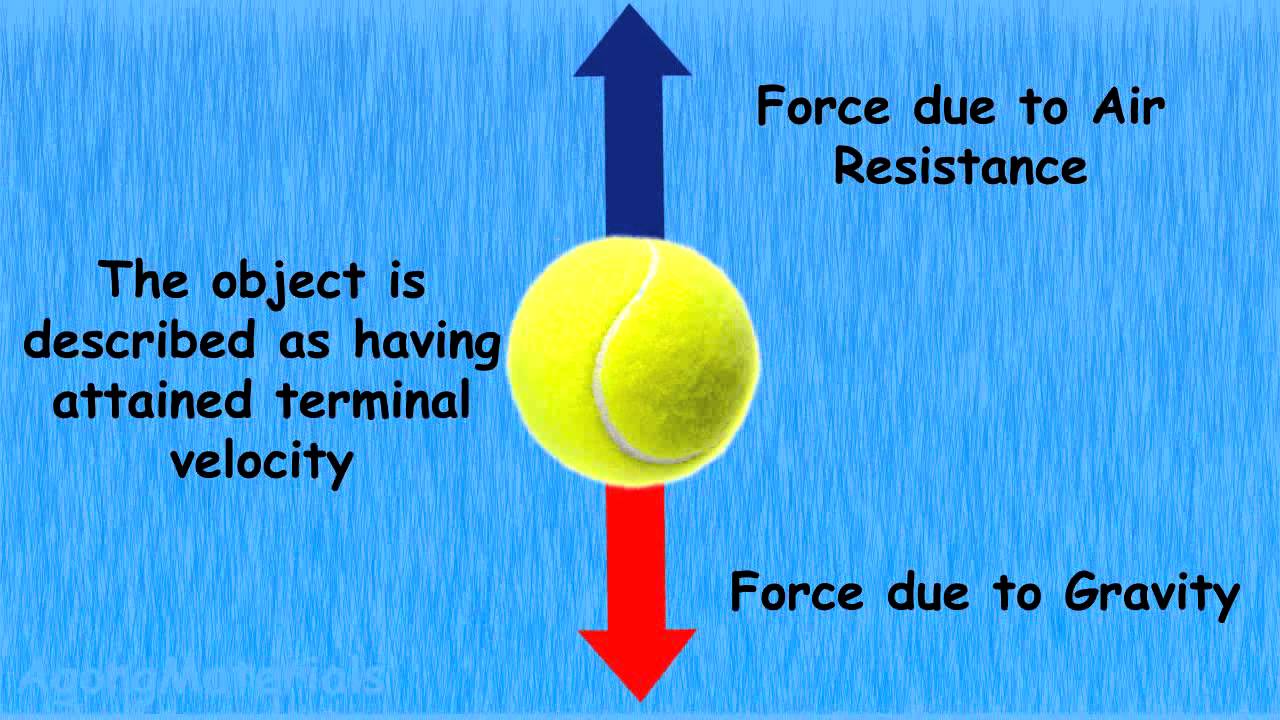
Terminal Velocity Animation Youtube Terminal Velocity Physical Science Velocity

Doppler Effect Https Scienceterms Net Physics Doppler Effect Physics Fun Facts Light Wave



Post a Comment for "Definition Of Speed Physics"