Definition Of Temperature Entropy
During a thermodynamic process the temperature of an object changes as heat is applied or extracted. It is the thermodynamic quantity equivalent to the total heat content of a system.

Pin By Leslie On Reading Material In 2021 Entropy Reading Material Entropy Definition
Since thermodynamics deals only with the macro scale entropy is defined here to be the heat transfer into the system divided by the temperature.

Definition of temperature entropy. This gives an expression for internal energy that is consistent with equipartition of energy. Temperature andEntropy Temperature and entropy were introduced initially as thermodynamic quantities and interpreted in terms of macroscopic properties of a body in Chapter 2. Means if we have a pure crystalline solid substance and if its temperature is absolute zero 0 K then its entropy will be zero.
Energy stored in a chaotic way the random-pile library has high entropy. An isentropic process is depicted as a vertical line on a T-s diagram whereas an isothermal process is a horizontal line. Because work is obtained from ordered molecular motion the amount of entropy is also a measure of the molecular disorder or randomness of a system.
Shown in Figure 1 this is represented as the energy quality which decreases as the entropy of a system increases. The Clausius theorem states that this equality only holds for reversible processes. Ultra terse version.
A more correct definition of the entropy is the differential form that accounts for this variation. For example for a system that has an equilibrium pressure the system pressure fluctuates to some extent about the equilibrium value. I am going to stay in a classical framework so that I dont need to overwhelm you with the quantum mechanical machinery of the density operator.
Lets say we have a system of N particles. At a uniform temperature a substance has a maximum entropy and is unable to drive a heat engine. Temperature is the inverse of the Lagrange multiplier ensuring the conservation of energy in the maximisation of the statistical entropy.
You can see that the gas is filled inside the container. Entropy loosely is a measure of quality of energy in the sense that the lower the entropy the higher the quality. The definition of entropy according to one dictionary is that it is a measure of thermal energy per unit temperature that is not available for any useful work.
The internal energy U can be represented by q times the oscillator energy. Then making use of the definition of temperature in terms of entropy. With kT2 of energy for each degree of freedom for each atom.
Entropy definition is - a measure of the unavailable energy in a closed thermodynamic system that is also usually considered to be a measure of the systems disorder that is a property of the systems state and that varies directly with any reversible change in heat in the system and inversely with the temperature of the system. Entropy change in a system can be calculated from the reversible heat p 2 1 atm V 2 15 L T 298 K n 1 mol p 1 15 atm V 1 1 L T 298 K n 1 mol p 2 Volume Pressure p 1 15 atm V 1 1 L p 2 1 atm V 2 15 L w -142 kJ w -412 kJ kJ 12. In thermodynamics the enthalpy is the measure of energy in a thermodynamic system.
The degree of disorder or uncertainty in a system. The enthalpy is defined to be the sum of the internal energy E plus the product of the pressure p and volume V. Thermodynamic variables such as pressure temperature or entropy likewise undergo thermal fluctuations.
Let me explain this to you with a simple image. The term was introduced by Rudolf Clausius in the mid-nineteenth century from the Greek word τρoπή to explain the relationship of the internal energy that is available or unavailable for transformations in form of heat and work. Entropy can also be described as a systems thermal energy per unit temperature that is unavailable for doing useful work.
Another example of this approach to temperature is the Einstein solid with q units of energy and N oscillators. In an idealized state compression is a pump compression in a compressor and expansion in a turbine are isentropic processes. 4 ln 1 2 V V nRT w rev q rev -w rev 412 kJ The system entropy increases by the same amount in both expansions state function.
Entropy the measure of a systems thermal energy per unit temperature that is unavailable for doing useful work. For example for every fluid it is possible to find a unique func-tion TPV of its parameters of state PV which takes the same numerical. In a thermodynamic sense Entropy is defined as a state function with is the ratio of the heat added reversibly to a system divided by the temperature at which it is added.
In classical thermodynamics entropy is a property of a thermodynamic system that expresses the direction or outcome of spontaneous changes in the system. This enables the definition of a proper probability density according to. Energy stored in a carefully ordered way the efficient library has lower entropy.
By the definition of entropy the heat transferred to or from a system equals the area under the T-s curve of the process. Therefore entropy can be regarded as a measure of the effectiveness of a specific amount of energy.

Entropy Flow Chart Physical Chemistry Communication Theory Thermodynamics

Percent Yield Easy Science Teaching Chemistry Ap Chemistry

Pressure Volume And Temperature Entropy Diagram For The Air Standard Atkinson Cycle Thermodynamics Cycling Entropy

Thermal Conductivity Thermal Resistance Mechanical Engineering Surface

Thermodynamic Patentials Thermodynamics Classical Physics Internal Energy

Thermodynamic Relationships Physics And Mathematics Thermodynamics Chemistry Lessons

The Laws Of Thermodynamics Chemistry Education Thermodynamics Engineering Science

Pin On Mathematics Physics Geometry And More
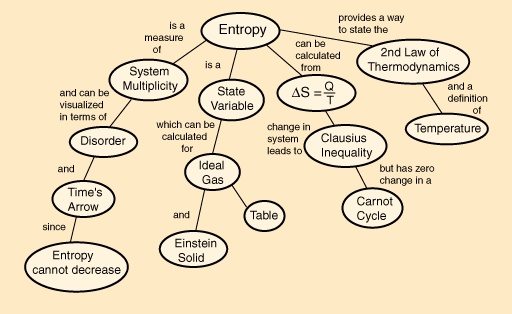
Entropy Flow Chart Physical Chemistry Communication Theory Thermodynamics

Critical Constants Of Gas And Van Der Waals Equation Critical Phenomena And Expression Of Critical Constants In T Chemistry Physical Chemistry Study Chemistry

Difference Between Entropy And Enthalpy In Thermodynamics Thermodynamics Teaching Chemistry Engineering Science

First Law Of Thermodynamics Thermodynamics Physics Mechanics Advanced Physics

P V And T S Diagram For The Stirling Cycle Stirling Thermodynamics Cycling

Image Result For Laws Of Thermodynamics Thermodynamics Second Law Of Thermodynamics Physics

Energy Absorption Easy Science Sound Energy Science Flashcards Chemical Energy

Measure Of Entropy Entropy Thermodynamics Chemistry

Enthalpy Gif Gif Image 621 466 Pixels Physics And Mathematics Science Chemistry Mathematics Quotes

4 Laws Of Thermodynamics Explained Thermodynamics Science Anchor Charts Physics Formulas

Post a Comment for "Definition Of Temperature Entropy"