Definition Of Organelle Bbc Bitesize
The cell is the basic building block of an organism and the fundamental unit of life. It plays a major role in the production processing and transport of proteins and lipids.

Gcse Science Revision Biology Plant Cells Youtube
There are many organelles including the nucleus mitochondria ribosomes chloroplasts.
Definition of organelle bbc bitesize. The inner membrane is folded inwards to form projections called cristae. Contains genetic material including. Include organelles and processes that they carry out eg respiration photosynthesis and protein synthesis.
7 rows Animal cells and plant cells. Eukaryotic cells contain membrane-bound organelles such as a nucleus where DNA is stored in chromosomes and mitochondria. It is where many of the chemical reactions happen.
An animal cell is one type of eukaryotic cell enclosed by a cell membrane and containing membrane-bound organelles and a true nucleus that carry out different functions. The endoplasmic reticulum smooth and rough ER the Golgi complex lysosomes mitochondria peroxisomes and ribosomes. In fact during fetal development your bones were just cartilage molds into which bone material was laid.
They are eukaryotic cells meaning that they have a true nucleus and specialized structures called organelles that carry out different functions. BBC Bitesize Stages of mitosis or cell division. The idea that all organisms were made up of cells was put together in 1837 by two colleagues Schleiden and Schwann who discussed what they had been observing.
Definition of diffusion and factors affecting rate. A jelly-like material that contains dissolved nutrients and salts and structures called organelles. A jelly-like material that contains dissolved nutrients and salts and structures called organelles.
Homeostasis maintains optimal conditions for enzyme action throughout the body as well as all cell functions. Organelle In cell biology an organelle is one of several structures with specialized functions suspended in the cytoplasm of a eukaryotic cell. Cell fractionation is the process in which cells are broken up and the different organelles they contain separate out.
Cell structure that is specialised to carry out a particular function or job. Bones in the human body are constantly remodeled. The endoplasmic reticulum ER is an important organelle in eukaryotic cells.
I use this PowerPoint in my biology classes at Beverly Hills High SchoolTopics- 3 Main sections- Cytoplasm-. But before fractionation the tissue must be placed in a cold isotonic buffer solution this reduced enzyme activity that breaks down organelles being isotonic it prevents the organelles. Examples of organelles found in eukaryotic cells include.
Inside this is the matrix. A jelly-like material that contains dissolved nutrients and salts and structures called organelles. Animal cells are the basic unit of life in organisms of the kingdom Animalia.
It is where many of the chemical reactions happen. Definition of homeostasis bbc bitesize. The ER produces transmembrane proteins and lipids for its membrane and for many other cell components including lysosomes secretory vesicles the Golgi appatatus the cell membrane and plant cell vacuoles.
Generally they are sausage-shaped organelles whose walls consist of 2 membranes. These automatic control systems may involve nervous responses nervous system or. Definition of Osteoblasts.
Most of the reactions for aerobic respiration take place in the mitochondria so it is an incredibly important organelle. Homeostasis is the regulation of conditions in the body such as temperature water content and carbon dioxide levels. This video is taught at the high school level.
BBC Bitesize The building blocks of cells first part of Mitosis and meiosis. Organelles are structures within a cell that perform specific functions like controlling cell growth and producing energy. This is used to help us study cell structures and functions.
Cell fractionation is a two stage process which consists of. These are suspended in the cytoplasm. Definition of organelle.
A specialized cellular part such as a mitochondrion chloroplast or nucleus that has a specific function and is considered analogous to an organ Examples of organelle. Animal cells usually have an irregular shape and plant. It is where many of the chemical reactions happen.
Basic structural and functional unit of a living organism.
Https Www Theebbsfleetacademy Kent Sch Uk Site Data Files Images Curriculum 1bd5c1e12bd5be7198c08fe54f4bdebf Pdf

Bbc Gcse Biology Levels Of Organisation Revision 3 Science Revision Biology Writing Words

Bbc Gcse Bitesize Photosynthesis Plant Science Photosynthesis Biology Lessons

Science Cells Jordan Girling Ppt Video Online Download

Plant Cell Nucleus High Res Stock Images Shutterstock

Gcse Biology Eukaryotic And Prokaryotic Cells Edexcel 9 1 Youtube

Image From Http Www Docbrown Info Page20 Page20images Animalplantbacteriacells1 Gif Plant And Animal Cells Animal Cell Biology Revision

Definition Of Homeostasis Bbc Bitesize Definitoin
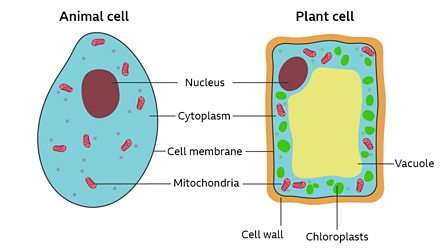
What Happens In The Cytoplasm Of A Plant Cell
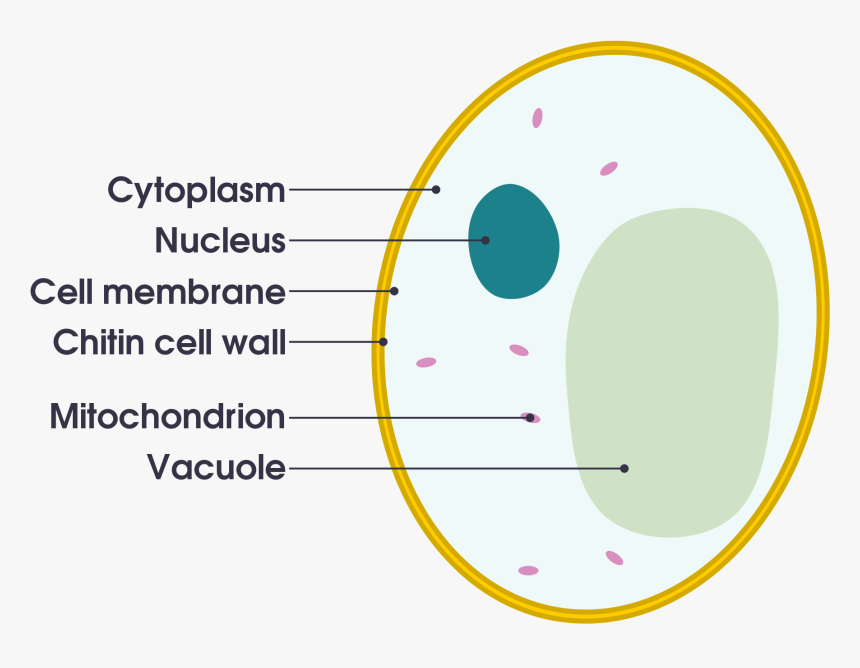
Cells 5th Definition Of Life Lessons Blendspace

Chloroplast Vs Mitochondria Process Educational Scheme Vector Illustration Mitochondria Biology Diagrams Photosynthesis And Cellular Respiration
Https Www Theebbsfleetacademy Kent Sch Uk Site Data Files Images Curriculum 1bd5c1e12bd5be7198c08fe54f4bdebf Pdf

Gcse Biology Variety Of Living Organisms Revision 3 Plant Cell Cell Wall Cell Membrane

Bbc National 5 Biology Cell Structure Revision 1 Cell Structure Plant Cell Cell Membrane
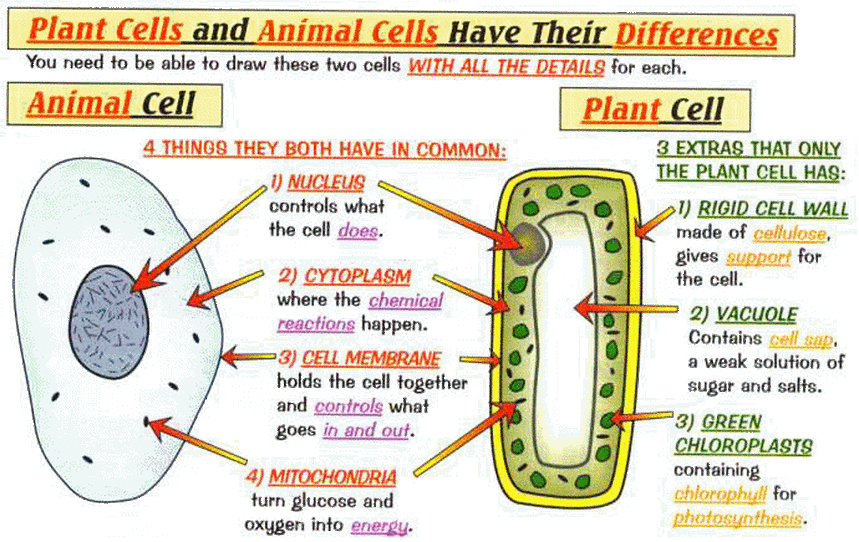
1 Cell Biology Thomas Tallis Science
Http Bishopschester Co Uk Wp Content Uploads 2020 05 Biology Transition From Gcse To A Level Pdf

Gcse Notes Properties Of Fungi

Gcse Biology Transport In Plants Revision 1 Plant Lap Book Biology Plants Plant Study

Post a Comment for "Definition Of Organelle Bbc Bitesize"