Definition Of Unstable Atom
Like a hydrogen atom that has absorbed energy that puts the electron at an n2 level. It will soon fall back to ground state and emit the energy.

Atom Rutherford S Nuclear Model Britannica
Jump to other results.

Definition of unstable atom. Liable to undergo spontaneous decay into some other form. Many subatomic particles such as muons and neutrons are unstable. In physics a radioactive decay chain is a sequence of unstable atomic nuclei and their modes of decays which leads to a stable nucleus.
Radioactive decay is a random process at the level of single atoms in that according to quantum theory it is impossible to predict when a particular atom will decay. Protons and neutrons can only be put together in certain ways and remain stable in nature. In some atoms the binding energy is not strong enough to hold the nucleus together and the nuclei of these atoms are said to be.
An atom is stable because of a balanced nucleus that does not contain excess energy. Unstable Atom - The nuclei of some atoms where the binding energy is not strong enough to hold the nucleus together. Atoms with electrons less than eight in their outermost or valence shell are chemically unstable.
Unstable atoms will lose neutrons and protons as they attempt to become stable. If the forces between the protons and the neutrons in the nucleus are unbalanced then the atom is unstable. The splitting of the atom.
Such atoms gain or lose electrons to attain a. The scientist Ernest Rutherford was the first person to split the atom. During radioactive decay an unstable nucleus spontaneosly and randomly decomposes to form a different nucleus or a different energy state gamma decay giving off radiation in the form of atomic partices or high energy rays.
Radioactive decay also known as nuclear decay or radioactivity is a random process by which an unstable atomic nucleus loses its energy by emission of radiation or particle. Which means that they do not decay over time. Radioactive decay also known as nuclear decay or radioactivity is the process by which a nucleus of an unstable atom loses energy by emitting radiation.
See also stable nucleus. Liable to undergo spontaneous decay into some other form. The smallest particle of a chemical element that can exist.
In simplest terms an unstable atom or unstable isotope is simply an atom that has an imbalance of neutrons to protons. Unstable nuclei which emit radiations The vast majority of atomic nuclei found in Nature are stable. As per the octet rule to be chemically stable an atom of an element must have eight electrons in its outermost orbit or shell.
We dont always understand these rules but look at it this way. 1934 and the discovery of artificial radioisotopes. Most naturally occurring atoms are stable and do not decay.
The nucleus of this kind of atom is said to be. The reason is that almost all unstable nuclei by definition have decayed and vanished over time. For example the nucleus of uranium 238 atom is unstable and changes by radioactive decay into the nucleus of thorium 234 a lighter element.
A nucleus that contains an uneven number of protons and neutrons and seeks to reach equilibrium between them through radioactive decay ie the nucleus of a radioactive atom. A material containing unstable nuclei is considered radioactive. Sources of these unstable nuclei are different but mostly engineers deal with naturally occurring radioactive decay chains known as radioactive series.
Stable atoms retain their form indefinitely while unstable atoms undergo radioactive decay. Two atoms of hydrogen combine with one atom of oxygen to form a molecule of water. For example the nucleus of uranium 238 atom is unstable and changes by radioactive decay into the nucleus of thorium 234 a lighter element.
A material that spontaneously emits such radiation which includes alpha particles beta particles gamma rays. To me an unstable atom is one whose orbiting electrons are not in stable states.

Half Life Half Life Half Life Game Easy Science

Radioactive Element Science Nerd Science Facts Science Rules

Difference Between Compound And Mixture Definition Characteristics Types Of Bonding Compounds And Mixtures Study Chemistry Organic Chemistry Books

Nuclear Fission Nuclear Understanding Teaching

Difference Between Isotope And Radioisotope Definition Properties Examples Study Chemistry Chemistry Lessons Organic Chemistry Study

Periodic Law Easy Science Periodic Table Science Flashcards Physical And Chemical Properties
Nondestructive Evaluation Physics Atomic Elements

Complex Compounds Definition Examples Perfect Imperfect Complex Definition Teaching Chemistry Compound Complex Chemistry Classroom
Radtown Radioactive Atom Activity 4 Atomic Stability Us Epa

Atomic Radius Easy Science Radii Atom Flashcards

Discovery Of Proton In Urdu Hindi Lecture For 9th Class Protons Lecture Discovery

Nuclear Fission Nuclear Fission Reactor Nuclear Fission Equation Nukleer Enerji

Radiometric Dating Uses Unstable Isotopes Of Naturally Occurring Elements Decay Change Into Different Elements Or Isotopes Dating Problems Dating Half Life

Contents Show Overview The Basics Here S A Chart Explaining The Basics Of Radioactive Decay Imag Teaching Chemistry Physics And Mathematics Science Chemistry

Hydrogen Bonding Definition Examples And Types Digital Kemistry Hydrogen Bond Bond Molecules

Nuclear Chemistry Learning Activities Distance Learning Chemistry Worksheets Chemistry Activities Chemistry

Radiometric Dating Back To Basics Creationism Dating Creation Science

Radioactive Decay Chemistry Worksheets Nuclear Physics Nuclear Reaction
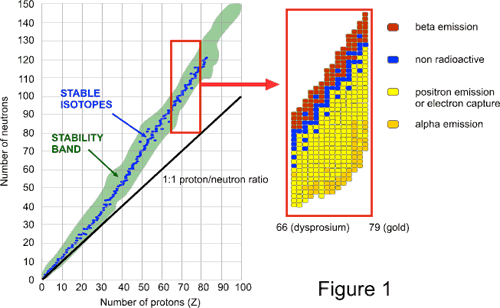
Post a Comment for "Definition Of Unstable Atom"