Quantum Definition Gamma Radiation
Characterized by deep penetration and low dose rates gamma radiation effectively kills all living cells including bacteria and microorganisms throughout a product and its packaging. Gamma radiation also known as gamma rays refers to electromagnetic radiation of extremely high frequencies.

Pin By Rea Kal On Alpha Beta Gamma Radiation Science Chemistry Teaching Chemistry Physics And Mathematics
Photons are massless a so they always move at the speed of light in vacuum 299 792 458 ms or about 186282 mis.
Quantum definition gamma radiation. The process causes little effect on the temperature of the product. The effort to construct a practical gamma-ray laser is interdisciplinary encompassing quantum mechanics nuclear and optical. It is the quantum of the electromagnetic field including electromagnetic radiation such as light and radio waves and the force carrier for the electromagnetic force.
Therefore to be precise we should think of the projection image at the face of the gamma camera as a probability density function governing the photon detection process. Gamma rays are high-energy photons with very short wavelengths and thus very high frequency. Radioactivity refers to the particles which are emitted from nuclei as a result of nuclear instability.
Medical Dictionary for the Health Professions and Nursing Farlex 2012. Some features of quantum optics related to inversionless amplification are translated to nuclear systems. The wavelength is generally in the range 1 10 10 to 2 10 13 metres 2.
The most common types of radiation are called alpha beta and gamma radiation. In quantum mechanics gamma decay is expressed as a transition from an excited to a ground state of a nucleusThen we can study the transition rate of such a decay via Fermis Golden rule 2π. Up to 10 cash back Some features of quantum optics related to inversionless amplification are translated to nuclear systems.
The exploration of quantum phenomena in a curved spacetime is an emerging interdisciplinary area at the interface between general relativity14 thermodynamics46 and quantum. γ radiation is stopped by several feet of heavy concrete or. They are the similar to X-rays distinguished only by the fact that they are emitted from an excited nucleus.
This formula is useful when the function g E is known. A quantum of light or other electromagnetic radiation. Gamma rays also known as gamma radiation refers to electromagnetic radiation no rest mass no charge of a very high energies.
In his 2003 Nobel lecture Vitaly Ginzburg cited the gamma-ray laser as one of the thirty most important problems in physics. The elementary particle of light and other electromagnetic radiation. Nuclei and nuclear transitions differ in several ways from atomic systems.
Gamma rays are photons and thus are governed by the laws of quantum physics and the randomness that this entails. A gamma-ray laser or graser is a hypothetical device that would produce coherent gamma rays just as an ordinary laser produces coherent rays of visible light. Because the nucleus experiences the intense conflict between the two strongest forces in nature it should not be surprising that there are many nuclear isotopes which are unstable and emit some kind of radiation.
Gamma radiation Gamma photon A quantum of electromagnetic radiation of 1 nm which is generated by unstable nuclei eg 60Co. Nuclei and nuclear transitions differ in several ways from atomic systems. γ fōton physics A corpuscle of energy or particle of light.
Nuclear Physics electromagnetic radiation emitted by atomic nuclei. Here Eγ is the energy of γ-radiation and c is the speed of light. General Physics electromagnetic radiation of very short wavelength emitted by any source esp the portion of the electromagnetic spectrum with a wavelength less than about 1 10 11 metres.
Gamma quantum synonyms Gamma quantum pronunciation Gamma quantum translation English dictionary definition of Gamma quantum. Gamma radiation has a much shorter wavelength of the order of lattice-distances nuclear transitions are many orders of magnitude weaker than atomic ones making nuclear pumping extremely hard no coherent gamma. Gamma rays are a form of electromagnetic radiation EMR.
The quantum of electromagnetic energy. The recoil energy ER received by a free atom with mass M is defined by the energy conservation law E R E γ 2 M c 2 ER 0002 eV for 57 Fe. Electromagnetic radiation can be described in terms of a stream of photons which are massless particles each travelling in a wave-like pattern and moving at the speed of light.

Lesson Video Gamma Radiation Nagwa

Pin On Chemistry Nuclear Processes

Gamma Ray Definition Uses Wavelength Production Examples Facts Britannica

Gamma Radiation An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Gamma Radiation An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
How Can Electrons Produce Gamma Rays Quora

Gamma Rays Spewed As A Black Hole Forms Might Reverse Time Black Hole Space And Astronomy Abstract Backgrounds

Gamma Ray Definition Uses Wavelength Production Examples Facts Britannica

Contents Show Overview The Basics Here S A Chart Explaining The Basics Of Radioactive Decay Imag Teaching Chemistry Physics And Mathematics Science Chemistry
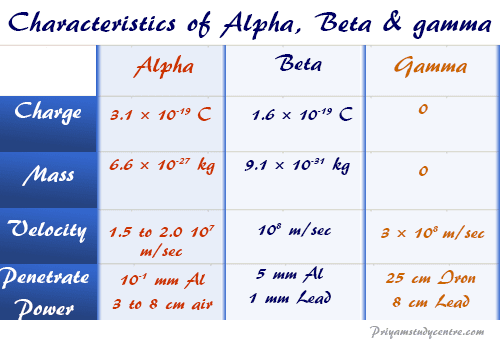
Alpha Beta Gamma Particle Properties Emission Charge Mass

Gamma Irradiation Applied In The Synthesis Of Metallic And Organic Nanoparticles A Short Review Sciencedirect
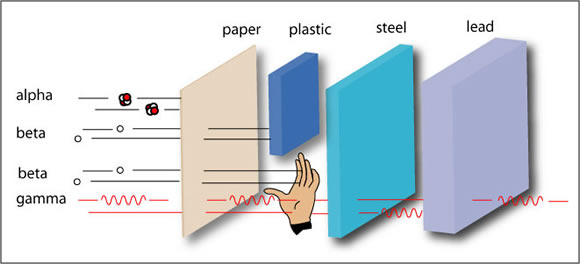


Post a Comment for "Quantum Definition Gamma Radiation"