Definition Of Mass Defect And Binding Energy
The binding energy of the system can appear. Every nucleon has to donate some of its mass to deliver the energy resulting in a mass defect.
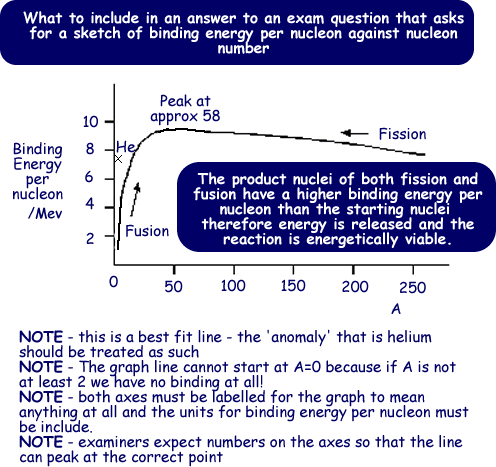
Nuclear Binding Energy And Mass Difference
The difference is a measure of the nuclear binding energy which holds the nucleus together.
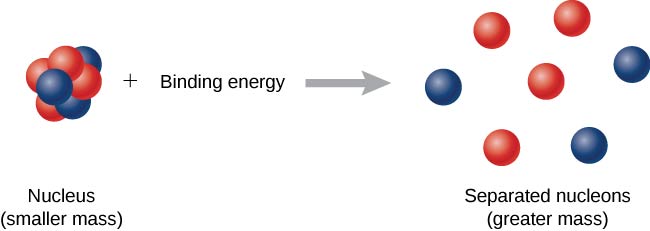
Definition of mass defect and binding energy. Im assuming that mass is converted to energy and the mass defect will increase. According to Einstein mass m and the energy E produced from it have the following relationship. In physics and chemistry a mass defect refers to the difference in mass between an atom and the sum of the masses of the protons neutrons and electrons of the atom.
The nucleus is the collection of protons and neutrons present inside the atom. As the protons are positively charged and neutrons are neutrally charged particles. These component parts are neutrons and protons which are collectively called nucleons.
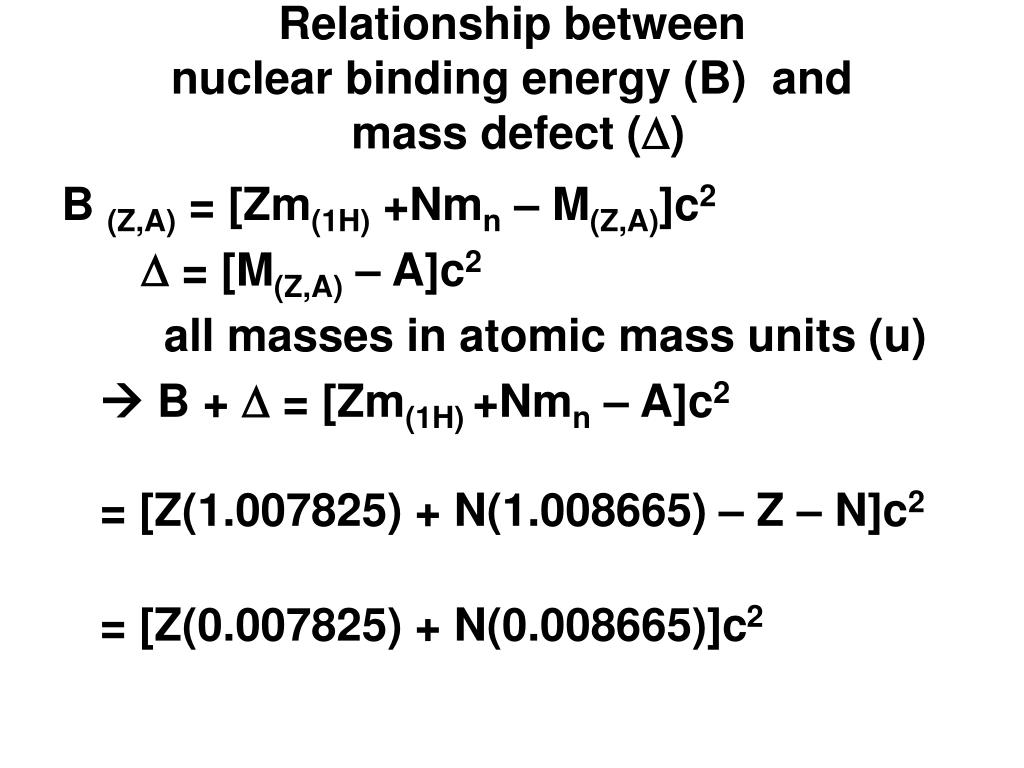
Here m A Z is the observed mass of the nucleus while Z m H N m n Z m A Z m A m is the sum of masses of the nucleons making up the nucleus and we assume that the proton and the neutron have equal mass m. From the rest mass we can determine the BE of the nucleus. According to the Einstein relationship Emc 2 this binding energy is proportional to this mass difference and it is known as the mass defect.
Your first formula Δ m A Z A c 2 is the binding energy which is equal to μ c 2 μ being the mass defect. The binding energy equation shows the energy equivalent to the mass defect. B inding energy is the energy required to split the nucleus of an atom into neutrons and protons while Mass defect is the difference bw the predicted mass and the actual mass of the nucleus of an Atom.
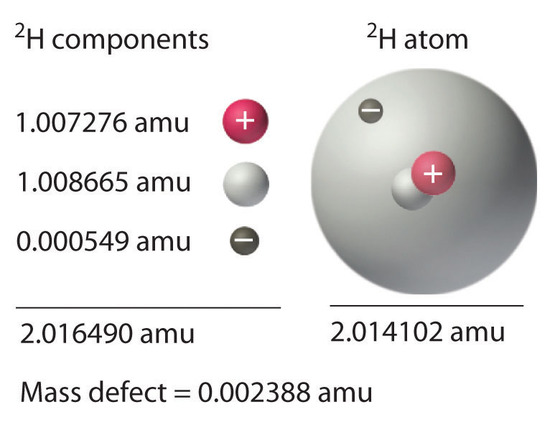
Mass defect is the missing mass and Einsteins equation E mc2 provides a relation of energy to this missing mass where. Mass defect- is the difference between the mass of the product and reactant when reaction takes place Binding energy is the mass defect in terms of energy. The mass of an atomic nucleus is usually less than the sum of the individual masses of the constituent protons and neutrons and this difference of mass is acknowledged as the mass defect and signifies the energy that is to be released if a nucleus form.
This is also termed binding energy. This mass is typically associated with the binding energy between nucleons. The energy that is required to disassemble the nuclei into separate protons and neutrons completely is known as the binding energy BE of the nucleus.
Mass was no longer considered unchangeable in the closed system. The difference in mass can be calculated by the Einstein equation Emc 2 where E is the nuclear binding energy c is the speed of light and m is the difference in mass This missing mass is known as the mass defect and represents the energy that was released when the nucleus was formed. Thus we expect that mass of the nucleus will be the same as the sum of individual masses of neutrons and protons.
The binding energy of the nucleus is related to the mass defect of the nucleus. Binding Energy is also defined as the energy required to break down a nucleus into its component nucleons. So that means you would have to put in energy to seperate the atom since both of the products require more.
The same amount of energy would be needed to break the atom into its constituent particles and the energy equivalent of the mass defect is therefore a measure of the binding energy of the nucleusThe mass defect can then be written Δ M Z m H A Z m n M Z A. Nuclear binding energy curve. Mass Defect and Binding Energy An atom comprises a nucleus at the center and electrons revolving around it in an orbital fashion.
The missing mass is the energy released by the formation of the atomic nucleus. Nuclei constitute of Protons and Neutrons Combined called nucleons. Binding energy of nucleus - definition Nuclear binding energy is the energy that would be required to disassemble the nucleus of an atom into its component parts.
When Nuclear fission of uranium occurs the binding energy of the two products is higher and so the overall binding energy is higher than it was before. Relation in mass defect and binding energy of the nucleus according to Einstein if the material is destroyed then energy is produced. Binding Energy is expressed in terms of kJmole of nuclei or MeVsnucleon.
The above formula can be used for calculation of mass defect and energy calculations. Compared Alpha Fission decay 20654 MeV MeV 18.
21 6 Energy Changes In Nuclear Reactions Chemistry Libretexts

Important Questions For Cbse Class 12 Physics Mass Defect And Binding Energy

Binding Energy And Mass Defect Definition Examples Diagrams

Mass Defect Binding Energy 1 Of 7 An Explanation Youtube

10 3 Nuclear Binding Energy Physics Libretexts

A Nucleus Is More Than Just Mass Ppt Video Online Download
Difference Between Binding Energy And Mass Defect
How To Calculate The Binding Energy Per Nucleon Quora

Mass Defect And Binding Energy Ib Physics Youtube
Ppt Relationship Between Nuclear Binding Energy B And Mass Defect D Powerpoint Presentation Id 699522

Ppt 26 1 Properties Of Nucleus 26 2 Binding Energy And Mass Defect Powerpoint Presentation Id 1596224
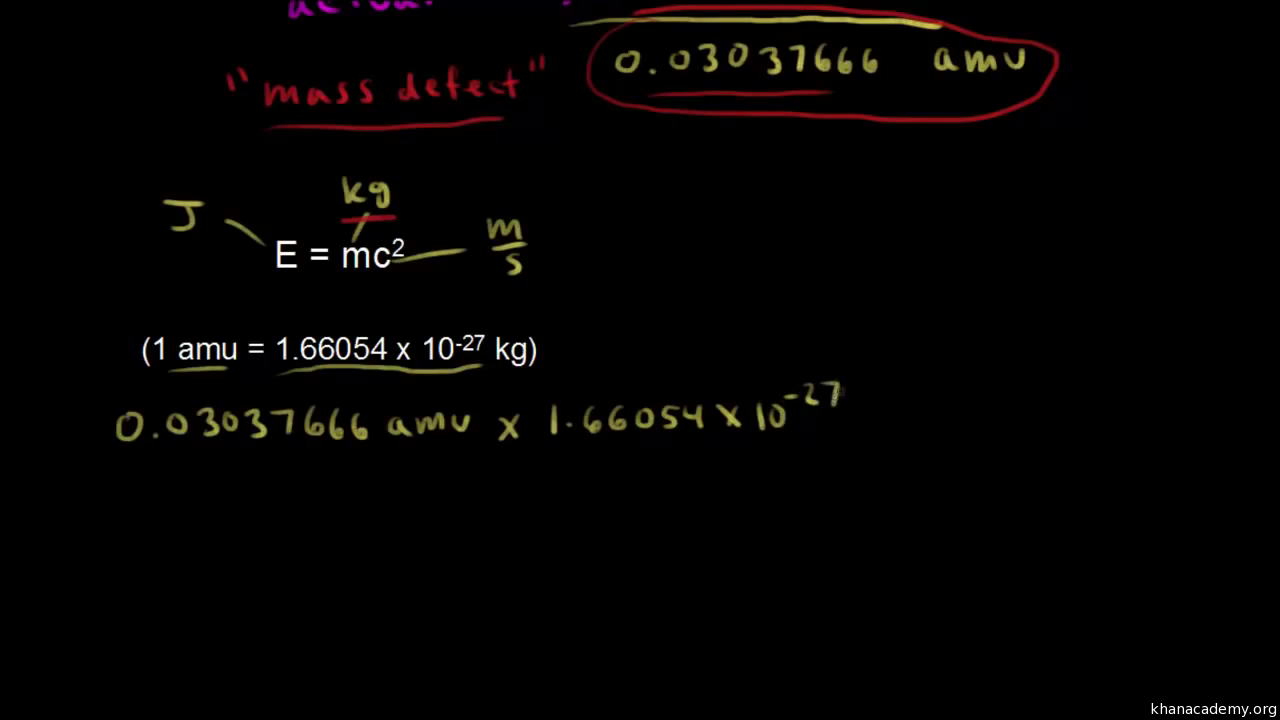
Mass Defect And Binding Energy Video Khan Academy

Properties Of Nucleus 26 2 Binding Energy And Mass Defect Unit 26 Nucleus Is Defined As The Central Core Of An Atom That Is Positively Charged Ppt Download
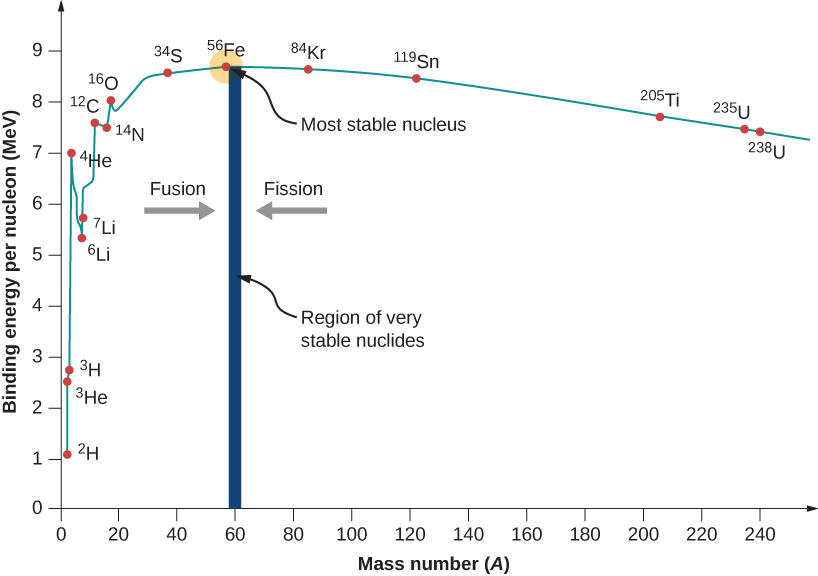
Nuclear Binding Energy University Physics Volume 3

Nuclear Binding Energy Per Nucleon Mass Defect Problems Nuclear Chemistry Youtube
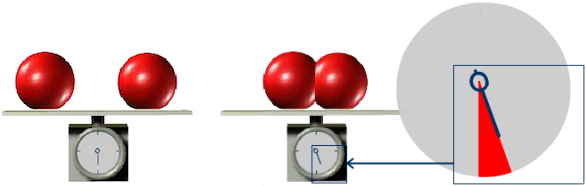
E Mc2 And Binding Energy From Einstein Light
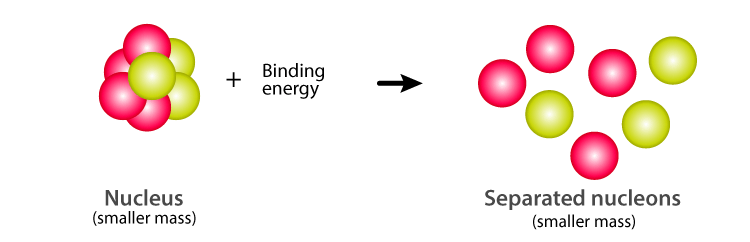
Nuclear Binding Energy Definition Formula Explanation

Mass Defect And Binding Energy Video Khan Academy

Mass Defect And Binding Energy In Hindi Youtube
Post a Comment for "Definition Of Mass Defect And Binding Energy"