Definition Of Biological Yield
Biological yield is the real content of dry matter considering the fresh weight and the calculated water content. This definition of biofertilizer does not comply with the above mentioned definition proposed by Okon and Labandera-Gonzalez 1994 and is a contraction of the term biological fertilizer.

Electroforesis De Dna Biology Units Science Lesson Plans Science Lessons
Definition of the term chemical biological radiological nuclear or high-yield explosives incidents per official documentation of the United States Department of Defense.
Definition of biological yield. Production of a biological resource such as timber or fish under management procedures which ensure replacement of the part harvested by regrowth or reproduction before another harvest occurs Other Words from sustained yield Example Sentences Learn More About sustained yield. Biological Yield The total dry matter produced per plant or per unit area. It is calculated to be the experimental yield divided by theoretical yield multiplied by 100.
Its effect when manifested is to bring about a change of some kind. Maximum Yield Explains Bioactive Compounds. Alcohol would be a bioactive compound as it is not required to sustain life but does have an effect on the body.
The total dry matter produced by a crop is known as biological yield and a fraction of the biological yield which is useful for human is known as economic yield. To produce or furnish as return this soil should yield good crops. Grain yield increases to a maximum value but declines as density is further increased.
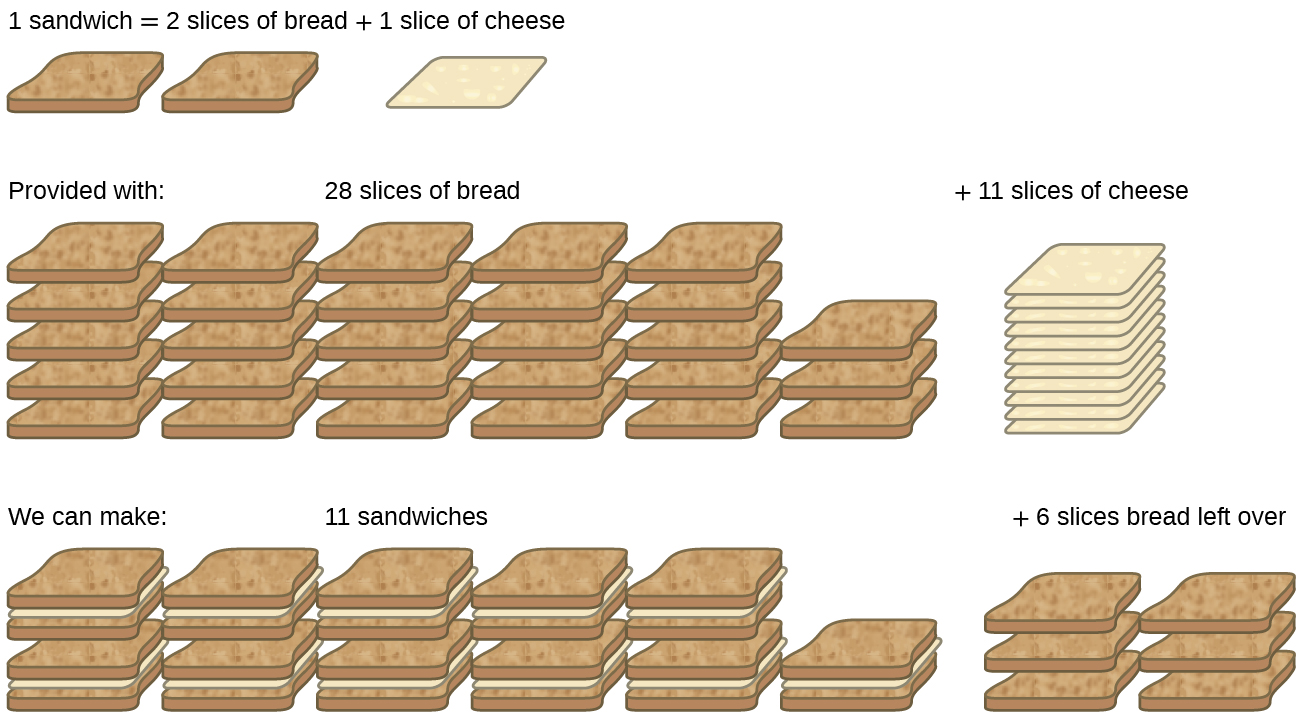
Yield Estimation of Field Crops Yield estimation of various crops have been attempt with the use of yield components. Growing growth ontogenesis ontogeny maturation development - biology the process of an individual organism growing organically. Usually percent yield is lower than 100 because the actual yield is often less than the theoretical value.
He proposed an indicator of. Biological yield biological zone biological-chemical process biological-chemical warfare capability biological-statistical theory biological-value protein biological-weapon biological related to or caused by biological organisms biologically biologically accumulative. 71 Leafy Top Fleshy Root Leaves Stalk Grain Roots Leaves Stems Seed Roots Crop Plant Part Sugar beet Corn Alfalfa Biological Yield If sold or fed becomes economic yield Biological Yield Biological Yield.
Biohydrogen is defined as the biofuel or the source of energy that uses living microorganisms to convert hydrogen via biological processes like fermentation and photolysis in a specialized container or a bioreactor. To bear or bring forth as a natural product especially as a result of cultivation the tree always yields good fruit. A commercial biological filter often comes in the form of a box that contains a sponge or hair curler-like material where beneficial bacteria can grow and feed on the impurities of the water as it flows through the box.
They can stimulate cause anxiety or intoxicate. It includes all of the leaf stem grain and root dry matter produced by the plant. Energy occurs in several forms-potential as in a compressed spring or a mass in a high position kinetic as in motion chemical as in petroleum and nuclear as in the binding forces of the atomic nucleus.
Furnish as profit or interest a bond that yields 12 percent. Bioactive compounds can cause numerous effects. To produce as return from an expenditure or investment.
One may define yearly ecological yield for a fixed ecological product as follows. Later in 2005 Fuentes-Ramirez and Caballero-Mellado defined a biofertilizer as a. Maximum Yield Explains Biological Filter.
An emergency resulting from the deliberate or unintentional release of nuclear biological radiological or toxic or poisonous chemical materials or the detonation of a high-yield explosive. Biological yield increases with density to a maximum value determined by some factor of the environment and at higher densities tends to remain constant provided there are no interfering factors such as lodging. A purely biological unfolding of events involved in an organism changing gradually from a simple to a more complex level.
If the actual and theoretical yield are the same the percent yield is 100. The capacity of a body to do work. The yield is the amount of the product which may be removed from the ecosystem so that it is capable of recovering in one year.
Bioactive compounds in foods are those that are not required to sustain life but still have an effect on the organism.
What Is Biology Definition Branches Books And Scientists The Engineering Projects

Percent Yield Easy Science Teaching Chemistry Ap Chemistry

What Is Foliar Feeding Definition From Maximum Yield Feeding Nutrient Plants

Gmo Vector Illustration Infographic Scientific Dna Diagram Dna Activities Dna Project Dna Artwork

Yield And Yield Components Of Various Wheat Cultivars As Affected By Different Sowing Dates Scialert Responsive Version

Actual Vs Theoretical Yield Definitions Formulas Study Com

Example Of Theme Sub Theme Research Methods Analysis Phd

What Is Rooting Hormone Definition From Maximum Yield Rooting Hormone Propagating Plants Plant Growth

What Is A Dioecious Plant Definition From Maximumyield Female Reproductive System Reproductive System Plants

What Is A Plasmid Origin Of Replication Molecular Biology Molecular Genetics

What Is Boron B Definition From Maximumyield Plant Growth Boron Definitions

Difference Between Mendel S First And Second Law Genetics Activities Study Biology Teaching Biology

Legume Inoculation For Organic Farming Systems Eorganic In 2021 Farming System Soil Garden Gifts

Basal Fasted State Metabolism Biochemistry Physiology Medical Studies

What Is A Perennial Definition From Maximumyield Perennials Types Of Plants Definitions

What Are Cytokinins Definition From Maximumyield Cell Division Biology Plants Stimulation

Biomedical Open Access Journals Nutrition Biomedical Science Biomedical Science Journal

Post a Comment for "Definition Of Biological Yield"