Definition Of High Latitude Climate
Up to 10 cash back Middle latitude climates. This type of climate is called arctic in the Northern Hemisphere Antarctic in the Southern Hemisphere or simply polar.
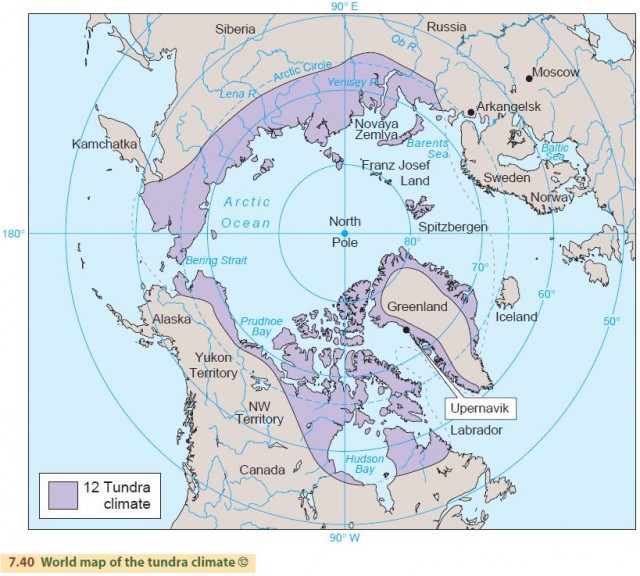
High Latitude Climates Group Iii
The Equator is the line of 0 degrees latitude.

Definition of high latitude climate. There is no exact definition where that boundary lies but the high latitude is situated around the 60 magnetic latitude and higher. Latitude is the measurement of distance north or south of the Equator. The horse latitudes lie within this range.
B - Dry Climates. A regions elevation proximity to the ocean or freshwater and land-use patterns can all impact climate. These lines are known as parallel s.
The temperature goes down roughly 4 degrees Fahrenheit for every 1000 feet you climb. Altitude affects climate in that the higher up you get the more the temperature drops. Geographically part of the north and south temperate zones they cover the latitudes between 2326113 and approximately 35 in the northern and southern hemispheres.
Consequently a latitude remote from the equator. The humid subtropical climate is generally located between 25 and 35 latitude on the east sides of continents. High latitude oceans are crucial components of the global climate system.
In these climates all months have average temperatures greater than 18 degrees Celsius. It is measured with 180 imaginary lines that form circles around the Earth east-west parallel to the Equator. Climates are impacted by several factors including latitude elevation and distance to large bodies of water so differences exist between each high altitude climate.
The middle latitudes between the 50 and 60 magnetic latitude and everything below the 50 magnetic latitude is considered to be in the category of low latitude. It is primarily influenced by the warm maritime tropical air masses on the west sides of the subtropical oceanic high-pressure centers. In the Köppen climate system these climates grade off toward temperate climates equator-ward where winters are less severe and semi-arid climates where precipitation becomes inadequate for tall-grass prairies.
Tropical moist climates extend northward and southward from the equator to about 15 to 25 degrees of latitude. Annual precipitation is greater than 1500 mm. Although there is no specific definition for high latitude climate these environments typically exist above 60 degrees of latitude.
Climate features also include windiness humidity cloud cover atmospheric pressure and fogginess. The subtropical zones or subtropics are geographic and climate zones located to the north and south of the tropical zone. Landscape can also help define regional climate.
ABSTRACT Aim High-latitude coral reef communities composed of tropical subtropical and temperate species are heralded as climate change refuges for vulnerable tropical coral reef species giving them high but as yet unrealized conservation. One designated by the higher figures. Subtropical climates are often characterized by hot summers and mild winters with infrequent frost.
Altitude is the subjects distance from the sea. A circle of latitude is an imaginary ring linking all points sharing a parallel. Latitude plays a huge factor in determining climate.
At mid to high latitudesin the upper part of the troposphereabove roughly 5 km the mean windflow exhibits a broadly west-to-east motion - this applies in both hemispheres. The middle latitudes are regions of great atmospheric variability and a zone of major eddies in the atmosphere with the climate dominated by a succession of cyclones and anticyclones normally moving from west to east. In these climates all months have average temperatures greater than 64F 18C and annual precipitation greater than 59.
High-Latitude Climates Group III By and large the high-latitude climates are climates of the northern hemisphere occupying the northern subarctic and arctic latitude zones. Steve HicksCC-BY 20. That part of the earths surface near either pole esp.
They play a disproportionately large role in the heat balance of the planet are home to some of the strongest carbon fluxes both into and out of the oceans and are acting as a canary in the coal mine of climate change. The fall of temperature toward the poles occurs not in a uniform manner but with the strong thermal. This is why a lot of high-up places such as mountaintops often get snow for most of the year when other places do not no matter how low the temperature drops.
A - Tropical Climates Tropical moist climates extend north and south from the equator to about 15 to 25 latitude. But they also extend southward into the midlatitude zone as far south as about the 47th parallel in eastern North America and eastern Asia.

Features Of The Southern Hemisphere High Latitudes Showing Present Day Download Scientific Diagram

Weather Climate Crash Course Kids Video Https Www
Climate Systems And Change Earth Science

High Latitude Climates Group Iii
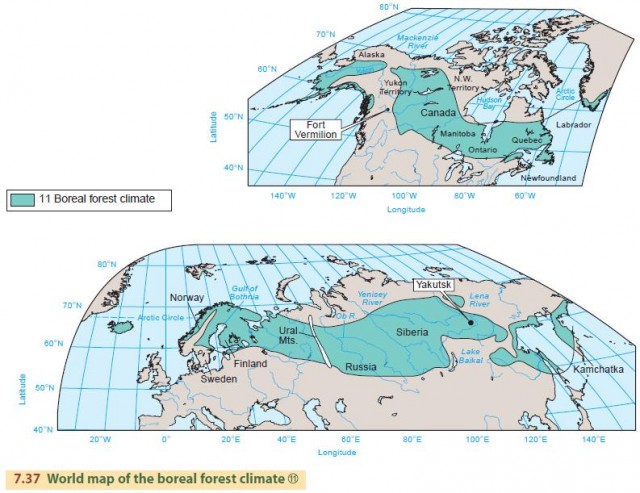
High Latitude Climates Group Iii

World Climate Regions Low Latitudes Flashcards Quizlet
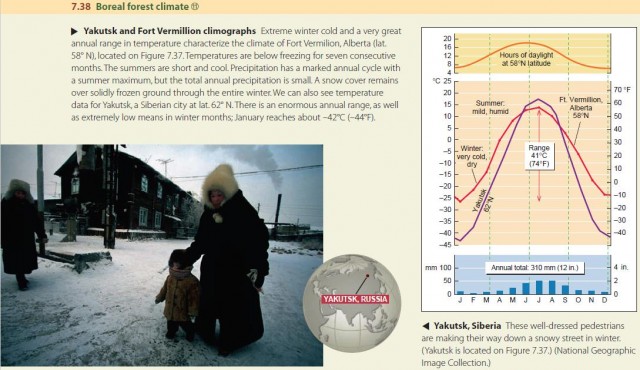
High Latitude Climates Group Iii

Journey North Global Climate And The Seasons

Humid Continental Climate Types For Kids

World Climate Regions Low Latitudes Flashcards Quizlet

The 7 Major Factors That Affect Climate Ppt Video Online Download

Highland Climate Meteorology Britannica
High Latitude Climate Coastal Systems Group
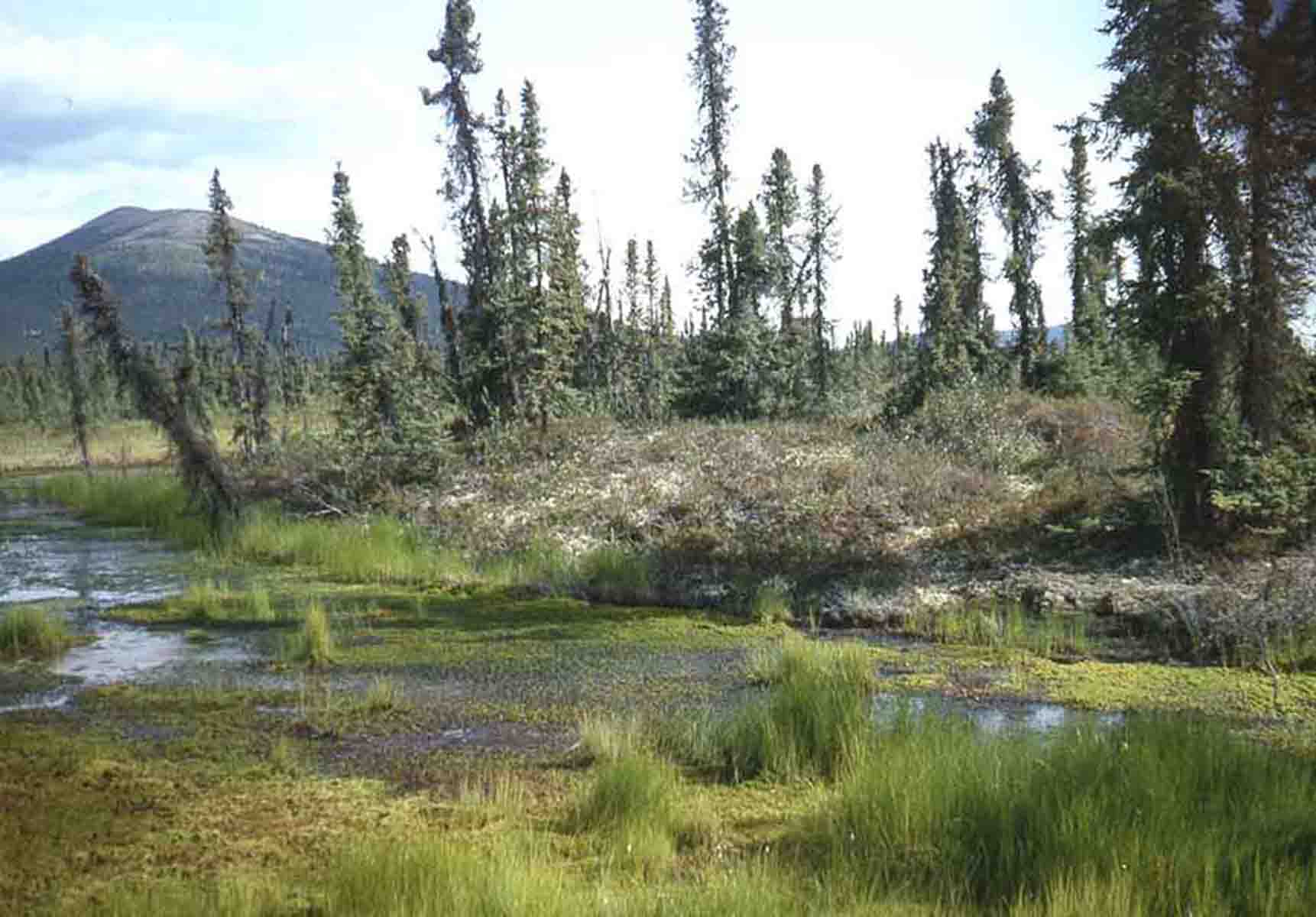

High Latitude Climate Change Alaska Nature And Science U S National Park Service


Post a Comment for "Definition Of High Latitude Climate"