Definition Of Us Federalism
The definition of dual federalism primarily concerns the balance of power between the two governing. Federalism is the oldest form of government in the United States.

Principles Of Government Sort Activity Free Social Studies Middle School 6th Grade Social Studies Constitution Activities
In a federal system power is shared by the national and state governments.

Definition of us federalism. The Founders wrote the Constitution so that it would always remain open to interpretation. Federalism is the sharing of power between a national government and the states that reside within its borders instead of one or the other having all the authority. The timelessness of the Constitution and the strength of the arguments presented by The Federalist Papers offer a clue to its endurance.
As defined by the United States Constitution federalism is a fundamental aspect of American government whereby the states are not merely regional representatives of the federal government but are granted independent powers and responsibilities. The United States government functions according to the principles of federalism. 1 day agoA federal judge in Arizona tossed out the Trump Administrations limited definition of federally-protected US water bodies saying that it has fundamental substantive flaws that cannot be.
Federalism attempts to reconcile a desire for unity and communality on certain issues with a desire for diversity and autonomy on others see Figure 21. Constitution gives certain powers to the federal government other powers to the state governments and yet other powers to both. Federalism is a compromise meant to eliminate the disadvantages of both systems.
Its distinctive feature is a relationship of parity between the two levels of government established. Federalism is the theory or advocacy of federal principles for dividing powers between member units and common institutions. 1 a often capitalized.
Federalism is a mixed or compound mode of government that combines a general government the central or federal government with regional governments provincial state cantonal territorial or other sub-unit governments in a single political system. We have witnessed a significant shift in the balance and boundaries between these two governments since the turn of the millennium. States have their own legislative branch executive branch and judicial branch.
Federalisms Ambiguity has contributed to its longevity. Federalism mode of political organization that unites separate states or other polities within an overarching political system in a way that allows each to maintain its own integrity. In the United States the US.
Political system evolved from the philosophy of federalism. The Constitution designates certain powers to be the domain of a central government and others are specifically reserved to the state governments. Federalism is a system of government in which power is divided between a national federal government and various regional governments.
Israel compare centralism. The question of whether federalism is suitable for a given country and if so what form federal institutions should take and to what extent the federal. The distribution of power in an organization such as a government between a central authority and the constituent see constituent entry 2 sense 1 units under our system of federalism states bear the primary responsibility for defining and controlling criminal behavior W.
Federalism is defined as a system of government where there is one strong central controlling authority or the principles of a political party called the Federalists. Relationships among state governments within constitutional restrictions spelled out in Article IV of the US. Federalism is a basic concept of American government in which the states are not merely regional representatives of the federal government but are granted independent powers and responsibilities.
The central or federal government and regional governments provincial state cantonal territorial or other sub-unit governments share the governing power. Horizontal Federalism Definition of Horizontal Federalism In the areas of the US. Federalism is a system of government in which power is divided between a national federal government and various state governments.
The term federalism refers to the political understanding or system where ultimate authority is shared between the state or regional governments and the central government. Learn more about the history and characteristics of federalism in this article. Federalism is a system of government in which entities such as states or provinces share power with a national government.
Federalism is a political system that believes each state under a central government can have its own laws and customs while still sharing unified laws customs and currency. Constitution and Federalism Horizontal Federalism has the following meaning. An example of federalism is when there is one strong main government for the entire United States that has a lot of power and the individual states dont have much power.

Understanding Federalism In The Context Of The U S Constitution No 86 Lecture Youtube

American Federal Government Federalism What Is This Federalism
Federal Democracy 50 Shades Of Federalism

Why Is Federalism Important The Freeman Online

Defining Democracy Federalism Renew Democracy Initiative
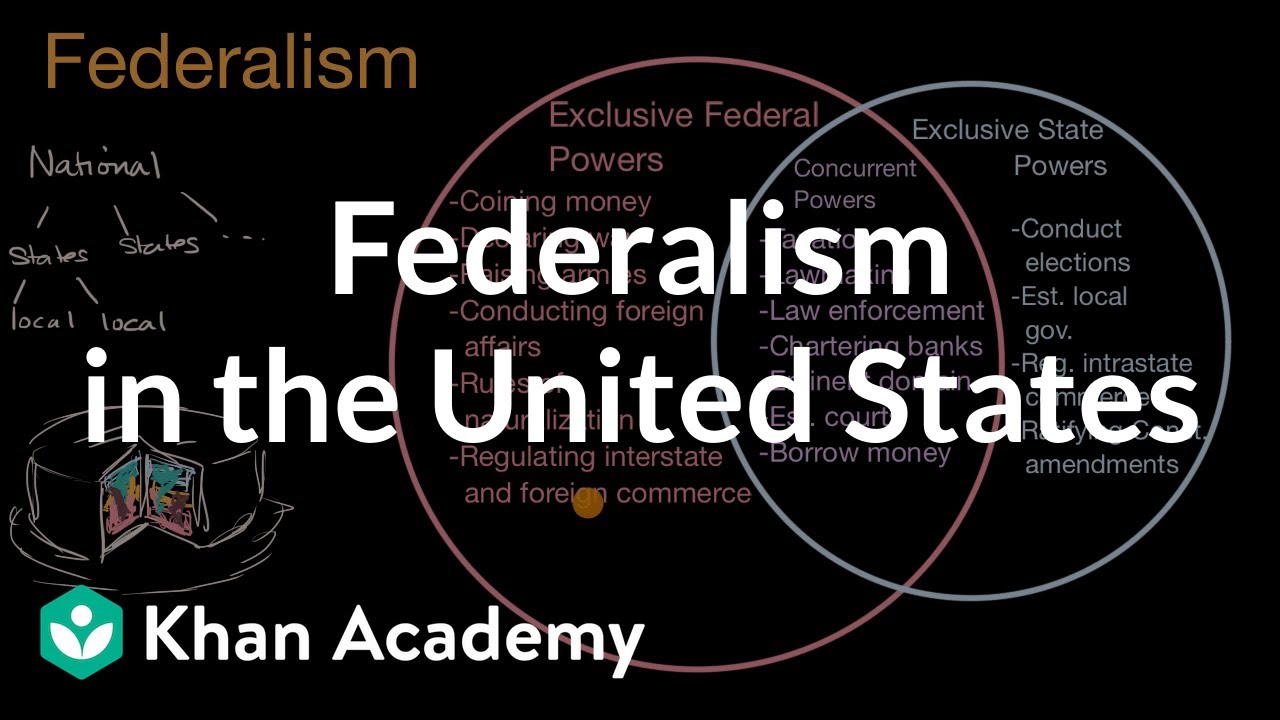
Federalism In The United States Video Khan Academy

Federalism Basic Structure Of Government United States Government
What Is Federalism Federalism Is A Form Of
Week 04 Gov A Federalism Quiz 2018 Fall Government

Federalism The Relationship Between State Governments And The Federal Government This Sp Teaching Government Government Lessons Social Studies Middle School

Federalism How Should Power Be Structurally Divided United States Government

Advanced Placement United States Government Politics Federalism

Federalist Vs Anti Federalist On Constitution Social Studies Middle School Social Studies Classroom Teaching History
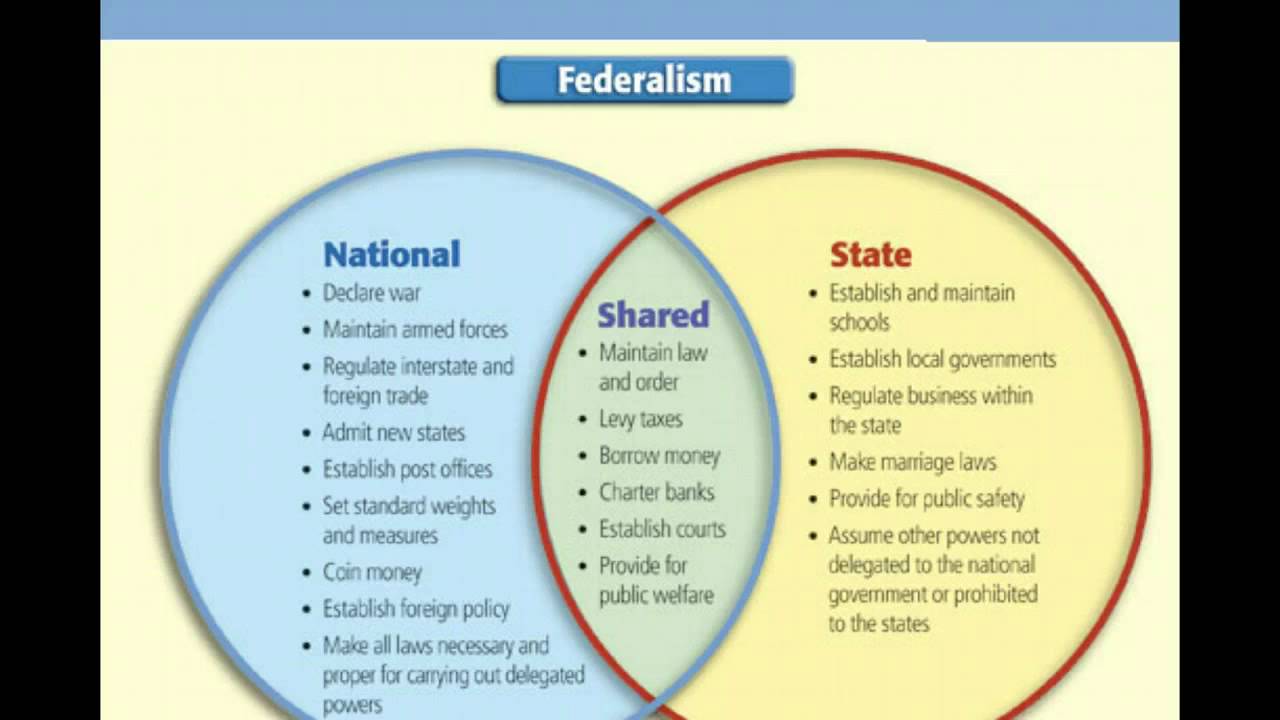
Chapter Five U S Federalism U S Government And Politics In Principle And Practice




Post a Comment for "Definition Of Us Federalism"