Definition Disaster Hazard Vulnerability Resilience Risks
Definitions of hazard vulnerability risk and disasters. In recent years there has been growing recognition that disaster risk cannot be reduced by focusing solely on physical hazards without considering factors that influence socio-economic impact.
Realization of a risk Strengths.

Definition disaster hazard vulnerability resilience risks. Presents contextual factors that improve the general understanding of how communities plan for and manage disasters and build community resilience. Potential threat to humans and their welfare vulnerability. The paradigm developed here focuses attention on facilitating recovery and growth in professionals.
Vulnerability sensitivity resilience adaptation adaptive capacity risk hazard coping range adaptation baseline and so on IPCC 2001. It aims to reduce the physical and economic impacts of an event and limit the human material economic and environmental costs of an emergency or disaster. The Pressure and Release model PAR and the complex inter-relationships between the hazard and its wider context.
Disaster Vulnerability and Resilience. The relationships between these terms are often unclear and the same term may have different meanings when used in different contexts and by different. Definition of a natural hazard and a disaster the importance of vulnerability and a communitys threshold for resilience the hazard risk equation.
It combines the likelihood or possibility of a disaster happening and the negative effects that result if the disaster occurs. This provides evidence to inform decisions relevant to Health EDRM. Resilience and vulnerability is discussed at dispositional cognitive and organisational levels.
The hazards of concern to disaster risk reduction are of natural origin and related environmental and technological hazards and risks. Measures taken to prevent avoid or reduce loss Resilience. Ability to recover prior state or achieve desired post-disaster state.
At risk property and population Resistance. How-ever when disaster is defined as a hazard this allows mem-bers of all stakeholder groups to remain blameless for social. In disasters there are three broad areas of risk to health.
Vulnerability Exposure Resistance Resilience Exposure. 2003 using the model of disaster places DROP model Disaster Resilience of Place suggests that social vulnerability is a multidimensional concept that helps to identify those characteristics and experiences of communities and individuals that allow them to respond and recover from natural disasters and in this sense it is not disconnected from the concept of resilience. Disaster resilience is the ability of individuals communities organisations and states to adapt to and recover from hazards shocks or stresses without compromising long-term prospects for development.
116 Vulnerability and Resilience in Natural Disasters should protect them from risk of disaster Quarantelli Lagadec and Boin 2007 perhaps because some people believe that nature can be controlled and managed. The susceptibility to the damaging impacts of hazards and resilience. Therefore it is necessary to have good information on the costs of natural disasters.
Disaster research often strives to show that these risks affect morbidity mortality or well-being in some way. If vulnerability rises poverty lack of preparedness lack of awareness of potential hazards. The UN and Disaster Risk Reduction.
Risk is hazard multiplied by vulnerability less the capacity of the population to cope. A hazard can be defined as a dangerous phenomenon substance human activity or condition that may cause loss of life injury or other health impacts property damage loss of livelihoods and services social and economic disruption or environmental damage. Since the beginning of the 1990s the United Nations has been promoting efforts to change the paradigm of disasters advocating for the incorporation of disaster risk reduction efforts worldwide as a way to reduce the effects of natural hazards on vulnerable communities.
With the shift from a hazard-centered disaster paradigm to one that places emphasis on vulnerability and resilience disasters triggered by natural hazards have begun to. The ability to recover have become popular concepts in natural hazard and risk management. Vulnerability and exposure are key determinants of disaster risk and help explain why non-extreme physical events and chronic hazards can also lead to extreme impacts and disasters while some extreme events do not.
These are estimated with a risk analysis. Probability of hazard occurrence disaster. Adger et al 2002.
Exposure and susceptibility to losses risk. RISK Risk is generally defined as the expected impact caused by a particular phenomenon. Burton et al 2002.
Theory Modelling and Prospective 8 risk to derive from the conjunction of vulnerability with hazard so that increases in either can worsen disaster risk and. Offers a systematic examination of the concepts of hazards vulnerabilities and disaster resilience focusing on communities in Florida. Level of complexity and explanation.
According to the Hyogo Framework for Action UNISDR 2005 disaster resilience is determined by the degree to which individuals communities and public and private organisations are capable of. The hazard that can cause damage exposure to the hazard and the vulnerability of the exposed population see also Chapters 13 and 25 1. Conceptual frameworks that account for this kind of vulnerability must be developedCutter et al.

What Is Disaster Resilience Gsdrc

Disaster Hazards Vulnerability Capacity Disaster Risk Ppt Download

Natural Hazards Natural Hazards 101 The Concept Of Risk
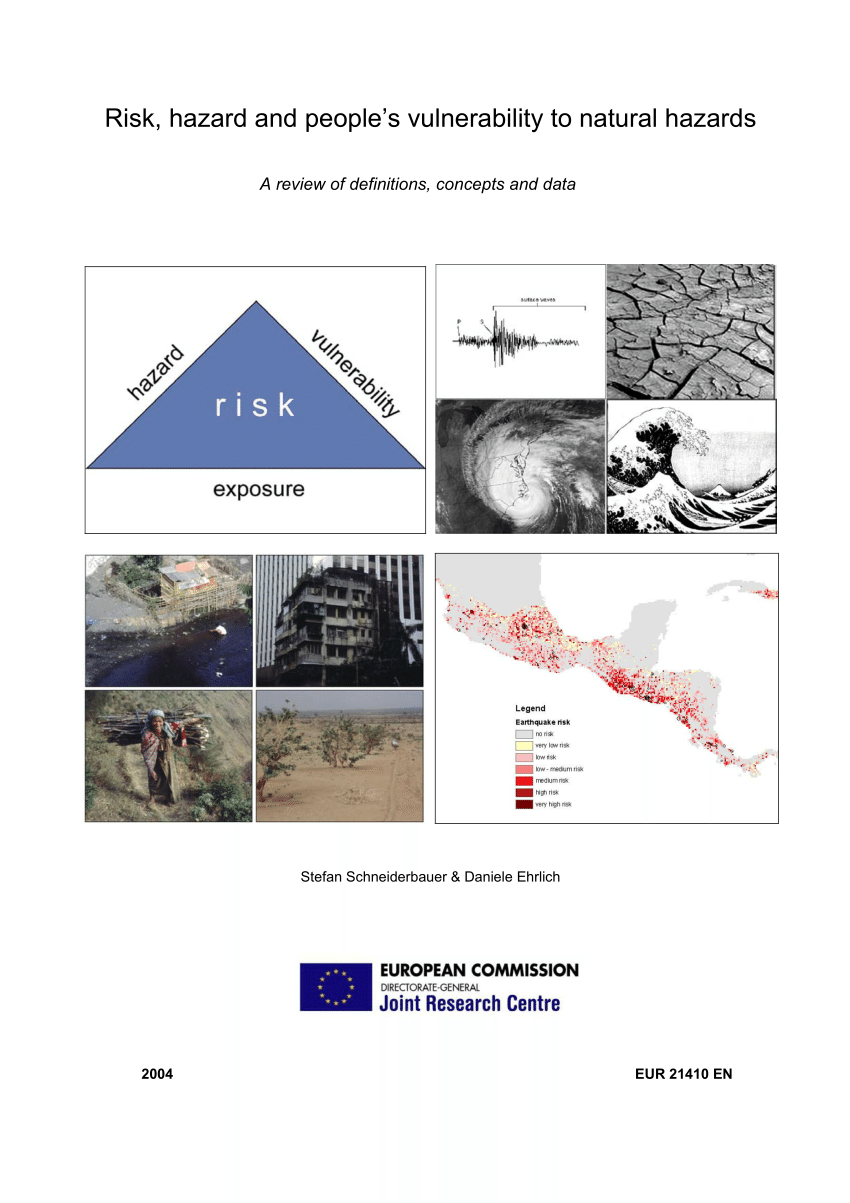
Pdf Risk Hazard And People S Vulnerability To Natural Hazards A Review Of Definitions Concepts And Data

Disaster Hazards Vulnerability Capacity Disaster Risk Ppt Download
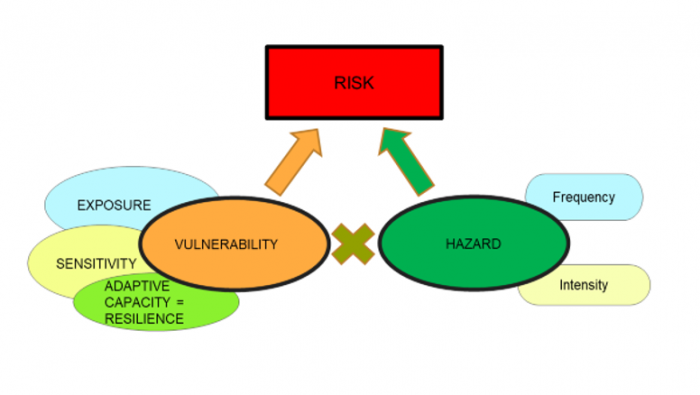
Vulnerability S Three Dimensions Introduction Coastal Processes Hazards And Society

The Disaster Risk Reduction Drr Diagram Executive Functioning Skills Social Development Disasters
Understanding Risk Vizrisk Understanding And Communicating Disaster Risk

1 Emergency Assistance Vs Hazard Risk And Disaster Management Download Table
Living With Risk A Global Review Of Disaster Reduction Initiatives Preliminary Version Chapter 2 Risk Awareness And Assessment 2 3 Risk Assessment

No 38 Human Activity Economic Activity Environmental Factors
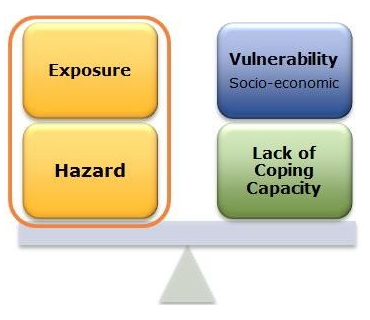
Inform Inform Risk Methodology
5 1 Introduction To Exposure Vulnerability And Risk Assessment Charim

Urban Climate Change Vulnerability And Risk Assessment Framework Download Scientific Diagram


Post a Comment for "Definition Disaster Hazard Vulnerability Resilience Risks"