Describe Biological Definition Of Homeostasis
Homeostasis in a general sense refers to stability balance or equilibrium. Extracellular fluid pH homeostasis.

7 8 Homeostasis And Feedback Human Biology
Homeostasis refers to the bodys ability to maintain a stable internal environment regulating hormones body temp water balance etc.
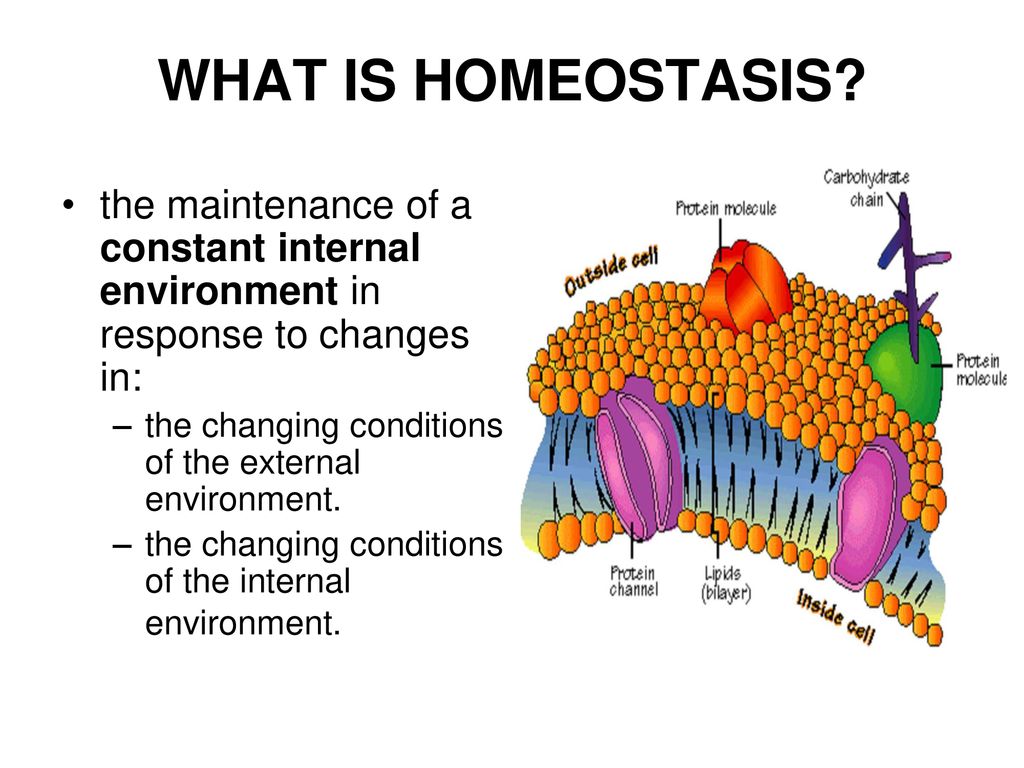
Describe biological definition of homeostasis. If its unsuccessful it results in a disaster or death of the organism. Maintaining a stable internal environment requires constant monitoring andadjustments as conditions change. Positive and negative feedback loops are essential for homeostasis in the human body.
Homeostasis means to maintain dynamic equilibrium in the body. Organismal homeostasis as originally defined by Cannon 6 refers to physiological mechanisms that maintain relatively constant the variables related to the internal milieu of the organism. It is a physiological mechanism that aims to prevent internal disruption and maintain balance.
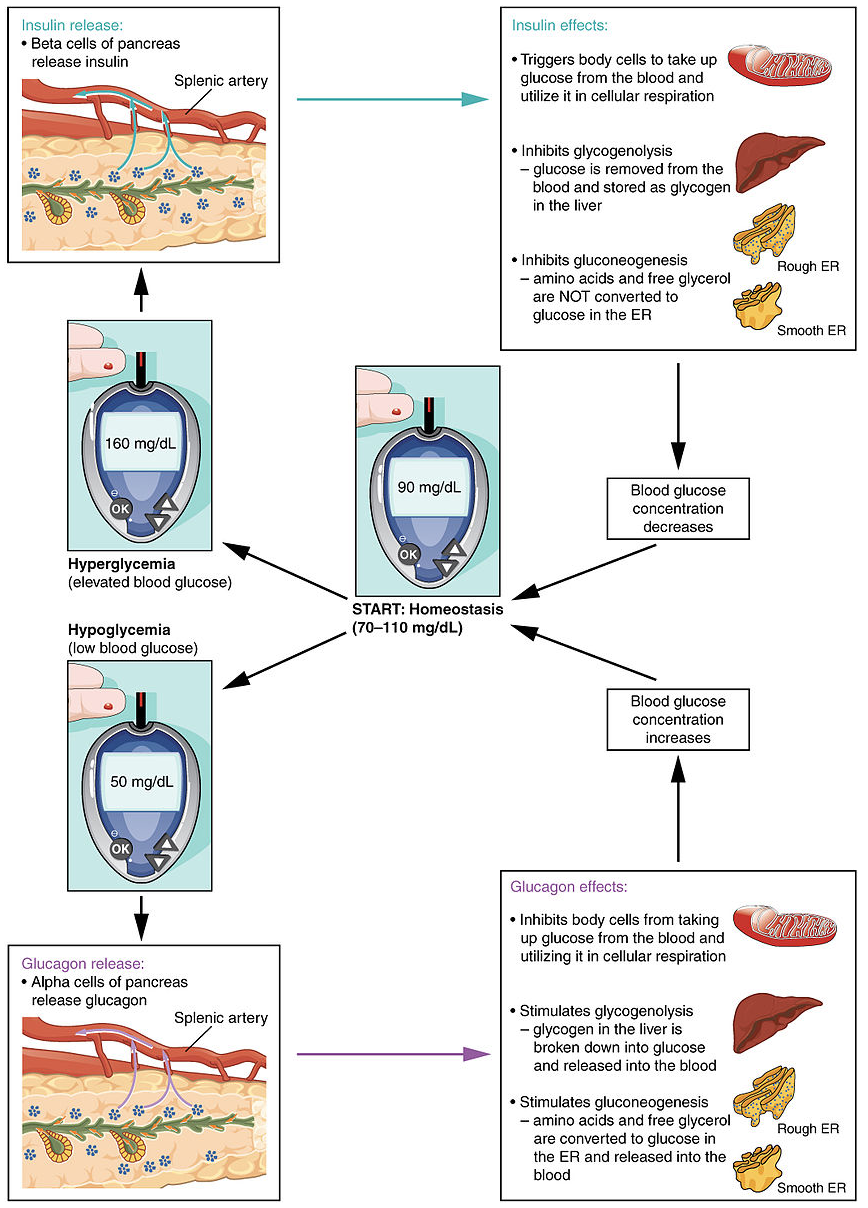
Blood oxygen content homeostasis. To date this term stands for the processes all the living beings employ in order to maintain the internal conditions they require for the survival. For example cells in the pancreas detect a rise.
This includes variables related to the entire ECF compartment. It is the bodys attempt to maintain aconstant internal environment. The original meaning of this word is same.
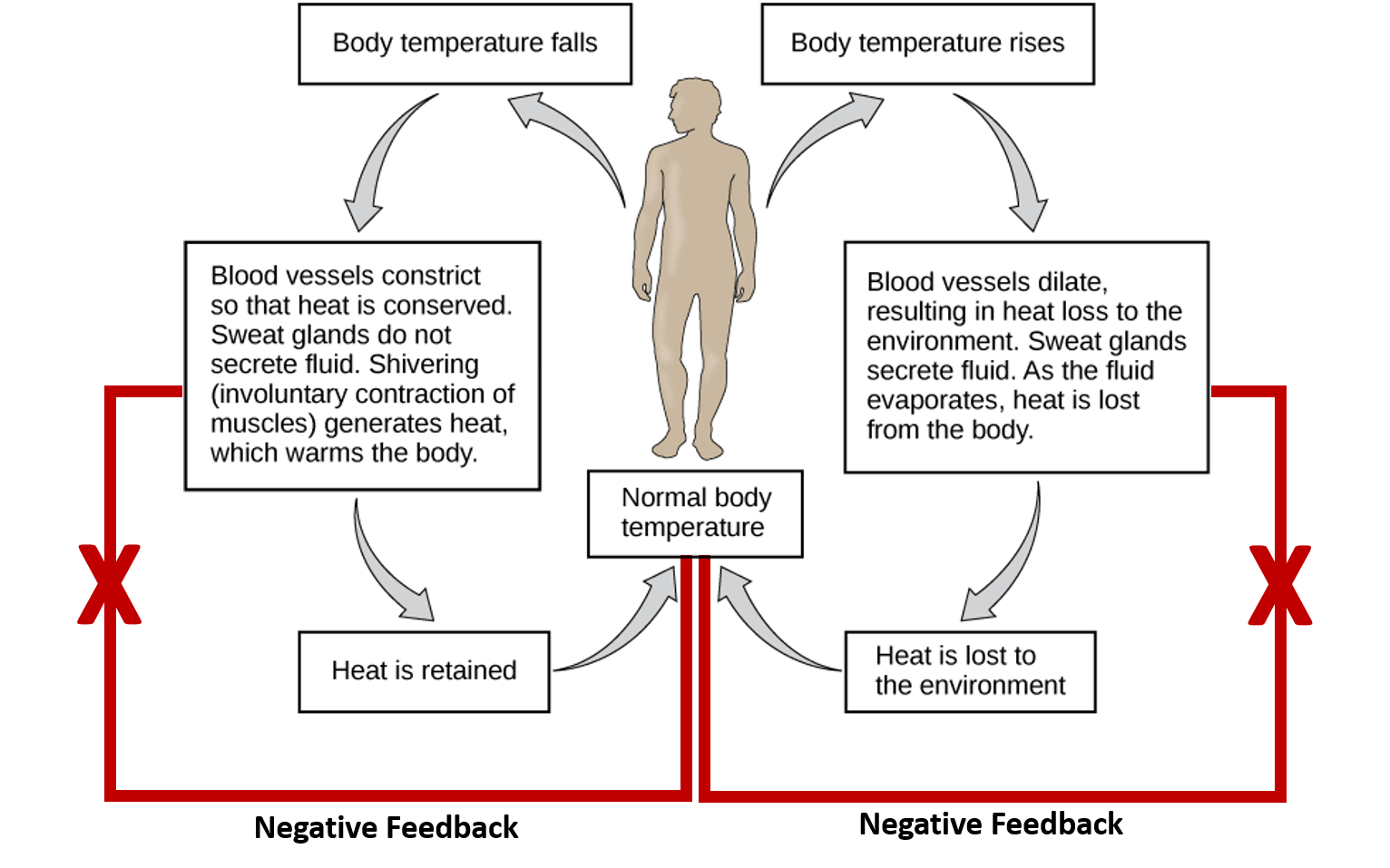
This adjusting of physiological systems within the body is called homeostaticregulation. Negative feedback loops act to reverse changes in the bodys physiological condition. This includes variables related to the entire ECF compartment.
The nervous system and hormones are responsible for this. Maintaining homeostasis requires that the body continuously monitors its internal conditions. Core body temperature homeostasis.
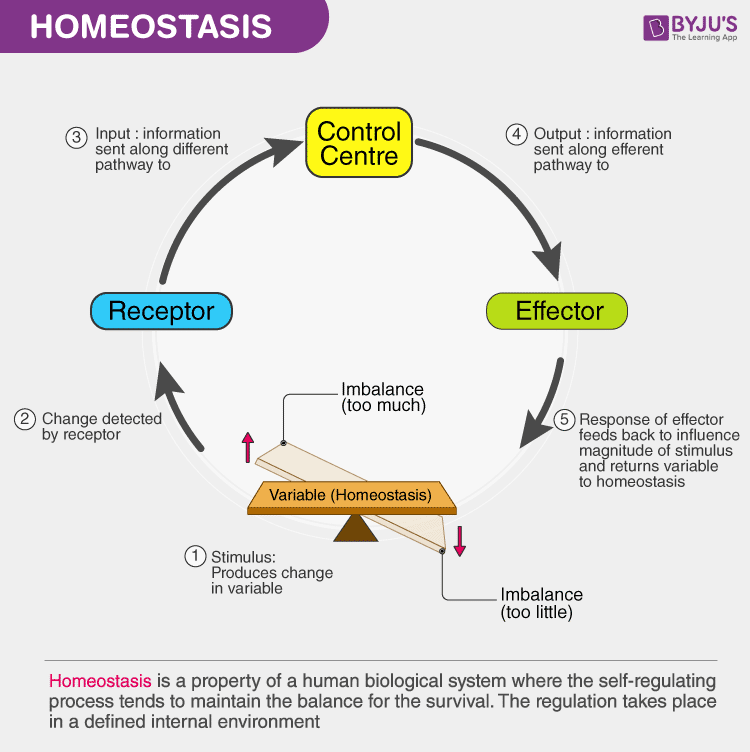
It is a unifying principle of biology. A more formal definition of homeostasis is a characteristic of a system that regulates its internal environment and tends to maintain a stable relatively constant condition of properties. They provide the controls needed to keep the effects of hormones and hormone chain reactions from spiraling out of control.
Homeostasis is one such character found specifically in life forms. Arterial blood pressure homeostasis. Homeostasis The principle of self-regulating information feedback by which constant conditions are maintained in a biological system such as the human body.
Homeostasis is the ability to maintain a constant internal environment in response to environmental changes it is a unifying principle of biology the nervous and endocrine systems control homeostasis in the body through feedback mechanisms involving various organs and organ systems. Homeostasis is any self-regulating process by which an organism tends to maintain stability while adjusting to conditions that are best for its survival. It is equilibrium because body functions are kept within specific ranges.
Plasma ionized calcium homeostasis. If homeostasis is successful life continues. One example of homeostasis is the concentration of carbon dioxide in the.
Other Examples of Homeostasis. Homeostasis is the ability to maintain a constant internal environment in response to environmental changes. In short homeostasis in biology.
The word homeostasis derives from Greek with home meaning similar and stasis meaning stable. Even an animal that is apparently inactive is maintaining this homeostatic equilibrium. When used as an adjective it is homeostatic.
Organismal homeostasis as originally defined by Cannon 6 refers to physiological mechanisms that maintain relatively constant the variables related to the internal milieu of the organism. Homeostasis is the ability to maintain a constant internal environment in response to environmental changes it is a unifying principle of biology the nervous and endocrine systems control homeostasis in the body through feedback mechanisms involving various organs and organ systems. The volume of body water homeostasis.
Homeostasis is an organism s process of maintaining a stable internal environment suitable for sustaining life. Homeostasis is the ability of living systems to maintain a steady and uniform internal environment to allow the normal functioning of the systems. The nervous and endocrine systems control homeostasis in the body through feedback mechanisms involving various organs.
The stability that the organism reaches is rarely around an exact point such as the idealized human body temperature of 37 C 986 F. Homeostasis is the maintenance of a constant internal environment. It is dynamic because it is constantly adjusting to the changes that the bodys systems encounter.
In other words homeostasis refers to stability in the vital biological environments within the bodies of the living things. It is the tendency to achieve equilibrium against various natural and environmental factors. Homeostasis is essential to life and applies to thousands of bodily parameters.

What Does Homeostasis Mean Quora
Ch103 Chapter 8 Homeostasis And Cellular Function Chemistry
What Is Homeostasis Meaning Definition And Examples
21 2 Homeostasis And Disease Biology Libretexts

10 7 Homeostasis And Feedback Biology Libretexts

Homeostasis Biology Ppt Download

Homeostasis Steady States And Equilibria
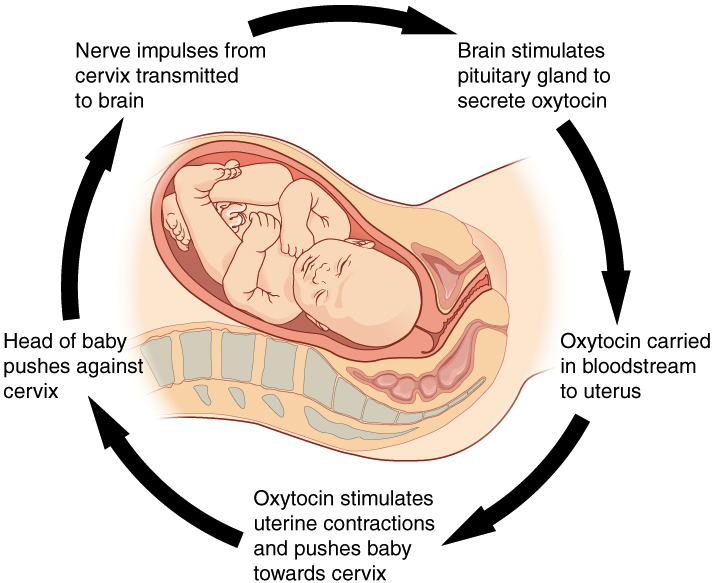
Homeostasis Article Feedback Khan Academy

Homeostasis And Negative Feedback Starter Remembering Back To

How Do Cells Maintain Homeostasis Biology Dictionary

What Is Homeostasis Course Hero

Definition Of Homeostasis Enzymes Biology Youtube
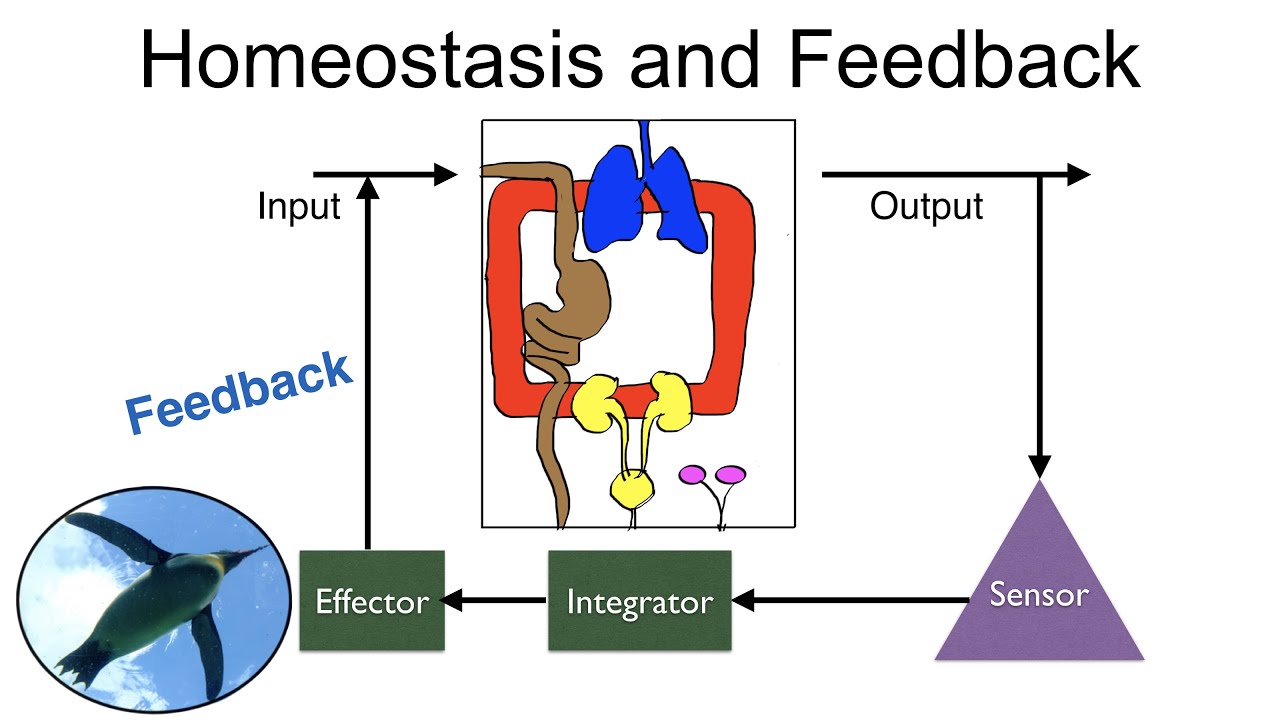
Homeostasis And Feedback Youtube

Difference Between Hemostasis And Homeostasis Definition Steps Function Di Basic Anatomy And Physiology Medical Laboratory Science Medical School Studying
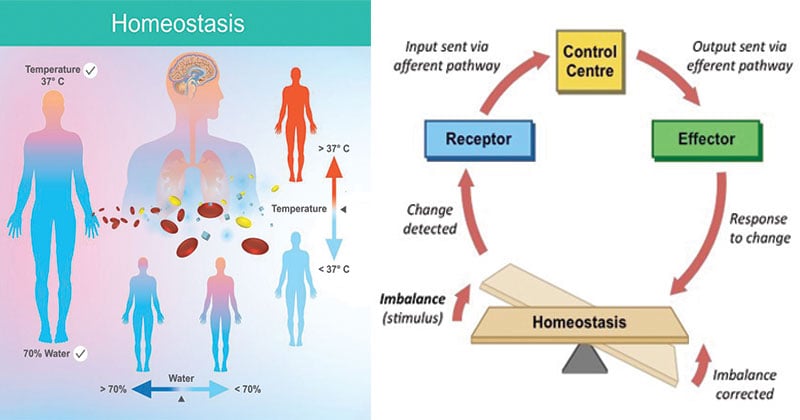
Homeostasis Definition Types Examples Applications
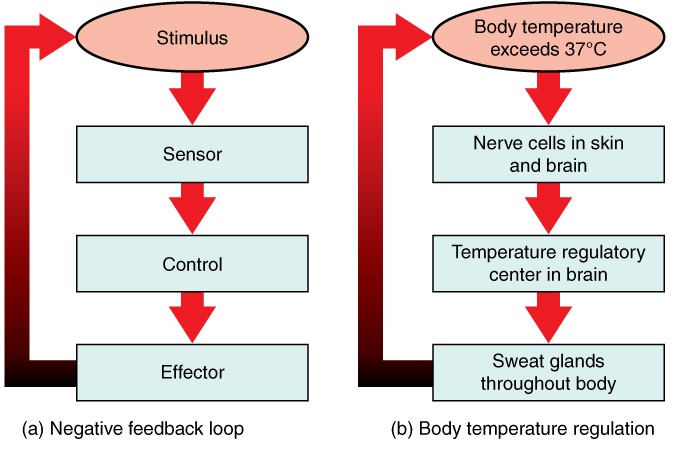
10 7 Homeostasis And Feedback Biology Libretexts

Nerves Hormones And Homeostasis Basic Anatomy And Physiology Physiology Human Anatomy And Physiology

Ls1 3 Feedback Mechanisms And Homeostasis Biology Dictionary

Post a Comment for "Describe Biological Definition Of Homeostasis"