Vaccine Definition Science Example
The media sometimes uses the term vaccine skepticism interchangeably with vaccine hesitancy. A live vaccine like the measles mumps and rubella MMR vaccine only requires two doses and delivers what is effectively lifetime protection.
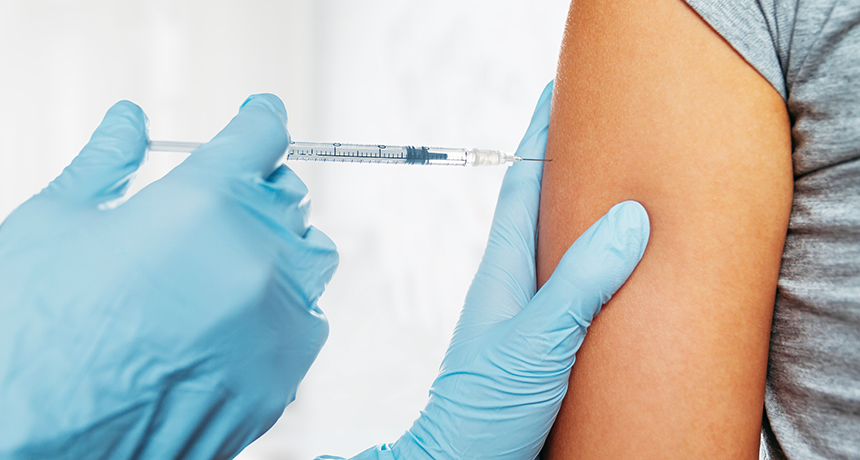
Explainer What Is A Vaccine Science News For Students
An inactivated vaccine like the one used for rabies may be needed every six months to two years for those at increased risk of exposure such as veterinarians animal control and wildlife officers and those who work in rabies virus research labs.
Vaccine definition science example. First COVID-19 mRNA vaccines are given in the upper arm muscle. There are many others. A vaccine is defined as any substance which is used to stimulate the production of antibodies in-turn providing immunity against one or few diseases A vaccine is defined as a biological preparation formulated to provide acquired immunity for a particular disease.
The name comes from the Latin vaccinus of cows and relates to the work of Edward JENNER on cowpox. Vaccine hesitancy is unwillingness or refusal to accept a vaccine even when one is available. Here are 2 exciting examples.
The smallpox vaccine used cowpox a poxvirus that was similar enough to smallpox to protect against it but usually didnt cause serious illness. The first step of this extensive process involves several years of laboratory research in which scientists and. Toxoid vaccines prevent diseases caused by bacteria that produce toxins poisons in the body.
For example smallpox killed some 2 million people in 1967. Giving people vaccines can save millions of lives. A preparation that is administered as by injection to stimulate the bodys immune response against a specific infectious agent or disease.
Even though they are very effective not everyone can receive these vaccines. A ribonucleic acid RNA vaccine or messenger RNA mRNA vaccine is a type of vaccine that uses a copy of a molecule called messenger RNA mRNA to produce an immune response. For example tetanus can cause extreme pain muscle spasms lockjaw and blood clots measles can cause encephalitis an infection of the brain and blindness.
Like in live attenuated vaccines the toxins are weakened so they cannot cause illness. They are considered an intermediate phase between the inactivated and attenuated vaccines. COVID-19 mRNA vaccines give instructions for our cells to make a harmless piece of what is called the spike protein.
Other examples of diseases for which vaccines have been developed include mumps measles typhoid fever cholera plague tuberculosis tularemia pneumococcal infection tetanus influenza yellow fever hepatitis A hepatitis B some types of encephalitis and typhusalthough some of those vaccines are less than 100 percent effective or are used only in populations at high risk. For example cholera polio smallpox hepatitis B and so long. Children with weakened immune systemsfor example those who are undergoing chemotherapycannot get live vaccines.
The Salk polio vaccine is an example of a vaccine that contains inactivated viruses whereas the Sabin polio vaccine is a LIVE VACCINE. Examples of live attenuated vaccines include measles mumps and rubella vaccine MMR and varicella chickenpox vaccine. In some areas or populations infectious diseases are endemic.
Some vaccines contain inactivated but previously virulent micro-organisms that have been destroyed with chemicals heat or radiation ghosts with intact but empty bacterial cell envelopes. The polio vaccine has saved millions of people. By 1979 the disease had disappeared.
Common vaccines include ones for strains of the flu polio hepatitis A hepatitis B tetanus diphtheria whooping cough chickenpox measles mumps and rubella. An antigenic preparation of a typically inactivated or attenuated see attenuated sense 2 pathogenic agent such as a bacterium or virus or one of its components or products such as a protein or toxin a trivalent. The Science Behind Vaccine Research and Testing How Vaccines Are Made And Tested.
Vaccines are substances that prevent the spread of disease. Once the instructions mRNA are inside the muscle cells the cells use them to make the protein piece. ˌvæksəˈneɪʃ ə n C2 the process or an act of giving someone a vaccine a substance put into a persons body to prevent them getting a disease.
Weakened toxins are called toxoids. DNA vaccines are easy and inexpensive to makeand they produce strong long-term immunity. The first human vaccines against viruses were based using weaker or attenuated viruses to generate immunity.
Rabies was the first virus attenuated in a lab to create a vaccine for humans. Examples include IPV polio vaccine hepatitis A vaccine rabies vaccine and most influenza vaccines. Vaccine hesitancy is a general term that is used to refer both to people hesitant to take some specific vaccines as well as the so-called antivaxxers who refuse to take any vaccines at all.
Examples of live attenuated vaccines include MMR chickenpox and the flu vaccine nasal spray also known FluMist. The spike protein is found on the surface of the virus that causes COVID-19. Recombinant vector vaccines platform-based vaccines act like a natural infection so theyre especially good at teaching the immune system how to fight germs.
A substance that is put into the body of a person or animal to protect them from a disease by causing them to produce antibodies proteins that fight diseases. Vaccines are not quick-acting but rely on the recipient to build up a supply of ANTIBODIES gradually. This vaccine protects against some kinds.
MRNA in vitro transcription and innate immunity activation. To fight against these diseases we need vaccines. All the children were given two vaccinations against.
Many vaccine-preventable diseases can even result in death. The creation of a vaccine involves scientists and medical experts from around the world and it usually requires 10 to 15 years of research before the vaccine is made available to the general public. Vaccines are very important because they protect us from infectious diseases.
Is There A Coronavirus Vaccine Here S Everything You Need To Know Wired
Vaccine Hesitancy Meaning Examples Definitions By Dictionary Com

How Vaccines Work British Society For Immunology
Covishield Covaxin J J The Science Behind Different Vaccines And How They Work

Rna Vaccines A Novel Technology To Prevent And Treat Disease Science In The News

Inoculation Medicine Britannica

Differences Between Vaccinate Vs Inoculate Vs Immunize Dictionary Com
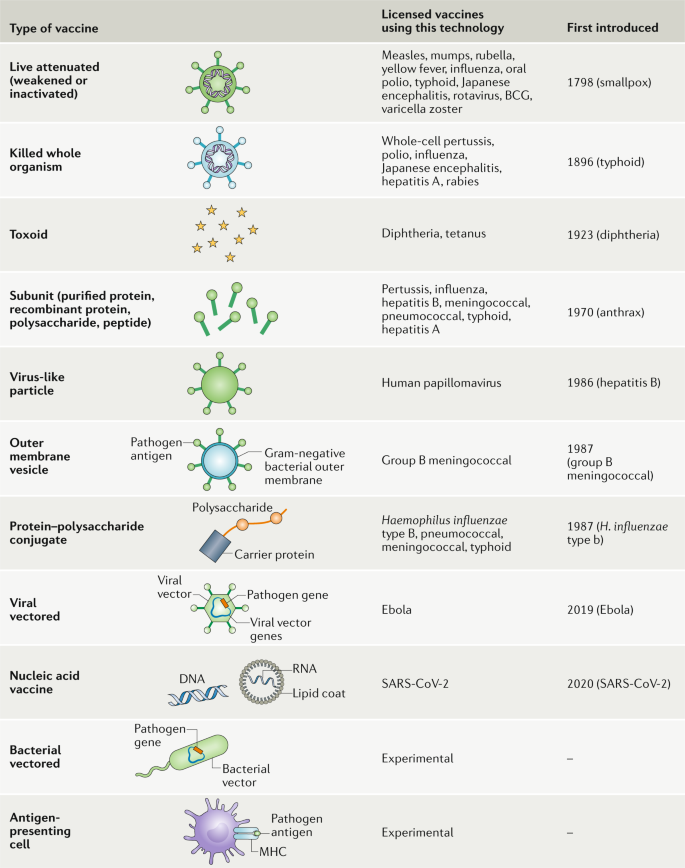
A Guide To Vaccinology From Basic Principles To New Developments Nature Reviews Immunology

Is The Covid Vaccine A Real Vaccine Kare11 Com

What Is An Example Of A Recombinant Vaccine
Is The Covid Vaccine A Real Vaccine Kare11 Com
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/21989625/vaccine_color_GettyImages_1268561234.jpg)
Covid 19 Vaccine Should Black And Latino People Get Priority Access Vox

The Emergence Of Inactivated Vaccines Bharat Biotech
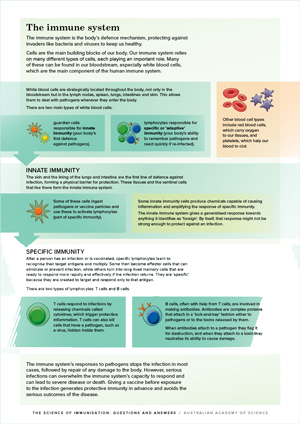
1 What Is Immunisation Australian Academy Of Science

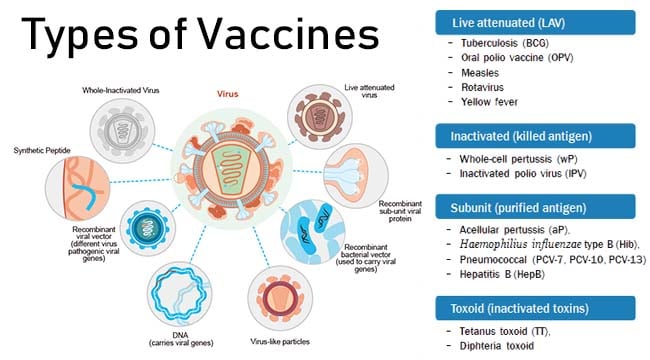
Vaccines Introduction And Types With Examples

Covid 19 Vaccinations What S The Progress Science In Depth Reporting On Science And Technology Dw 14 08 2021
Vaccination Importance Of Vaccines Vaccination And Immunization

What Is A Vaccine Definition Function Examples Video Lesson Transcript Study Com

Post a Comment for "Vaccine Definition Science Example"