Definition Of Acceleration Basic
Acceleration is a vector in the same direction as the change in velocity Δv. Since velocity is a vector it can change either in magnitude or in direction.

Force And Motion Word Wall Force Potential Energy Word Wall
Acceleration is described as the rate of change of velocity of an object.

Definition of acceleration basic. The definition of acceleration is a little more complex than that of the speed or the velocity. Acceleration - the rate of velocity change over time. Acceleration can be defined as the rate of change of velocity with respect to time.
Explore the concepts of speed velocity and acceleration through real. The orientation of an objects acceleration is given by the orientation of the net force acting on that object. Its dimensional formula is MLT -2.
The act or process of accelerating rapid acceleration the acceleration of economic growth. In order to properly measure any of these quantities youll need to know how both velocity and acceleration work. You can calculate this from the above formula where velocity is meters per second and time is in seconds.
Acceleration Acceleration is the rate of change of velocity with time. Positive acceleration means velocity increasing with time zero acceleration means velocity is uniform while negative acceleration retardation means velocity is decreasing with time. The speed is how fast you can get somewhere.
Constant speed does not guarantee that acceleration is zero. ækˌsɛləˈreɪʃən. The act of accelerating or the state of being accelerated.
The standard unit of measurement for acceleration is meters per second squared or ms 2. A few examples of acceleration are the falling of an apple the moon orbiting around the earth or when a car is stopped at the traffic. In calculus instantaneous acceleration is the first derivative of velocity with respect to time dv dt.
It is a vector quantity. When an object moves in a circular path at a constant speed it is still accelerating because the direction of its velocity is changing. The SI unit for.
Its SI unit is ms². Usually acceleration means the speed is changing but not always. The act or process of moving faster or happening more quickly.
So what is the difference between speed and acceleration. Acceleration is the rate of change of velocity. An object is said to be accelerated if there is a change in its velocity.
Its unit is ms2. In mechanics acceleration is the rate of change of the velocity of an object with respect to time. Average acceleration is found by dividing the change in velocity by the change in time Δ v Δ t.
Acceleration is defined as the rate of change of velocity with time. Ability to accelerate a car with good acceleration. Acceleration change in velocity change in timeora Δv Δt.
It is measured in meters per second squared or meters per second the objects speed or velocity per second. Acceleration is one of the most basic concepts in modern physics underpinning essentially every physical theory related to the motion of objects. It states that when demand for consumer goods increases demand.
Accelerations are vector quantities in that they have magnitude and direction. It is a vector meaning that it has both magnitude and direction. An acceleration strategy may include a variety of methods such as.
Acceleration can be positive zero or negative. How to Measure Acceleration. As you can see velocity requires speed for its measurement and acceleration requires velocity for its measurement.
Acceleration refers to an instructional strategy that aims to help students who have fallen behind to meet or exceed grade-level learning standards. A bodys acceleration is the final result of all the forces being applied to the body as defined by Newtons second law. The acceleration principle is an economic concept that draws a connection between fluctuations in consumption and capital investment.
The rate of increase of speed or the rate of change of velocitySymbol. It is a vector quantity. The change in the velocity of an object could be an increase or decrease in speed or a change in the direction of motion.
Acceleration is therefore a change in either speed or direction or both. Acceleration is a vector quantity that is described as the frequency at which a bodys velocity changes. May be if you clearly see the difference between the two it will help you to avoid common pitfalls.
Acceleration is defined as the rate that a moving object changes its velocity. The power to accelerateSymbol. Acceleration is the rate of change of velocity as a function of time.

Formal Definition Newtons Second Law Fig Newtons Physics
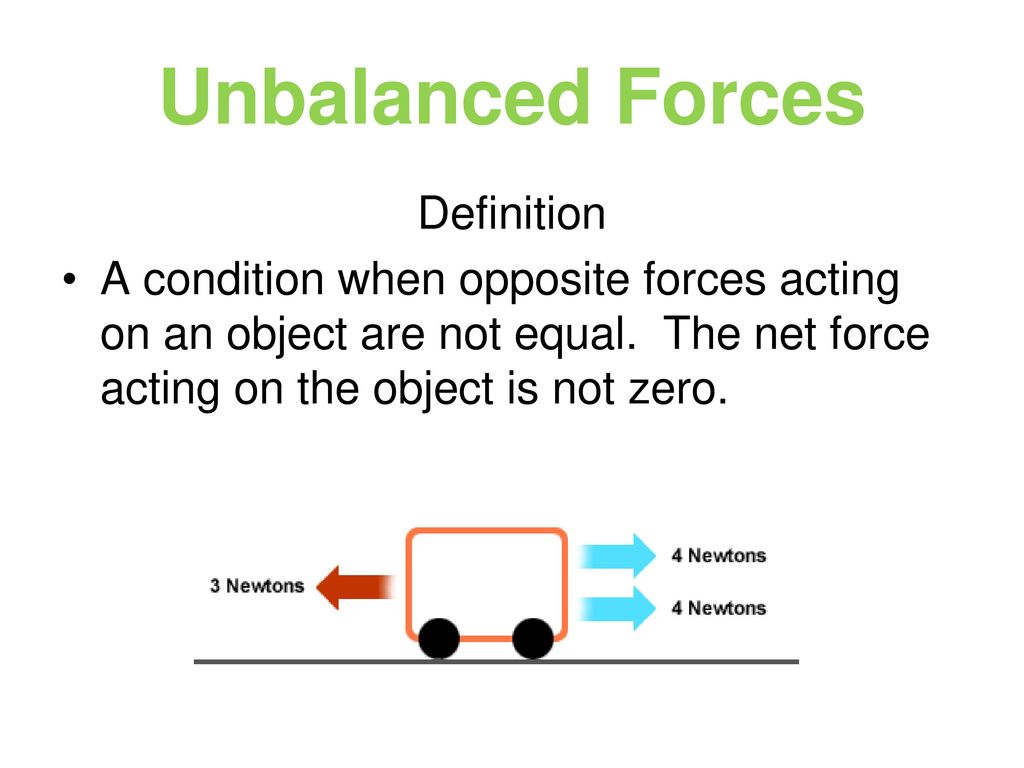
Science Worksheets Force Definition Science

Mrs Atwood S Math Class Math School Middle School Math Math

This Image Shows How Speed Can Go To Velocity And How Velocity Can Go To Acceleration It Shows How Speed Relates To Accel Ap Calculus Physics Lessons Calculus

Angular Acceleration Derivation Angular Acceleration Learning Science Angular

Newtons Second Law Of Motion Easy Science Newtons Second Law Motion Force And Motion

Angular Displacement Velocity Acceleration Physics Mechanics Engineering Science Physics

Informal Definition Newtons Second Law Physics Fig Newtons

Velocity Definition And Acceleration Definition Is Our Topic For Today Through Graphical Representation You Can Visualize The Meaning Of Velocity And Accelerat

Force Acceleration Relationship Acceleration Newtons Second Law How To Apply

Science Journal Force Triangle Foldable Completed Physics Classroom Science Journal Physical Science

Mass Acceleration Relationship Physics High School Science Fair Experiments Science

Awrobinson S Image Cool Websites This Or That Questions Acceleration

A 3 Page Worksheet That Covers Acceleration Types Of Acceleration And Interpreting Acceleration On Graphs Through A Acceleration Worksheets Physics Concepts
Mr Gortney S 8th Grade Science Class Class Notes And Topics 8th Grade Science Science Anchor Charts Sixth Grade Science

Sci 8 Newton S Laws Of Motion Interactives Newtons First Law Newton S First Law Of Motion Newtons Laws Of Motion



Post a Comment for "Definition Of Acceleration Basic"